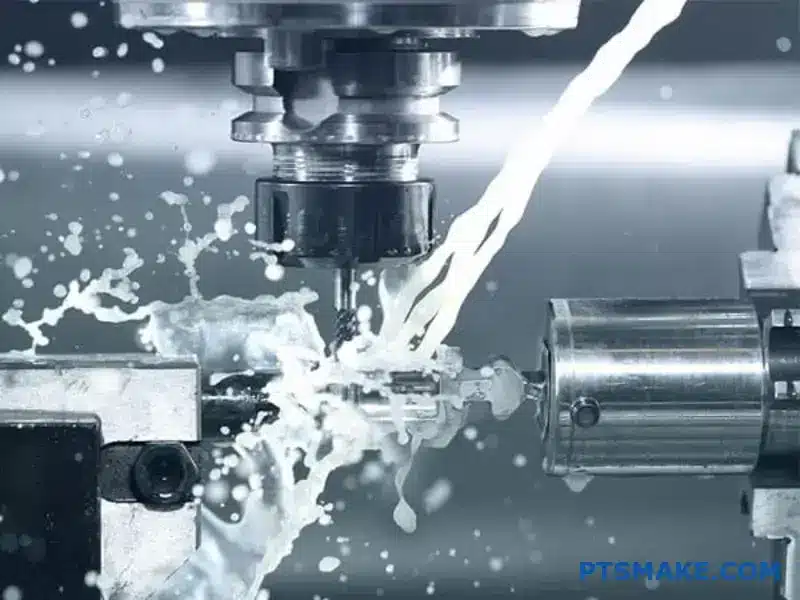
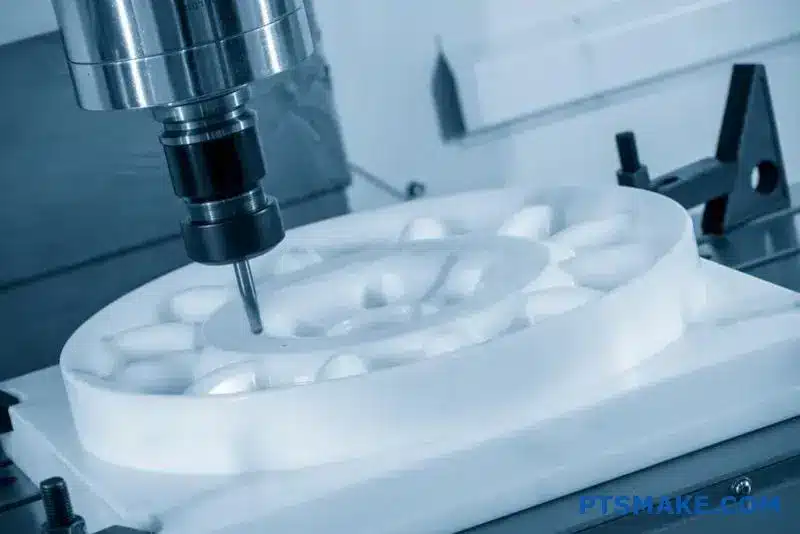
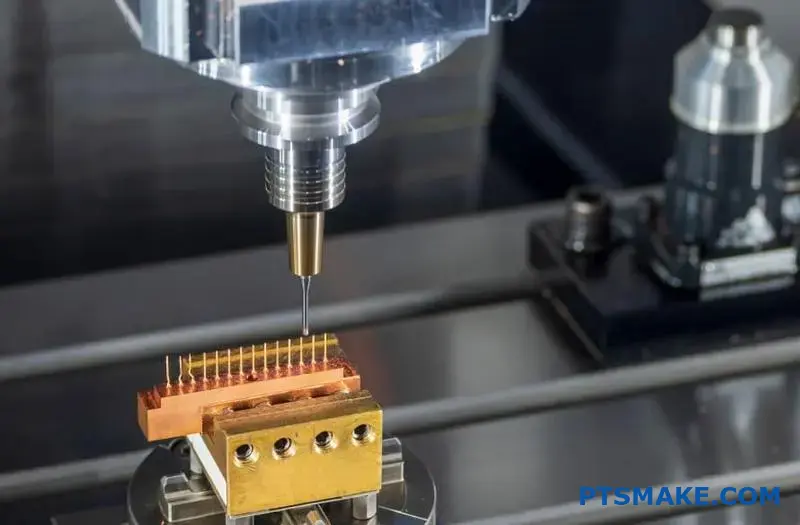
Titanium machining demands extreme precision, yet many CNC shops struggle with its notorious reputation for work hardening, rapid tool wear, and thermal challenges. These difficulties often lead to rejected parts, blown budgets, and missed deadlines for critical aerospace and medical components.
CNC machining titanium requires specialized cutting tools, precise thermal management, and strategic machining parameters to overcome its low thermal conductivity and tendency to work harden, ensuring successful production of high-performance parts.

This comprehensive guide covers everything from titanium grade selection and tooling strategies to achieving tight tolerances and scaling production. You’ll discover proven techniques that address common titanium machining challenges and learn how to evaluate suppliers for your most demanding projects.
The Complete Guide to Titanium Grades for CNC Machining
Choosing the right titanium grade is critical. It directly impacts your part’s performance and cost. Not all titanium is the same.
The differences between grades can be huge. This is especially true for CNC machining titanium parts.
We’ll look at the most common options. You’ll learn which one fits your project best. Let’s compare some popular titanium grades for machining.
| グレード | 強さ | 耐食性 | 加工性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| グレード2 | 中程度 | 素晴らしい | グッド |
| グレード5 | 高い | 非常に良い | フェア |
| グレード23 | 高い | 素晴らしい | フェア |
This guide helps you in choosing the titanium alloy wisely.

Grade 2: The Workhorse
Grade 2 is commercially pure titanium. It offers excellent corrosion resistance and formability. This makes it a great choice for many applications.
Think of marine or chemical processing parts. Its lower strength compared to alloys is its main trade-off. However, its machinability is a significant advantage. It saves time and tool wear during production.
Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V): The Aerospace Standard
Grade 5, or Ti-6Al-4V, is the most popular alloy. It provides a fantastic combination of high strength, low weight, and good corrosion resistance. The Ti-6Al-4V properties make it ideal for aerospace.
You’ll find it in structural components and engine parts. Its strength-to-weight ratio is simply unmatched by most other metals. This is why it’s so valued in high-performance fields.
Grade 23: The Medical Choice
Grade 23 is a higher purity version of Grade 5. It has lower oxygen, nitrogen, and iron content. This improves its ductility and fracture toughness.
Its key feature is its excellent 生体適合性1. This makes it the top choice for medical implants. Think of bone screws, pins, and dental implants. It’s safe for long-term contact with the human body.
| 特徴 | グレード2 | グレード 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) | グレード23(ELI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 構成 | 商業的純度 | Ti, 6% Al, 4% V | Ti, 6% Al, 4% V (Extra Low Interstitials) |
| 強さ | より低い | 高い | 高い |
| 延性 | 高い | 中程度 | 高い |
| 主要用途 | インダストリアル | 航空宇宙、自動車 | 医療用インプラント |
Selecting the right titanium grade is crucial. Grade 2 offers great machinability. Grade 5 provides superior strength for aerospace. Grade 23 is the standard for medical implants due to its purity and safety. Your application dictates the choice.
The Four Core Challenges of Titanium Machinability
So, why is titanium so hard to machine? It’s not just one thing. It’s a combination of four distinct properties. Each one creates a unique problem for machinists.
Engineers and procurement managers must understand these issues. They directly impact production costs, timelines, and final part quality.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the main culprits:
| チャレンジ | 第一次影響 |
|---|---|
| 低熱伝導率 | Extreme heat on the cutting tool |
| 仕事のハード化 | Material becomes harder during cutting |
| Galling (Adhesion) | Titanium welds to the tool surface |
| 工具の摩耗が激しい | Tools break down very quickly |
Addressing these titanium machining problems is not optional. It is essential for success.
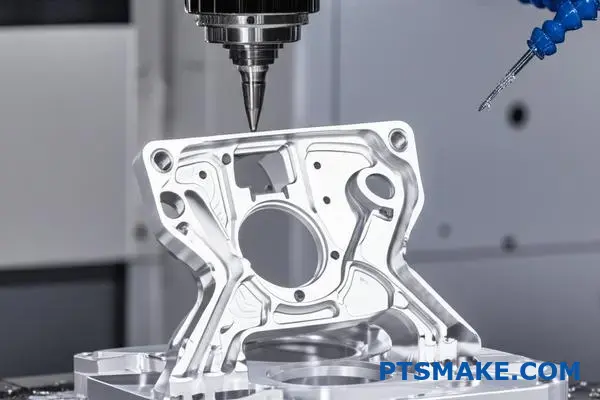

Understanding the "why" behind these challenges is the first step toward finding a solution. At PTSMAKE, we’ve spent years developing strategies to counter each of these specific issues in the cnc machining of titanium. It requires a different mindset than machining steel or aluminum.
Low Thermal Conductivity: The Heat Problem
Titanium doesn’t dissipate heat well. About 80% of the heat generated during cutting transfers directly into the cutting tool, not the chip. This extreme heat can cause tool deformation and failure.
Chemical Reactivity and Galling
Titanium is highly reactive at high temperatures. This causes chips to weld onto the tool’s cutting edge. This phenomenon, known as 凛々しい2, leads to a poor surface finish and can cause the tool to fracture prematurely. It’s a constant battle against adhesion.
Understanding Titanium Work Hardening
Titanium has a tendency to harden when it’s being machined. The pressure and heat from the cutting tool can make the surface layer significantly harder than the base material. This makes subsequent cuts much more difficult, increasing tool wear.
The Domino Effect on Tool Wear
These factors combine to create rapid and severe tool wear. The high heat, chemical reactivity, and work hardening all attack the cutting tool simultaneously. Based on our internal testing, tool life can be drastically shorter compared to other common metals.
| 素材 | Relative Tool Life Expectancy |
|---|---|
| アルミニウム6061 | 100%(ベースライン) |
| ステンレス304 | 25% |
| チタン Ti-6Al-4V | <10% |
This makes tool management and replacement a critical cost factor.
Overcoming titanium’s machining difficulties—heat, hardening, and galling—is crucial. These issues directly increase tool wear, elevate costs, and can compromise part quality if not managed by an experienced partner. Success requires specific strategies for each challenge.
Secrets to Selecting the Right Cutting Tools for Titanium
Choosing the right tool is critical for titanium machining. The main enemy is heat. It doesn’t dissipate through the chip as with steel. Instead, it concentrates on the cutting edge, leading to rapid tool wear.
This is why specialized tools are non-negotiable. Sub-micron grain carbide grades are a great starting point. They offer the necessary toughness. A proper coating then provides the thermal barrier.
Let’s look at some common material choices.
| 工具材料 | 耐熱性 | 耐摩耗性 | 申し込み |
|---|---|---|---|
| 非コーティング超硬合金 | グッド | グッド | 汎用 |
| AlTiN Coated Carbide | 素晴らしい | 素晴らしい | 高速加工 |
| PVD Coated Carbide | 非常に良い | 非常に良い | 仕上げ作業 |
Selecting the best cutting tools for titanium means matching the material and coating to your specific operation.
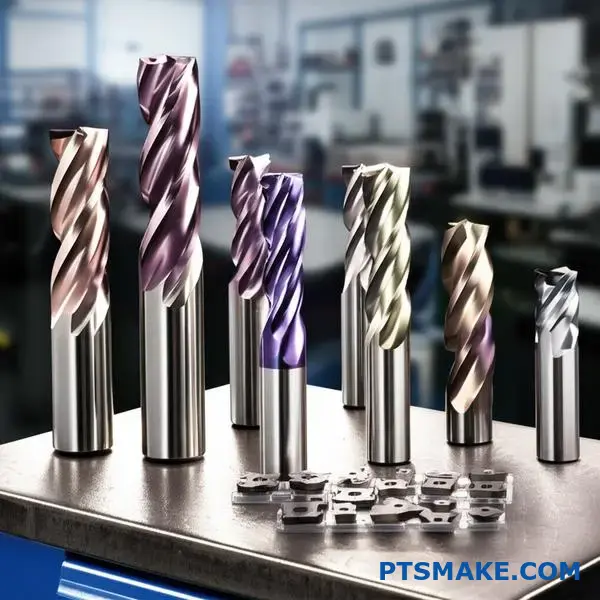

Beyond the material, tool geometry is key. For successful cnc machining titanium, I always look for tools with a sharp cutting edge and a positive rake angle. This reduces cutting forces and, consequently, heat generation. A higher helix angle, often around 35-45 degrees, helps with chip evacuation. Poor chip evacuation can lead to re-cutting, which is disastrous for tool life.
Coatings like Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) are standard. They form a protective layer of aluminum oxide at high temperatures, insulating the carbide substrate. This is a game-changer. We’ve seen tool life extend significantly in our tests just by switching to the right coating.
However, toolpath strategy is just as vital. Avoid sharp corners and abrupt changes in direction. Instead, use trochoidal milling or high-efficiency milling (HEM) paths. These maintain a consistent tool engagement angle. This prevents shock loading and controls the heat, which is a primary cause of adhesion wear3. It smooths out the entire process.
The best titanium machining tools are often not the cheapest. There is a clear trade-off.
| ファクター | High-Performance Tools | Standard Tools |
|---|---|---|
| 初期費用 | より高い | より低い |
| 工具寿命 | かなり長い | より短い |
| 加工速度 | より速く | 遅い |
| 部品単価 | より低い | より高い |
Investing more upfront in premium carbide tools for titanium pays off. You get longer life, faster cycle times, and ultimately, a lower cost per finished part. At PTSMAKE, we guide our partners through this decision.
Success in machining titanium hinges on a strategic combination of tool material, specific geometry, and intelligent toolpaths. This holistic approach manages heat and wear, balancing initial tool cost against long-term performance to reduce the final cost per part.
How to Achieve Tight Tolerances on Titanium CNC Parts
Achieving a precision of ±0.001 inches or tighter on titanium is a true test of a machine shop’s skill. It’s not just about cutting metal. It’s about controlling a difficult material.
Success in high-precision titanium machining demands a holistic approach. You must manage heat, secure the part perfectly, and use the right equipment. Every step is critical.
| チャレンジ | Core Strategy |
|---|---|
| 熱の蓄積 | Effective Coolant Management |
| 部品のたわみ | Robust Fixturing |
| 寸法精度 | 工程内検査 |
Holding these tight tolerance titanium parts requires mastering these core areas. There is very little room for error.

Engineering Strategies for Precision
To succeed in titanium precision machining, you have to go beyond standard practices. It requires a deep understanding of the material’s behavior under stress. Here at PTSMAKE, we focus on four key areas.
Thermal Management is Crucial
Titanium does not dissipate heat well. This means heat concentrates at the cutting tool, causing rapid wear. High-pressure coolant is not just a suggestion; it’s a requirement. It flushes chips and prevents heat from ruining the part’s surface and dimensions.
Fixturing for Absolute Rigidity
When machining titanium, cutting forces are high. A weak fixture will allow the part to vibrate or deflect, making tight tolerances impossible. We often design custom fixtures that support the component rigidly, preventing any movement during the cnc machining titanium プロセスだ。
The Right Machine for the Job
Your CNC machine must be up to the task. This means a rigid, heavy-duty machine with high-torque spindles and minimal runout. Without a capable machine, you will fight a losing battle against tool deflection and vibration.
| Machine Requirement | なぜ重要なのか |
|---|---|
| 高い剛性 | Prevents vibration and chatter |
| High-Torque Spindle | Maintains cutting speed under load |
| Precision Ways/Guides | Ensures accurate tool positioning |
Failure in any of these areas compromises the entire process. The risk of 凛々しい4 also increases with improper setups, which can weld chips to the tool.
工程内検査
You cannot wait until the end to measure the part. We use in-process probing to check critical dimensions throughout the machining cycle. This allows us to compensate for tool wear or thermal expansion in real-time, ensuring the final part is perfect.
Achieving tight tolerances in titanium requires a system. It combines thermal control, rigid workholding, capable machinery, and constant measurement. This systematic approach transforms a challenging material into a finished part that meets the most demanding specifications.
The Complete Guide to Titanium Part Finishing and Deburring
After CNC machining titanium, the journey isn’t over. Post-processing is where a good part becomes exceptional. This crucial stage defines its final look, feel, and performance.
効果的 titanium deburring removes sharp edges left by machining. This is critical for safety and proper function.
Surface finishing then enhances aesthetics and properties. Options range from durable coatings to high-gloss polishes. Choosing the right finishing titanium parts method is key.
| プロセス段階 | 主要目標 | インパクト |
|---|---|---|
| デバリング | Remove burrs and sharp edges | Safety, Functionality |
| 仕上げ | Alter surface properties | 美学、耐久性 |

Effective Titanium Deburring Techniques
Titanium’s toughness makes burrs stubborn. Manual deburring is common but can be inconsistent. For precision, we often turn to automated methods.
Vibratory tumbling is excellent for small parts. It uses abrasive media to smoothly remove burrs. For complex internal features, electrochemical deburring offers a non-contact solution. It dissolves burrs without affecting the part’s integrity.
Key Titanium Surface Treatment Options
The right finish depends entirely on the application. Each titanium surface treatment offers unique benefits for both function and appearance.
陽極酸化処理
Anodizing creates a durable, oxide layer on the titanium. This process enhances wear and corrosion resistance. It also allows for vibrant, permanent coloring without paint. This is achieved through an 電気化学的パッシベーション5 that thickens the natural oxide film.
ビーズブラスト
Bead blasting produces a uniform, non-directional matte finish. It cleans the surface and can improve fatigue life by creating compressive stress. It is a cost-effective way to achieve a clean, professional look.
研磨
For applications requiring a smooth, reflective surface, polishing is ideal. It reduces surface friction and enhances aesthetic appeal. This is often a multi-step process, starting with coarse abrasives and ending with fine compounds.
| 仕上げ方法 | 主なメリット | 共通アプリケーション |
|---|---|---|
| 陽極酸化処理 | 耐食性、色 | 医療用インプラント、航空宇宙 |
| ビーズブラスト | 均一なマット仕上げ | Automotive Parts, Tooling |
| 研磨 | 低摩擦、美観 | Consumer Electronics, Jewelry |
Post-machining is not an afterthought. Proper titanium deburring ensures safety and fit, while strategic surface finishing dictates the part’s final performance, corrosion resistance, and aesthetic value, which are vital after cnc machining titanium.
Cost Drivers in Titanium CNC Machining: A Transparent Breakdown
Understanding titanium part pricing requires a clear look at its core cost drivers. It’s not just one thing that makes it expensive; it’s a combination of factors.
Primary Cost Factors
The main reasons why titanium machining is expensive are straightforward. High raw material cost is the starting point.
Then comes the slow machining time. We must run machines at lower speeds to manage heat and tool wear. This directly increases the hours required per part.
Finally, rapid tool consumption and necessary secondary operations add to the final cost.
| コストドライバー | Impact on Final Price | 理由 |
|---|---|---|
| 原材料 | 高い | Inherent scarcity and difficult extraction process. |
| 加工時間 | 高い | Low cutting speeds required for thermal management. |
| 金型費用 | 高い | Rapid wear of specialized, expensive cutting tools. |
| Secondary Ops | ミディアム | Often required for surface integrity and finish. |

Let’s dig deeper into why these elements impact the cost of machining titanium so much. It’s more than just the price of the metal bar. The true cost emerges on the workshop floor.
The Machining Time Multiplier
Slow machining isn’t just an inconvenience; it’s a major cost multiplier. Titanium’s low thermal conductivity traps heat at the cutting edge. This forces us to reduce speeds to prevent tool failure and material damage.
This slow process also increases the risk of 加工硬化6, where the material becomes even harder during cutting. This makes subsequent passes more difficult and further wears down tools. It’s a challenging cycle.
Tooling and Secondary Processing Costs
At PTSMAKE, we use specialized carbide tools with specific coatings for cnc machining titanium. These are more expensive and wear out faster than standard tools, requiring frequent replacement. This consumption is a direct, recurring cost.
Secondary operations like heat treatment or anodizing are often not optional. They are critical for achieving the part’s required mechanical properties or corrosion resistance. Each step adds another layer of cost and time to the project.
| オペレーション | 目的 | 相対的なコストへの影響 |
|---|---|---|
| 熱処理 | Stress relief, strength enhancement | ミディアム |
| 陽極酸化処理 | Corrosion resistance, surface finish | 低~中 |
| 研磨 | Achieving tight tolerances | 高い |
| 不動態化 | 耐食性の向上 | 低い |
The primary cost drivers—material, extensive machining time, high tool consumption, and essential secondary operations—collectively explain why titanium CNC machining is a premium service. Proper planning is crucial for accurate budgeting and cost control.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Secrets for Titanium Parts
When designing titanium parts, you must follow specific rules. This is not a material that forgives design flaws easily.
Following a clear titanium DFM guide is essential. It helps you sidestep common and costly machining issues before they happen.
Key Dimensions for Machinable Titanium Design
Let’s focus on the core geometry first. Wall thickness and internal radii are critical starting points for any successful design.
Generous radii allow us to use larger, more stable tools. This reduces chatter and improves surface finish, directly impacting part quality.
Based on our tests, sticking to these parameters is a safe bet.
| 特徴 | Recommended Specification | 主な理由 |
|---|---|---|
| 最小肉厚 | > 1.0 mm (0.040") | Prevents part warping and chatter |
| Minimum Internal Radius | > 0.8 mm (0.031") | Reduces tool stress and cutting forces |
These simple rules form the foundation of an effective, machinable titanium design.
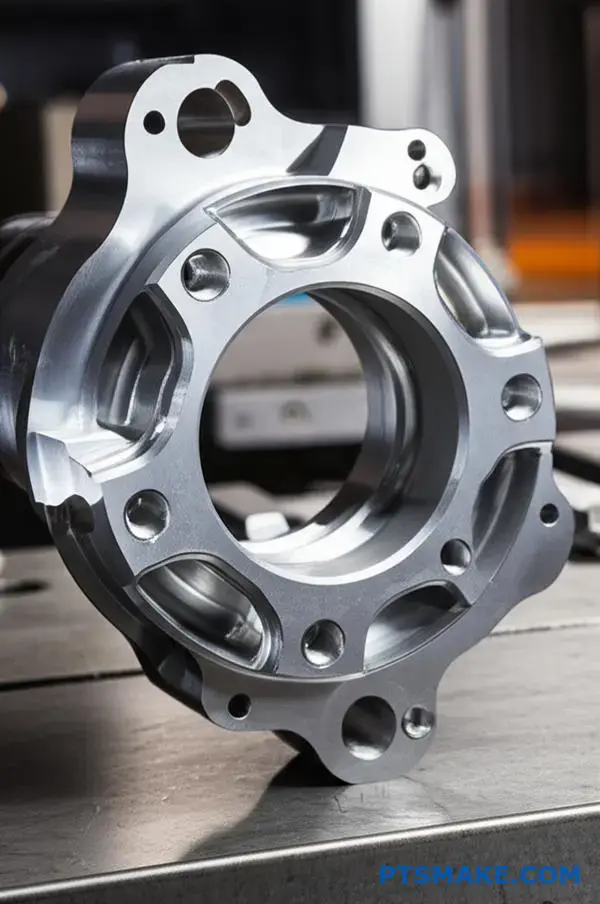

Deeper Dive: Hole Depth and Feature Accessibility
Many designs stumble when it comes to holes and complex features. The unique properties of titanium make these areas especially challenging for CNC machining.
Deep holes, for instance, are a major source of tool failure. Heat doesn’t dissipate well, and chip evacuation becomes incredibly difficult. Poor tool access also complicates things. It often requires custom fixtures or longer tools, which reduces rigidity and precision.
During the machining process, incorrect feeds and speeds can cause 加工硬化7, making the material even tougher to cut. This is a problem we see often with designs that aren’t optimized.
Optimizing for Tool Access and Efficiency
Always consider how a tool will approach each feature. If access is blocked, it forces more complex and expensive multi-axis setups.
We’ve found these guidelines greatly improve machinability.
| デザイン面 | DFM Guideline | Impact on CNC Machining Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| 穴の深さ対直径比 | Keep below 6:1 | Enhances chip removal, lowers tool breakage risk |
| 機能アクセシビリティ | Ensure clear tool paths | Minimizes setups, allows for shorter/stiffer tools |
By simplifying geometry and ensuring good access, you make the part inherently easier and cheaper to produce. It’s a fundamental principle of good design for manufacturing.
Adhering to these titanium DFM guidelines for wall thickness, radii, and hole depths is crucial. Proper design significantly reduces machining time, lowers costs, and prevents production delays, ensuring a smoother process from prototype to production at PTSMAKE.
5-Axis CNC Machining for Complex Titanium Geometries
When machining titanium, complexity is often a given. This is especially true for parts like aerospace brackets or medical implants. These components demand absolute precision.
This is where 5-axis titanium machining excels. It allows us to approach intricate features from multiple angles in a single setup.
This method directly enhances accuracy and integrity. It minimizes the risks that come with re-clamping a part. The benefits for complex titanium parts are clear.
| メリット | Impact on Titanium Parts |
|---|---|
| Fewer Setups | Reduces cumulative error |
| Better Tool Access | Enables complex contours |
| より高い精度 | Meets tight aerospace/medical specs |
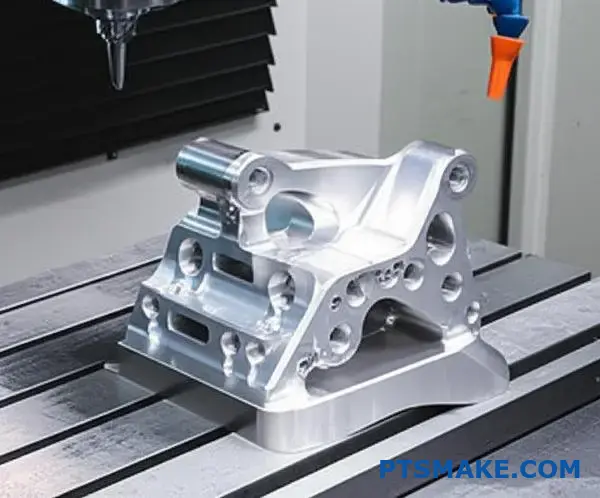

シングル・セットアップの利点
The main benefit of multi-axis CNC titanium machining is the "single-setup" approach. Every time you move and re-clamp a part, you introduce a small risk of error. This can be a huge issue.
By machining on five sides without re-fixturing, we virtually eliminate this variable. This protects the part’s geometric accuracy from start to finish. It’s a core principle we follow at PTSMAKE for all critical components.
複雑な形状を解き明かす
For components with contoured surfaces, like fluid components or implants, 5-axis isn’t just better; it’s necessary. It lets the cutting tool remain tangent to the surface.
This continuous movement creates superior surface finishes. It also lets us machine deep, complex pockets that are impossible on 3-axis machines. The cumulative error, also known as トレランス・スタックアップ8, is significantly reduced with this method.
3-Axis vs. 5-Axis for Titanium
| 特徴 | 3軸加工 | 5軸加工 |
|---|---|---|
| 必要なセットアップ | 複数 | Single (often) |
| Accuracy on Contours | より低い | 非常に高い |
| サイクルタイム | 長い | より短い |
| 完全性 | Good, but risks from re-fixturing | 素晴らしい |
This efficiency in cnc machining titanium leads to better parts, faster.
In summary, 5-axis machining is a game-changer for complex titanium parts. It cuts down on setups, boosts accuracy on curved surfaces, and ensures superior part integrity. This makes it essential for critical applications in aerospace and medical industries.
How to Ensure Material Traceability for Critical Titanium Components
In high-stakes industries like aerospace and medical, material traceability isn’t just a best practice. It is an absolute requirement.
Every critical titanium component must have a verifiable history. This process ensures performance, safety, and reliability under extreme conditions.
It all begins with certified material sourcing. Meticulous heat and lot number tracking follows. This is central to certified titanium machining.
The entire journey, from raw material to finished part, must be documented.
| 特徴 | Traceable Titanium | Non-Traceable Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Verification | Certified Mill Reports | Unknown Origin |
| リスク | Low; Meets Standards | High; Potential Failure |
| コンプライアンス | Audit-Ready | Non-Compliant |

The Pillars of Traceability: Sourcing, Tracking, and Documentation
Certified sourcing is the foundation. We only partner with suppliers who provide complete documentation for every batch of titanium. This always includes Mill Test Reports (MTRs) that verify the material’s exact chemical and physical properties against required specifications.
Heat and Lot Number Tracking
Once the certified material arrives at our facility, we assign it a unique internal tracking number. This number is directly linked to the original supplier’s heat or lot number.
This link is maintained throughout the entire cnc machining titanium workflow. From cutting and milling to finishing and final inspection, every step is recorded against this number. This creates an unbroken chain of custody9 from the raw bar stock to the final component you receive.
Ensuring Audit Readiness
This meticulous documentation makes audits simple and transparent. We can instantly pull the complete manufacturing history for any part. This readiness is crucial for meeting strict aerospace titanium standards like AS9100 and proves our process control.
| 文書タイプ | 目的 |
|---|---|
| Mill Test Report (MTR) | Certifies raw material properties from the mill. |
| 適合証明書(CoC) | Confirms parts meet all specified requirements. |
| Internal Work Order | Tracks the part’s journey through production. |
Robust titanium material traceability is built on certified sourcing, diligent tracking, and thorough documentation. This system is not just for compliance; it’s a fundamental part of risk management and quality assurance for every critical component we manufacture.
The Ultimate Guide to Titanium vs. Aluminum for CNC Parts
Choosing between titanium and aluminum is a critical decision. It directly impacts your part’s performance, weight, and final cost. This is not just about picking the stronger material.
It’s about matching properties to your specific application needs. For hardware leaders, understanding this material comparison for CNC is key to success.
一目でわかる比較
A quick look at the core differences is essential. Here is a high-level overview of the most common grades we work with.
| 特徴 | チタン(Ti-6Al-4V) | アルミニウム(6061-T6) |
|---|---|---|
| 強さ | 非常に高い | 中程度 |
| 重量 | Heavier than Al | 非常に軽い |
| コスト | 高い | 低い |
| 加工性 | 難しい | 素晴らしい |
This table shows the fundamental trade-offs we manage daily.

Deeper Dive: Performance vs. Cost
When we analyze strength-to-weight, titanium is the clear winner. This makes it a staple in aerospace and medical implants. Its performance under stress and at high temperatures is unmatched by aluminum. However, this premium performance comes at a price.
The challenges in cnc machining titanium are significant. It has low thermal conductivity, which traps heat at the tool tip. This leads to faster tool wear and slower machining speeds. Our process at PTSMAKE involves specialized tooling and cooling strategies to manage this.
Corrosion Resistance and Application Nuances
Titanium forms a stable, passive oxide layer. This makes it incredibly resistant to corrosion from saltwater and many industrial chemicals. Aluminum is also corrosion-resistant but can be vulnerable. It is susceptible to ガルバニック腐食10 when in contact with more noble metals.
これは titanium vs aluminum machining decision often depends on the operating environment. A marine application might demand titanium, while a consumer electronics housing is perfect for aluminum.
Data-Driven Material Comparison
| プロパティ | チタン(グレード5) | アルミニウム(6061) | Aluminum (7075) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 密度 (g/cm³) | 4.43 | 2.70 | 2.81 |
| 引張強さ (MPa) | ~950 | ~310 | ~572 |
| 機械加工性評価 | 貧しい | グッド | フェア |
Our test results show even high-strength 7075 aluminum doesn’t reach titanium’s level. This data is crucial when choosing titanium or aluminum for demanding parts.
The choice between titanium and aluminum for CNC parts is a balance. You must weigh superior strength and corrosion resistance against higher material and machining costs. The application’s specific requirements will always guide the best material selection for your project.
How to Prevent Titanium Part Distortion During Machining
Titanium part distortion is a common headache. It stems from high residual stress within the material. The forces from machining release this stress unevenly.
This leads to warping and dimensional instability. Preventing titanium warping requires a thoughtful strategy from the very start. It’s not just about cutting metal.
The Core Problem: Machining Stress
Machining stress in titanium is significant. The material’s low thermal conductivity traps heat in the cutting zone. This heat, combined with cutting forces, induces stress. Poor strategy makes it worse.
A smart approach controls these factors carefully.

A multi-step process is crucial for preventing titanium warping. We can’t treat it like aluminum or steel. Each step must be designed to manage and relieve stress. Ignoring this guarantees dimensional problems later on.
Strategic Roughing and Finishing
We never machine a titanium part to its final dimension in one go. First, we perform a roughing operation. We leave a consistent amount of material, usually 0.5mm to 1.5mm, on all surfaces. This initial pass removes most of the material and absorbs the bulk of the 残留応力11.
After roughing, a stress-relief step is essential. This can be a thermal treatment. The part is heated to a specific temperature and then slowly cooled. This process relaxes the internal stresses introduced during roughing.
| Stress Relief Method | 主なメリット | 代表的なアプリケーション |
|---|---|---|
| サーマルアニーリング | Highly effective at reducing stress | Critical aerospace parts |
| 振動ストレス・リリーフ | Faster, no thermal distortion | Large, non-critical structures |
Advanced Fixturing Techniques
Finally, we perform the finishing pass. Proper fixturing is critical here. We use low-clamping force fixtures. This prevents introducing new stresses into the now-stabilized part. The goal is to hold the part securely without deforming it. This ensures the final dimensions are accurate and stable after the cnc machining titanium プロセスだ。
Managing internal stress is key to preventing titanium part distortion. A sequence of roughing, stress-relieving, and careful finishing is not optional. It is fundamental to achieving dimensional accuracy and stability in every titanium component we produce at PTSMAKE.
The Definitive Guide to Titanium Prototyping Best Practices
Efficient titanium prototyping saves time and money. The key is knowing when to commit to this premium material. For initial form and fit checks, using a substitute is often smarter.
This approach lets you refine your design quickly. Once the concept is solid, you can move to actual titanium. This protects your budget from costly early-stage revisions.
When to Use Substitute Materials
Consider substitutes for early-stage prototypes. This helps validate ergonomics and assembly without the high cost of titanium.
| 試作段階 | 推奨素材 | 主要目標 |
|---|---|---|
| Concept Model | 3D Printed Plastic (PLA, ABS) | Form and Fit |
| Functional (Low-Stress) | アルミニウム(6061など) | Basic Mechanics |
| プリプロダクション | チタン(Ti-6Al-4V) | Full Validation |
Using this staged method ensures you only invest in titanium prototype machining when you’re confident in the design.

Strategies for Fast-Turnaround Prototypes
Speed is critical in rapid prototyping titanium. Success depends on smart planning and clear communication with your manufacturing partner. We focus on this at PTSMAKE.
A well-defined Design for Manufacturability (DFM) review is the first step. For titanium, this means simplifying geometries where possible. It also means designing for optimal tool access to reduce machine time.
Titanium has unique properties. It is prone to work-hardening and has low thermal conductivity. These factors can lead to tool wear and surface finish issues. A common problem is 凛々しい12, where materials adhere under pressure.
Our DFM analysis, based on collaborative research with clients, helps prevent these issues. It streamlines the cnc machining titanium プロセスだ。
Validating Your Titanium Design
Before full production, rigorous testing is essential. This confirms your part meets all functional and performance requirements.
| Validation Step | 目的 | 方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 寸法分析 | Verify geometric accuracy | CMM Inspection, 3D Scanning |
| 機械試験 | Test strength and durability | Tensile, Fatigue, Impact Tests |
| 機能テスト | Confirm real-world performance | Assembly and Field Trials |
これら testing titanium designs steps ensure your final product is reliable and effective, preventing costly failures later.
Efficient titanium prototyping requires a strategic approach. Use substitute materials for early validation, apply DFM principles for speed, and conduct thorough testing before committing to full-scale production. This balances cost, time, and quality effectively.
How to Scale from Titanium Prototype to Production
Moving from a single titanium prototype to full-scale production is a major leap. It’s not just about making more parts. It requires a completely different mindset and a robust plan.
A successful transition is built on a solid strategy. This plan must cover everything. It includes tooling, process validation, quality control, and your supply chain. Without it, costs spiral and deadlines are missed.
Key Transition Pillars
| ステージ | フォーカス | ゴール |
|---|---|---|
| 工具 | Durability & Speed | Minimize downtime and cycle time |
| プロセス | 再現性 | Ensure every part meets spec |
| 品質 | スケーラビリティ | Maintain standards at high volume |
| サプライチェーン | 信頼性 | Secure material and delivery flow |

Scaling up your titanium part production requires a documented transition plan. This isn’t just a suggestion; it’s essential for success when moving from low to high volume titanium manufacturing. At PTSMAKE, we focus on four critical areas to ensure a smooth ramp-up.
Optimizing Your Tooling Strategy
Your prototype tooling won’t survive production runs. For large-scale cnc machining titanium, you need robust tooling made from carbide or other durable materials. We optimize tool paths and cooling strategies specifically for high-volume output. This reduces cycle times and extends tool life.
Validating the Manufacturing Process
A validated process is a repeatable one. We move from single-part checks to Statistical Process Control (SPC). This ensures stability and predictability. First Article Inspection (FAI) reports confirm that the production process consistently creates parts that meet every specification. Consistent ワークホールディング13 is a critical but often overlooked aspect of this stage.
Scaling Quality Control and Logistics
Manual inspection is not feasible for thousands of parts. We implement automated systems like CMMs and optical scanners. This scales quality control effectively. On the logistics side, we secure long-term contracts for raw titanium. This guarantees material availability and stabilizes pricing, which is crucial for manufacturing titanium parts at scale.
| アスペクト | Prototype Phase | 生産段階 |
|---|---|---|
| 工具 | Softer, less durable | Hardened, long-life carbide |
| バリデーション | 手動測定 | 統計的工程管理(SPC) |
| 検査 | 100%マニュアルチェック | Automated CMM, sampling plans |
| Supply | Spot buys | Long-term supplier agreements |
A structured plan is non-negotiable for scaling titanium production. By strategically addressing tooling, process validation, quality control, and supply chain logistics, you can transition smoothly from a single prototype to high-volume manufacturing, ensuring consistency and reliability.
The Complete Guide to Quality Inspection for Machined Titanium
Inspecting titanium parts is more than just measuring. It requires a systematic approach to quality control. This ensures every component meets exact specifications.
At PTSMAKE, we integrate advanced tools with strict process frameworks. This combination is crucial for achieving consistent results.
Key Inspection Methodologies
We rely on several high-precision instruments for thorough validation. Each tool serves a specific purpose in our quality control workflow for inspecting titanium parts.
| 工具 | 主要用途 | 精密水準器 |
|---|---|---|
| CMM | Complex 3D geometries | 非常に高い |
| 光学コンパレータ | 2D profiles and features | 高い |
| 粗さ試験機 | 表面仕上げ測定 | Micro-level |
| Thread Gauges | Thread accuracy (Go/No-Go) | Standardized |
These tools provide the data we need. But the process framework ensures data is used effectively for true titanium quality control.

A comprehensive inspection plan is the roadmap for quality. It details every check, from raw material verification to final sign-off. This plan is not static; it’s a living document.
第一条検査(FAI)
The First Article Inspection (FAI) is a critical milestone. It’s a full verification of the first production-run part against the design drawings. For complex cnc machining titanium parts, FAI confirms our entire process—tooling, programming, and setup—is correct before mass production begins. It prevents costly errors down the line.
インプロセスモニタリング
We don’t wait until the end to find problems. We use methods like 統計的工程管理(SPC)14 to monitor the manufacturing process in real time. This allows us to detect and correct any deviations as they happen. This proactive approach ensures stability and repeatability.
The table below outlines a typical inspection flow for a titanium component.
| ステージ | Activity | Key Consideration for Titanium |
|---|---|---|
| Receiving | Material Certificate Verification | Correct grade (e.g., Grade 5) and sourcing |
| インプロセス | Key Feature Monitoring (SPC) | Tool wear, thermal expansion |
| 決勝 | 100% Critical Dimension Check | Conformance to GD&T, CMM measurement |
This structured process is fundamental. It’s how we guarantee that every single part we deliver is identical and meets all requirements.
Effective titanium quality control integrates precision tools like CMMs with structured processes like FAI and SPC. This ensures that process stability and part conformity are maintained from the first article to the final production unit, guaranteeing reliability.
How to Evaluate a CNC Partner for Titanium Machining
Choosing a titanium machining supplier is critical. The right partner ensures your high-performance parts meet spec. The wrong one can cause costly delays and failures.
This checklist helps you evaluate CNC shops systematically. It covers the core areas that matter most for successful titanium projects.
Key Areas for Vetting
Use this guide for procurement and engineering teams. It provides a clear framework for making an informed decision.
| Evaluation Category | 主な質問 |
|---|---|
| マシン能力 | Do they have rigid, high-torque 5-axis machines? |
| 素材の専門知識 | Can they discuss specific titanium grades (e.g., Grade 5 vs. Grade 2)? |
| 品質システム | Are they certified to AS9100 or ISO 13485? |
| Relevant Experience | Can they show examples of similar complex parts? |
A capable titanium manufacturing partner will confidently answer these questions.
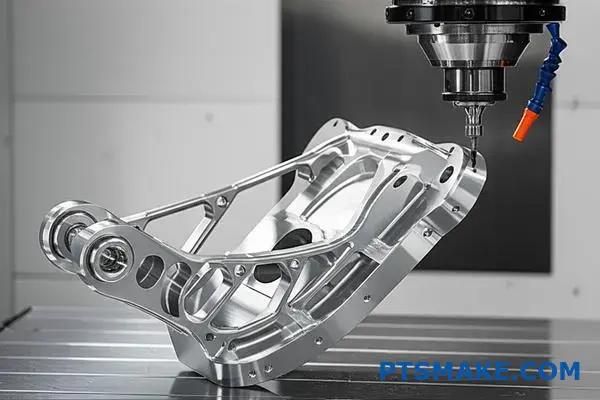

Finding the right partner for cnc machining titanium goes beyond a simple quote comparison. You need to dig deeper into their technical capabilities and quality processes. A robust evaluation protects your project from risk.
Machine Tool Capability
Standard machines struggle with titanium. Look for shops with modern, rigid 5-axis CNC centers. These machines minimize vibration, which is crucial for maintaining tight tolerances and achieving a good surface finish on titanium parts.
High-pressure coolant systems are also non-negotiable. They are essential for clearing chips and managing heat at the cutting zone. This prevents tool wear and material damage.
Material and Process Expertise
True expertise is vital when choosing a titanium machining supplier. The supplier should understand the nuances between different titanium alloys. Machining Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) is very different from machining commercially pure Grade 2.
Ask about their strategies for mitigating 加工硬化15. A knowledgeable partner will discuss specific tooling, feed rates, and cutting strategies designed to handle this challenge. At PTSMAKE, we have developed proprietary process parameters for various alloys.
| 認証 | 業界フォーカス | 保証内容 |
|---|---|---|
| AS9100 | 航空宇宙・防衛 | Strict process control, traceability, and risk management. |
| ISO 13485 | 医療機器 | Quality management for medical device components. |
| ISO 9001 | 一般製造業 | A foundational quality management system. |
Proven Experience
Finally, review their portfolio. Ask for case studies or examples of parts similar to yours in complexity and material. This is the best proof of their ability to deliver. A history of producing high-performance components demonstrates they are a reliable titanium manufacturing partner.
This checklist provides a structured approach for evaluating CNC shops. It helps you look beyond price to assess true capability, ensuring you find a partner who can handle the unique demands of cnc machining titanium and deliver quality parts consistently.
Case Study: Solving a Complex Titanium Bracket Machining Challenge
Theory is one thing, but results are what matter. Let’s walk through a real-world titanium machining case study.
An aerospace client approached us with a complex titanium bracket. This part had thin walls and intricate geometries. Their previous supplier struggled, facing high costs and inconsistent quality. This is a common story in cnc machining titanium.
The Initial Challenge
The primary issues were part deformation and rapid tool wear. This led to a high scrap rate, which drove up the unit price significantly.
| Challenge Area | 生産への影響 |
|---|---|
| Part Warping | Failed to meet dimensional tolerances |
| 工具摩耗 | Increased tooling costs and downtime |
| サイクルタイム | Long machining times, high labor cost |
| スクラップ率 | Over 20% of parts were rejected |
Our goal was to solve these problems. We needed to deliver a successful titanium part example that met performance and budget targets.
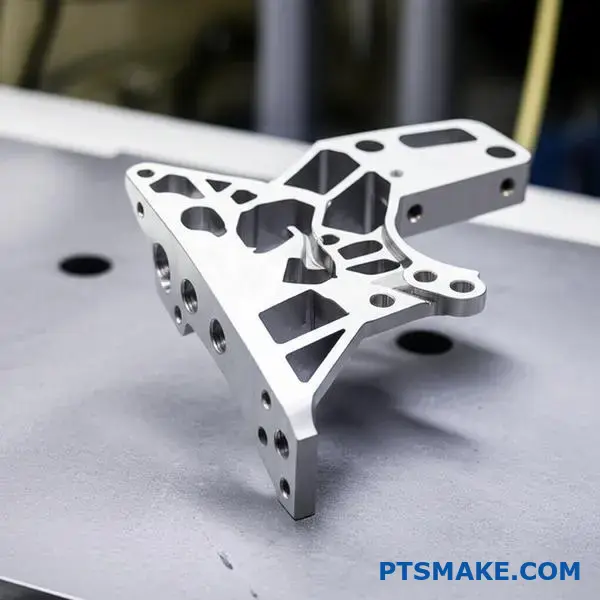
A Collaborative DFM Approach
The first step wasn’t to start machining. Instead, we initiated a Design for Manufacturability (DFM) review with the client’s engineering team. This collaborative process is key at PTSMAKE.
We identified a few internal corners with extremely tight radii. While possible to machine, these features were major drivers of tool stress and wear. We proposed a minor increase in the radii. This change had no impact on the bracket’s fit or function. The client quickly approved it.
The Machining Strategy
With the optimized design, we developed a multi-faceted machining strategy. Success with a complex titanium bracket requires more than just the right machine.
First, we chose a high-rigidity 5-axis CNC machining center. This minimized vibration, which is critical for thin-walled parts. Material selection for tooling was also crucial. We opted for specific carbide end mills with coatings designed for titanium alloys. These coatings reduce friction and combat 加工硬化16.
Our strategy focused on maintaining a constant tool engagement. High-speed milling with a trochoidal toolpath was employed. This approach prevents sudden impacts on the tool, extending its life and improving surface finish.
| Strategy Component | 根拠 |
|---|---|
| 5軸CNC | Access complex features, reduce setups |
| 超硬工具 | Resist heat and abrasive wear |
| 高圧クーラント | Efficient chip evacuation and cooling |
| トロコイド加工 | Maintain constant tool load, reduce wear |
The Successful Outcome
The results were immediate and significant. After implementing our strategy, we saw a dramatic improvement across all key metrics.
In collaboration with our client, we found that the scrap rate dropped to below 2%. The cycle time per part was reduced by approximately 35%. This successful titanium part example demonstrates how a smart, collaborative approach can conquer even the toughest machining challenges.
This titanium machining case study highlights a core principle. Proactive collaboration and a well-planned machining strategy are essential. They turn a difficult project into a repeatable, cost-effective success, delivering a part that performs flawlessly under demanding aerospace conditions.
The Future of Titanium Machining: Advanced Technologies to Watch
The world of CNC machining titanium is on the brink of a major shift. We’re moving beyond just faster spindles and sharper tools.
イノベーションの次の波
Three key areas are driving this change. These are hybrid manufacturing, advanced tool coatings, and AI-powered controls.
なぜこれが重要なのか
These aren’t just theories. They promise real-world benefits. Think faster production, better parts, and smarter processes. The future of titanium machining is exciting.
| テクノロジー | 伝統的なアプローチ | Future Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Part Creation | Purely Subtractive | Additive + Subtractive |
| 工具 | Standard Carbide | Coated, Smart Tools |
| プロセス | Manual Adjustment | AI-Driven, Adaptive |
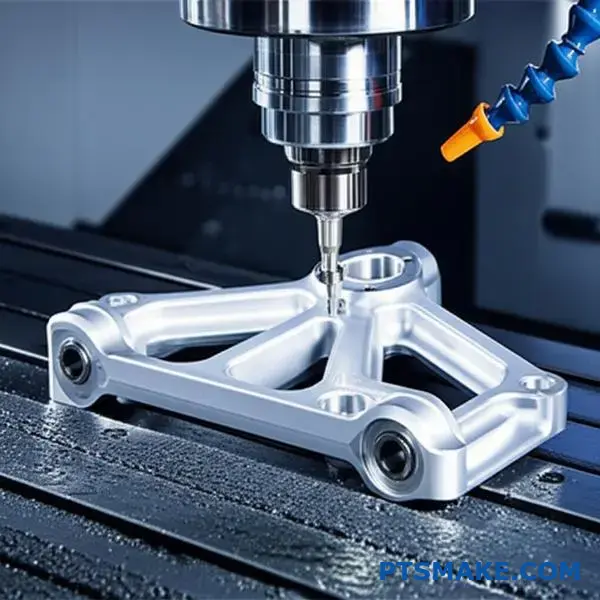

Let’s break down these titanium manufacturing innovations. Each one solves a different core challenge in CNC machining titanium, moving the industry toward a new standard.
Hybrid Machining: The Best of Both Worlds
Imagine building a complex titanium part close to its final shape using 3D printing. Then, you use CNC machining for the critical finishing touches. This is hybrid manufacturing.
This approach drastically cuts material waste. It also reduces overall machining time, which is a major cost driver for titanium projects. It’s a key part of advanced CNC titanium strategy.
Advanced Tool Coatings
Heat is the enemy when cutting titanium. New tool coatings are our best defense. They create an incredibly hard and slick barrier between the tool and the material.
These new coatings dramatically improve the トライボロジー17 properties at the cutting interface. Based on our internal tests, some coatings can extend tool life by over 30% while allowing for higher cutting speeds.
| コーティング・タイプ | 主なメリット | 理想的なアプリケーション |
|---|---|---|
| TiAlN | High-temperature hardness | High-speed roughing |
| AlCrN | 優れた耐摩耗性 | 仕上げ作業 |
| Nanocomposite | Extreme hardness & low friction | Demanding aerospace parts |
AI-Driven Adaptive Control
This is where manufacturing gets truly smart. Sensors on the machine listen to the cutting process. AI analyzes this data in real-time.
If it detects issues like tool wear or chatter, it automatically adjusts cutting parameters. This prevents failures and ensures consistent quality without constant operator oversight.
The future of titanium machining combines additive and subtractive methods, enhanced tooling, and AI. These innovations are set to revolutionize efficiency, reduce waste, and improve part quality, defining the next generation of advanced CNC titanium manufacturing.
Get a Custom CNC Machining Titanium Quote from PTSMAKE Today!
Ready to take your titanium CNC machining project from concept to production with unmatched precision and reliability? Contact PTSMAKE’s expert team for a fast, no-obligation quote—experience world-class quality, responsive support, and on-time delivery for your high-performance parts!
Learn more about why this property is essential for materials used inside the human body. ↩
Learn how adhesive wear occurs and impacts the surface integrity of your machined parts. ↩
Learn how this specific type of material transfer between tool and workpiece causes premature tool failure. ↩
Understand how this material adhesion can destroy your workpiece and tool, and learn effective prevention methods. ↩
Explore how this process boosts titanium’s inherent resistance to corrosion in harsh environments. ↩
Explore how this metallurgical effect impacts tool life and your project’s bottom line. ↩
Learn how this metallurgical effect complicates machining and what steps we take to prevent it. ↩
Learn how this cumulative error affects your final part quality and how to control it. ↩
Learn how a documented chain of custody protects your project and ensures full compliance. ↩
Learn how to prevent material failure when dissimilar metals are used in an assembly. ↩
Understand the internal forces that can compromise your part’s dimensional accuracy. ↩
Learn more about this critical machining challenge and how to prevent it. ↩
Learn how proper workholding boosts production efficiency and part consistency in high-volume CNC machining. ↩
Discover how SPC helps reduce defects and improve manufacturing consistency for your projects. ↩
Discover how this material property impacts tool life and part quality during machining. ↩
Learn how this material property affects machinability and tool life in our detailed guide. ↩
Understand the science of friction and wear to see how new coatings revolutionize tool performance. ↩