You’re developing a micro-scale component that demands tolerances tighter than a human hair’s width. Standard CNC machining keeps failing to meet your specifications, and every rejected batch pushes your project timeline further behind schedule.
Micro CNC machining delivers micron-level precision for components smaller than 10mm, using specialized tooling and advanced process control to achieve tolerances down to ±0.001mm for medical devices, robotics, and aerospace applications.
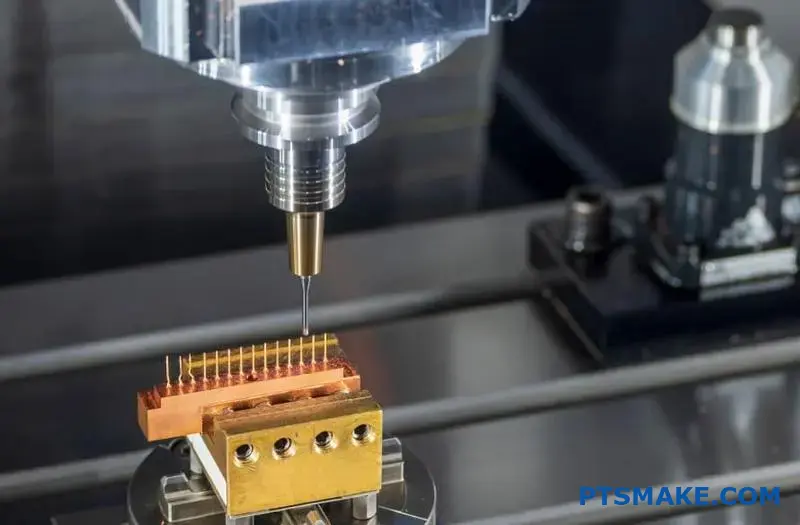
This guide covers everything from eliminating tolerance issues to scaling micro production volumes. You’ll discover why some micro machining projects fail while others succeed, plus get insider knowledge on material selection, quality control methods, and supplier evaluation strategies that can save your next project.
How To Eliminate Tolerance Issues With Micro CNC Machining
In industries like medical, robotics, and aerospace, there is no room for error. Even the smallest deviation from a design specification can lead to critical failures.
This is where micro CNC machining becomes essential. It directly addresses these precision tolerance problems.
We are not just talking about standard precision. We mean tight tolerance machining that achieves micron-level accuracy manufacturing. The ultimate goal is simple: zero-defect CNC parts, every single time. This technology makes that goal achievable.
| Industria | Common Tolerance Challenge | Micro CNC Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Médico | Implant fit and function | Sub-micron surface finishes |
| Aeroespacial | Component weight and strength | Ultra-thin walls, complex geometry |
| Robótica | Sensor and actuator precision | Miniature parts with high accuracy |

Traditional CNC machining often hits a wall when tolerances shrink to the micron level. Micro CNC machining pushes past this barrier. It’s not just a scaled-down version of conventional machining; it’s a fundamentally different approach.
The Core of Micron-Level Accuracy
Achieving this precision requires specialized equipment and processes. The machines themselves are built for extreme rigidity and thermal stability. This prevents minute expansions or contractions from affecting the workpiece during the machining process. We found this to be a critical factor in our tests.
Advanced Tooling and Spindles
The cutting tools are incredibly small, sometimes with diameters smaller than a human hair. They are paired with high-speed spindles that can reach over 100,000 RPM. This combination allows for material removal with minimal cutting forces, which reduces part deflection and stress.
This process is so precise because control systems use advanced components. For instance, some high-end machines use piezoelectric actuators1 for tool positioning, allowing for adjustments at the nanometer scale. This level of control is simply impossible with standard servo motors.
| Característica | CNC convencional | Micro CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Tolerancia típica | ±0.025 mm | ±0.001 mm |
| Velocidad del cabezal | < 20,000 RPM | > 60,000 RPM |
| Tool Diameter | > 1 mm | < 0.5 mm |
| Enfoque clave | Speed & Volume | Precision & Complexity |
Micro CNC machining utilizes specialized technology to solve critical tolerance challenges in demanding industries. It enables micron-level accuracy through advanced machinery, ultra-small tooling, and superior process control, making zero-defect parts a manufacturing reality for complex components.
Why Most Micro Machining Projects Fail—And How To Avoid It
In micro CNC machining, success is measured in microns. Small oversights quickly become major failures. Many projects fail before a tool even touches the material.
The most common issues are predictable. They usually fall into a few key categories.
Design and Material Pitfalls
Poor design-for-manufacturing (DFM) is a primary cause. Designers may specify features that are simply too small or complex for existing tools.
Material selection is another frequent problem. A material that performs well at a macro scale can behave unpredictably when machined into micro components.
| Pitfall Area | Error común | Buenas prácticas |
|---|---|---|
| Design (DFM) | Unrealistic feature sizes | Early collaboration with machinist |
| Material | Ignoring micro-scale properties | Material testing for application |
| Inspección | Using standard metrology tools | Investing in optical or CMM |

A thorough micro CNC failure analysis often points back to the initial planning phase. These early mistakes are the most expensive to fix later on.
Poor Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
Many CAD models look great on screen but are impossible to machine. Common DFM errors include internal corners with radii smaller than the cutting tool. Or, walls that are too thin to withstand cutting forces. Proper DFM is crucial for avoiding defects in CNC micro components.
Material Mismatch and Its Consequences
Material selection is more than just picking from a datasheet. At the micro-level, grain structure, hardness, and internal stresses have a magnified effect. We’ve seen projects where the specified material’s material anisotropy2 caused unexpected warping after machining. This is a classic example of a macro-level assumption failing in micro manufacturing.
Inadequate Inspection Methods
You cannot verify a micron-level tolerance with a pair of calipers. Relying on improper inspection tools gives a false sense of security. This leads to parts being shipped that are actually out of spec. Adopting the right quality control is one of the best practices for micro part production.
| Desafío | Ineffective Method | Effective Method |
|---|---|---|
| Verificación de tolerancias | Calibres digitales | Vision Measurement System (VMS) |
| Acabado superficial | Control visual | Optical Profilometer |
| Geometría compleja | Manual Probes | Máquina de medición por coordenadas (MMC) |
Projects often fail due to overlooked fundamentals. Poor DFM, incorrect material choice, and inadequate inspection create a recipe for failure. Addressing these areas early in the process is the most effective way to ensure the success of any micro CNC machining project.
The Secret To Consistent Quality In High-Precision Micro Parts
Achieving consistent quality in micro parts is not luck. It is a system built on robust strategies. Our approach to micro CNC quality assurance focuses on preventing issues before they become defects. This ensures every tiny part meets exact specifications.
These strategies work together. They form a comprehensive quality framework that we rely on daily.
| Estrategia | Objetivo principal | Stage of Use |
|---|---|---|
| SPC | Estabilidad del proceso | En proceso |
| Real-Time Monitoring | Immediate Correction | En proceso |
| Inspección MMC | Final Verification | Post-Production |
This systematic control is fundamental. It is how we deliver reliable parts for your projects.

Proactive Defect Prevention
We don’t just inspect finished parts. We aim to prevent defects from ever happening. This is where Control estadístico de procesos (CEP)3 becomes critical in our workflow. By analyzing process data, we can identify trends. This allows us to predict and correct deviations before they result in a non-conforming part.
Real-Time Process Adjustments
For micro CNC machining, immediate feedback is essential. We embed sensors in our machines for real-time monitoring. These sensors track variables like tool wear, temperature, and vibration. If a parameter drifts outside its control limits, the system alerts our technicians instantly for immediate adjustments.
Advanced Verification with CMM
When dealing with microscopic features, traditional measurement tools are not sufficient. A robust CNC micro part inspection process is necessary. We rely on advanced Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) for this critical step.
| Método de inspección | Aplicación | Beneficio clave |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Calipers | Dimensiones básicas | Quick Checks |
| Comparadores ópticos | 2D Profiles | Inspección visual |
| CMM for micro parts | Complex 3D Geometry | High Accuracy (Micron-level) |
High-resolution CMM for micro parts provides non-contact, precise measurements. It verifies that even the most complex geometries meet tight tolerance requirements, which is a core part of our quality guarantee at PTSMAKE.
This layered quality strategy is key. It combines predictive analysis with real-time adjustments and precise final verification. This ensures every micro component we produce consistently meets the highest standards of quality and precision.
Comparing Swiss Turning Vs. Micro CNC Milling: What You Must Know
Choosing the right process is critical in micro manufacturing. The debate over micro CNC milling vs turning often comes down to part geometry and production volume. Each method has distinct advantages.
Swiss turning excels at producing long, slender parts with high precision. It feeds material through a guide bushing, providing excellent support.
5-axis micro milling, on the other hand, is ideal for complex, non-symmetrical shapes. It can machine features on multiple faces in a single setup. Let’s compare them directly.
Comparación cara a cara
| Característica | Torneado suizo | 5-Axis Micro Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Geometría de la pieza | Long, slender, cylindrical | Complex, blocky, non-symmetrical |
| Lo mejor para | Pins, screws, shafts, connectors | Housings, molds, impellers |
| Tiempo de preparación | Más largo | Shorter for one-offs |
| Duración del ciclo | Very fast for high volumes | Slower per part |
| Material Use | Bar stock | Billet or block |

Deciding between these two powerful micro CNC machining methods requires a deeper look at specific applications. It’s not just about the machine; it’s about aligning the process with your design intent and business goals. I’ve seen projects where choosing the wrong method upfront led to significant cost overruns and delays.
Use Cases for Swiss Turning
Swiss turning for micro parts is unbeatable for high-volume production of small, intricate cylindrical components. Think of medical device components like bone screws or dental implants. It’s also perfect for electronic connectors and shafts used in robotics. The speed and efficiency in creating precision turning micro components from bar stock make it highly cost-effective at scale. The guide bushing system minimizes workpiece deflection4, which is crucial for maintaining tight tolerances on long, thin parts.
When to Choose 5-Axis Micro Milling
Conversely, 5-axis micro milling shines when complexity trumps volume. This process is for parts that are anything but cylindrical. Consider miniature sensor housings, complex mold inserts, or tiny impellers for microfluidics. The ability to machine five sides of a part in one clamping operation reduces setup time and improves accuracy by eliminating re-fixturing errors. It provides the design freedom needed for the most innovative micro-scale products.
The choice between Swiss turning and 5-axis micro milling depends on your part’s geometry, complexity, and production volume. Swiss turning is for high-volume slender parts, while milling is for complex, low-to-mid volume components. Both are essential tools in modern micro manufacturing.
Top Materials For Micro CNC Machining—And Their Trade-Offs
Selecting the right material is a critical first step. It directly impacts the final part’s performance and cost. For micro CNC machining, this choice becomes even more crucial.
The tiny features and tight tolerances demand specific material properties. This is a quick machining small parts material guide to help you navigate the options. We’ll focus on four popular choices.
Key Material Categories
Each material presents a unique set of trade-offs.
| Material | Característica principal | Desafío común |
|---|---|---|
| Titanio | Alta resistencia al peso | Difficult to Machine |
| PEEK | Resistencia química | Higher Cost (Plastic) |
| Inconel | Resistencia al calor | Extreme Machining Difficulty |
| Aluminio | Maquinabilidad | Fuerza inferior |

Choosing the best material involves a careful balancing act. You have to weigh performance needs against manufacturability and budget. Let’s break down these materials in more detail.
High-Performance Metals
Titanio
Titanium is a star in aerospace and medical fields. Its strength and biocompatibility are unmatched for its weight. However, micro part titanium CNC is challenging. It dissipates heat poorly, which can quickly wear down micro-tools.
Inconel
This superalloy thrives in extreme environments. Think jet engines or chemical reactors. Its resistance to heat and corrosion is incredible. But it is extremely tough to machine due to its tendency for endurecimiento del trabajo5. This drives up machining time and cost significantly.
Versatile and Lightweight Options
Aluminio
Aluminum is often the go-to for prototypes. It’s lightweight, affordable, and easy to machine. This makes it ideal for projects where speed and low cost are the primary drivers.
PEEK
Para high-precision plastic machining, PEEK is a top choice. This thermoplastic offers excellent mechanical strength and chemical stability. It’s often used as a metal replacement in demanding medical or electronic applications.
| Material | Maquinabilidad | Rendimiento | Coste relativo | Best Fit Industries |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanio | Difícil | Muy alta | Alta | Medicina, aeroespacial |
| PEEK | Moderado | Alta | Medio-Alto | Medicina, Electrónica |
| Inconel | Muy difícil | Extremo | Muy alta | Aerospace, Energy |
| Aluminio | Excelente | Medio | Bajo | Prototyping, Automotive |
Material choice in micro CNC machining dictates success. High-performance metals like Titanium and Inconel offer superior properties but come with machining challenges and higher costs. Aluminum and PEEK provide excellent, versatile alternatives for different application needs.
Speed Vs. Precision: How To Balance CNC Cycle Time With Accuracy
Achieving fast production cycles without sacrificing micron-level precision is a key challenge in micro cnc machining. It requires smart, tactical decisions. This is not about choosing one over the other.
It’s about creating a strategy where both can coexist. Balancing speed and precision in CNC is a dynamic process. It depends heavily on the project specifics.
Here are the initial trade-offs we consider at PTSMAKE:
| Factor | Impact on Speed | Impacto en la precisión |
|---|---|---|
| Velocidad de corte | High speed reduces time | Can increase tool wear/vibration |
| Selección de herramientas | Specialized tools are faster | Standard tools may lack accuracy |
| Velocidad de alimentación | Higher rates are quicker | May compromise surface finish |

Strategic Decision-Making for Micro Parts
In efficient micro part machining, every second counts. But so does every micron. We start by analyzing the part’s geometry and material. This dictates our entire approach to the project.
Optimizing Toolpaths and Machine Parameters
High-speed micro CNC relies on more than just fast spindle speeds. We focus on optimized toolpaths. This reduces unnecessary machine movement and air-cutting time. It’s a critical first step for efficiency.
We also carefully manage thermal expansion during machining. For micro parts, even slight temperature changes can cause deviations from the required specifications. This is where advanced machine features, like Volumetric Error Compensation, become invaluable for maintaining stability.
Our engineers often work with clients to define critical-to-quality (CTQ) features. This allows us to apply the highest precision only where it is absolutely needed. We can then increase speed on less critical features, optimizing the overall cycle time.
Here’s a look at our decision framework:
| Táctica | Objetivo | Benefit for Client |
|---|---|---|
| Simulación | Predict and prevent errors | Reduced waste and faster delivery |
| In-process Probing | Verify dimensions mid-cycle | Ensures consistency without stopping |
| Automated Tooling | Quick tool changes | Minimizes machine downtime |
| Hybrid Machining | Combine multiple processes | Reduces setups and cycle time |
Ultimately, balancing speed and precision isn’t a compromise. It’s a strategy. By using smart tactics like toolpath optimization and focusing on critical features, efficient micro part machining can achieve both rapid cycles and extreme accuracy for your components.
How Tighter Tolerances Reduce Failures In Assembly And Operation
Micron-level precision directly cuts downstream defects. This enhances the final product’s mechanical performance. It’s a core benefit of tight tolerance CNC machining.
The Direct Link to Assembly Yield
Mejor micro part fit accuracy means fewer rejects. Components simply fit together as designed. This is crucial for improving the assembly yield micro components.
We’ve observed a clear pattern in our projects.
| Nivel de tolerancia | Assembly Failure Rate |
|---|---|
| Estándar (±0,1 mm) | ~5-10% |
| Tight (±0.01mm) | <1% |
| Micron (±0.005mm) | Near 0% |
Enhancing Mechanical Function
Tighter tolerances are not just for assembly. They define how well a part performs over time. This is one of the key tight tolerance CNC benefits.

Beyond the Initial Fit
The real value of micron-level accuracy appears during operation. It’s about preventing failures long after a product leaves the factory. This precision is achievable through advanced micro cnc machining.
For example, in high-speed robotics, even a tiny imbalance can cause vibrations. These vibrations lead to premature wear and catastrophic failure. Precise components eliminate this risk from the start.
The Cumulative Effect on System Longevity
Think of a complex gearbox. If one gear has a slight deviation, it affects every other gear it touches. This small error multiplies, degrading the system’s propiedades tribológicas6 and shortening its lifespan.
At PTSMAKE, we focus on this system-level impact. Ensuring each micro component is perfect protects the entire assembly.
Our data from client studies highlights this relationship.
| Component Fit Accuracy | Estimated System Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Loose Tolerances | Línea de base |
| Tolerancias estrictas | +40% |
| Micron-Level Precision | +75% or more |
This shows that investing in precision upfront pays off. It creates more reliable and durable products. It also builds trust with end-users who depend on that performance.
Micron-level precision achieved through micro cnc machining dramatically reduces assembly defects. It also boosts the long-term mechanical performance and reliability of the entire system, preventing failures during operation and extending product life.
Designing For Manufacturability In Micro CNC Projects
Transitioning to micro-scale projects requires a new mindset. Standard CAD practices often fail here. Overly complex designs can make manufacturing impossible or extremely costly.
This is where Design for Manufacturability (DFM) is critical. I’ll share some key DFM guidelines for micro parts.
We will focus on practical micro CNC CAD design tips. Understanding CNC manufacturable micro geometries from the start saves time and money. It’s about designing smarter, not just smaller. This ensures successful micro cnc machining.

Rethinking Geometry for the Micro Scale
The biggest shift is embracing simplicity. Features that are easy on a larger scale become major challenges in micro cnc machining. Every line in your CAD model matters. This is a core principle we follow at PTSMAKE.
Key CAD Adjustments
Avoid sharp internal corners. All internal corners will have a radius left by the cutting tool. Specifying a radius slightly larger than the tool’s radius is ideal for tool life and surface finish.
Wall thickness is another critical factor. Walls that are too thin can warp or break during machining. This is due to cutting forces and material stress at such a small scale.
Tolerances and Tooling
Tolerances need careful consideration. Holding tight tolerances on micro parts is possible but increases costs. Only specify them where absolutely necessary. The process is sensitive to factors like desviación de la herramienta7, which can affect final dimensions.
Here is a quick comparison based on our internal studies:
| Característica | Standard DFM | Micro DFM Guideline |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Radii | As large as practical | At least 0.15mm, > tool radius |
| Espesor de pared | > 1.5mm (Metal) | > 0.5mm, material dependent |
| Profundidad del agujero | Up to 10x diameter | Max 6x diameter recommended |
| Tolerancias | Standard +/- 0.1mm | Tighter where needed, e.g., +/- 0.01mm |
These guidelines help hardware teams adapt designs effectively. They prevent over-complication from the very start.
Adapting CAD for micro fabrication is non-negotiable. Applying micro-specific DFM, simplifying geometries, and managing tolerances are key. This approach ensures your designs are manufacturable, cost-effective, and delivered on schedule, especially in high-precision micro cnc machining projects.
The Complete Validation Process For Micro CNC Parts
Validating CNC micro components is not just a final check. It’s a comprehensive process. This ensures every part meets exact specifications.
This process starts with a First Article Inspection (FAI). It then moves to capability studies and validation protocols.
Key Qualification Stages
These steps are critical for precision part certification. They build confidence in the manufacturing process.
| Procedure | Propósito | Métrica clave |
|---|---|---|
| Inspección del primer artículo | Verify process produces a correct part | Full dimensional report |
| Capability Study | Assess process stability and consistency | Cpk, Ppk |
| Validation Protocol | Formal proof of process integrity | IQ/OQ/PQ reports |
Adecuado FAI micro machining confirms our setup is perfect before full production begins.

A robust qualification plan is essential for any serious micro cnc machining project. It goes far beyond simply measuring the first part off the line.
Inspección del primer artículo (FAI)
FAI is the foundation. We conduct a full dimensional layout of the first production part. This verifies that our tooling, machine setup, and process parameters are correct. It’s a formal method for validating CNC micro components.
Proving Process Capability
After FAI, we run capability studies. This involves analyzing a sample of parts. We use tools from Control estadístico de procesos8 to measure process variation. Based on our studies with clients, a Cpk value of 1.33 or higher indicates a stable and capable process, ensuring long-term consistency. This is how we guarantee quality from the first part to the last.
Formal Validation Protocols
For industries like medical and aerospace, we implement formal validation protocols.
| Escenario | Nombre | Descripción |
|---|---|---|
| IQ | Installation Qualification | Verifies equipment is installed correctly. |
| OQ | Operational Qualification | Confirms equipment operates within set limits. |
| PQ | Performance Qualification | Proves the process consistently produces good parts. |
This rigorous framework provides the documented evidence needed for precision part certification. It demonstrates that every aspect of manufacturing is controlled and repeatable. At PTSMAKE, this systematic approach builds the trust our partners require.
A structured validation process is non-negotiable. From a detailed FAI to capability studies and formal protocols, these steps ensure every micro component meets the highest standards of quality and consistency for precision part certification.
Precision At Scale: Can Micro CNC Meet Your Production Volumes?
Many view micro CNC machining as a tool for prototypes. Or for very small, specialized runs. This is a common misconception.
True scalability is not just about more machines. It’s about a smarter, more automated process. With the right strategy, high-volume production is entirely feasible. This approach ensures scalable micro part production meets demand.
Scaling Factors
| Característica | Low-Volume Focus | High-Volume Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Configurar | Frequent, Manual | Minimized, Automated |
| Automatización | Bajo | High (Robotics, Cells) |
| QC Method | Inspección manual | In-Line, Automated |
At PTSMAKE, we’ve built systems to handle these demands. We achieve precision at any scale.

The main concern is maintaining quality during high-volume production. How do we ensure the ten-thousandth part is identical to the first? The answer lies in process optimization and automation. This is where volume capacity CNC micro machining truly shines.
Strategies for Scaling Production
We focus on creating a manufacturing ecosystem. This system is designed for consistency and efficiency, especially for micro parts batch production. It’s not just about running machines faster.
Automation and Dedicated Cells
Robotics for loading and unloading parts reduce cycle times. Automated in-line inspection systems check parts without stopping production. This ensures quality is maintained consistently. We use dedicated production cells for long-running projects. This minimizes setup and changeover delays significantly.
Quality at Scale
For high volumes, manual inspection is not enough. We rely on data-driven methods. Implementing Control estadístico de procesos (CEP)9 is essential. It allows us to monitor and control the process. This proactive approach prevents defects before they occur. It’s crucial for maintaining tight tolerances across entire production runs.
| Automation Benefit | Impacto en la producción |
|---|---|
| Higher Throughput | Machines run continuously with minimal downtime. |
| Calidad constante | Removes human error from repetitive tasks. |
| Estabilidad del proceso | Data monitoring ensures process stays within spec. |
Scaling micro CNC machining from prototype to production is achievable. It requires a dedicated strategy focused on automation, process control, and robust quality systems. The key is shifting from a job-shop mindset to a streamlined, high-volume manufacturing workflow.
Inside Look: How Industry Leaders Use Micro CNC In Product Development
Fortune 500 companies don’t guess. They validate. When moving from concept to production, they rely on micro CNC machining.
This method allows for rapid iteration. It ensures the first functional part is nearly identical to the final product.
Medical Device Prototyping
A top medical firm needed a complex surgical component. They started with micro CNC prototypes. This confirmed the design’s viability using the final, bio-compatible material.
This approach is standard. It de-risks the entire production ramp-up.
| Escenario | Método | Ventaja |
|---|---|---|
| Concepto | Impresión 3D | Speed, low cost |
| Prototipo | Micro CNC | Final material, tight tolerance |
| Producción | Micro CNC/Molding | Scalability, consistency |
From Prototype to Market
These micro CNC case studies reveal a clear pattern. Prototyping micro machined parts directly leads to a smoother production transition. It eliminates costly surprises.

The leap from a working prototype to mass production is full of challenges. For industry leaders, micro CNC machining bridges this gap effectively. It’s not just about making a small part; it’s about making it right, consistently, and at scale.
Enterprise Use of Micro Machining
In consumer electronics, a major brand needed a new miniature connector. They used micro CNC to test five different designs in two weeks. This rapid feedback is invaluable. It would be impossible with traditional molding.
This process highlights the importance of precise parameters. The final feel and function depend on factors like the Surface Roughness Average (Ra)10, which must be consistent. Based on our client collaborations, controlling these details early is key.
Enterprise use of micro machining is a strategic choice. It provides flexibility and reduces time-to-market. When production molds are being prepared, we at PTSMAKE often supply initial batches using micro CNC. This keeps the project moving forward without any downtime.
| Transition Phase | Desafío clave | Micro CNC Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Validación del diseño | Propiedades de los materiales | Use of final production-grade materials |
| Pruebas funcionales | Tolerancias estrictas | Achieving sub-micron precision |
| Producción de puentes | Tooling Lead Time | Immediate low-volume part supply |
| Producción en serie | Escalabilidad | Validated process for seamless handover |
This integrated approach ensures that what works in the lab also works on the assembly line. It is a core part of modern hardware development.
Fortune 500 companies use micro CNC machining to validate designs with final materials, ensuring a seamless and de-risked transition from prototyping micro machined parts to full-scale production. This strategy accelerates time-to-market and improves product quality.
What Questions Your CNC Supplier Should Be Asking About Micro Parts
The quality of your micro parts often depends on the quality of the conversation with your supplier. When vetting micro machining partners, listen to the questions they ask you. A proactive partner digs deeper than the CAD file.
Their questions reveal their expertise and commitment. They should be challenging your design for manufacturability. This is a key step in supplier evaluation for micro CNC projects.
The Critical Questions on Tolerance
A good supplier will want to understand the por qué behind your tolerances. They are not just numbers on a drawing.
| Tipo de función | A Good Supplier Asks… |
|---|---|
| Critical Dimensions | "Which tolerances are absolutely critical for function?" |
| Non-Critical Areas | "Is there any flexibility in non-critical areas to improve yield?" |
| Mating Parts | "What is the tolerance of the mating part for this component?" |
These questions show they are thinking about the final assembly and overall project success. This is what good CNC communication practices look like.

True partnership in micro CNC machining goes beyond simply executing an order. It involves a collaborative dialogue. A competent supplier acts as a manufacturing consultant. They identify potential risks before a tool ever touches metal. This dialogue is essential when vetting micro machining partners.
Probing Feature and Finish Limitations
For micro parts, certain features can be difficult or impossible to machine or inspect. Your supplier should be asking about these specific limitations early in the process. This prevents costly redesigns and delays down the line.
They must understand how the part will be used and tested. For instance, surface finish requirements directly impact tooling, cycle time, and cost. A supplier who doesn’t ask about your inspection methods might deliver a part that you cannot verify. This level of detail in Metrología11 no es negociable.
Here is how to spot a true partner:
| Tema | The Passive Supplier | The Proactive Partner (like PTSMAKE) |
|---|---|---|
| Esquinas afiladas | "Okay, a 0.05mm internal radius." | "Can this internal corner have a slightly larger radius to allow for a stronger tool, increasing reliability?" |
| Inspección | "The print calls for Ra 0.4 μm." | "How will you measure this Ra 0.4 μm finish on this internal feature? What equipment will you use?" |
| Material | "We will use the specified material." | "Given the part’s function, have you considered an alternative material that offers better machinability for these features?" |
This proactive communication is a core part of our process at PTSMAKE. We aim to be a trusted manufacturing partner, not just another vendor on your list.
A supplier who asks probing questions about tolerances, features, and testing is not creating problems. They are preventing them. This collaborative approach is the hallmark of a reliable partner for complex micro CNC machining projects.
Solving Unseen Challenges In Micron-Level Component Fabrication
When machining micro features, problems are not always visible. Tool deflection, burr formation, and heat distortion are major micro CNC challenges.
They can ruin a part’s tolerance and function. Ignoring them leads to costly failures. Effective process control is key.
The Micron-Level Battlefield
Controlling these tiny forces is crucial for success. Here’s a quick look at these common issues in micro cnc machining.
| Desafío | Causa principal | Impact on Part |
|---|---|---|
| Desviación de la herramienta | Cutting forces on tiny tools | Inaccurate dimensions, poor surface finish |
| Formación de rebabas | Material plastic deformation | Assembly problems, potential for shorts |
| Heat Distortion | Friction from cutting | Warping, altered material properties |
Successfully overcoming limitations micro parts face requires a deep understanding of these factors.

Mastering Process Control for Micro Parts
At PTSMAKE, our approach to process control is proactive, not reactive. We anticipate these issues when machining micro features. This ensures we meet specifications from the very first part. It’s about building quality into the process itself.
Mitigating Tool Deflection
Tiny tools bend easily under pressure. We use high-stiffness carbide tools and specialized coatings. Our CAM software also creates toolpaths with constant tool engagement. This avoids sudden shocks that cause deflection.
Preventing Burr Formation
Burrs are tiny, unwanted pieces of material. They are a nightmare for micro-electronics. We fine-tune feeds and speeds for each material. Sometimes, a final deburring step under a microscope is needed. This ensures clean, sharp edges.
Controlling Heat Distortion
Heat is the enemy of precision. High-pressure coolant is essential. It flushes away chips and cools the cutting zone instantly. We also manage cutting speeds to minimize friction. This prevents heat from building up and altering the part’s tensión residual12 and final shape.
| Control Strategy | Desviación de la herramienta | Formación de rebabas | Heat Distortion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trayectorias optimizadas | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Refrigerante de alta presión | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Herramientas especializadas | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Precise Feeds/Speeds | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
Mastering these controls is how we deliver reliable micro components.
Process control in micro CNC machining is about managing invisible forces. Anticipating tool deflection, burrs, and heat distortion with precise strategies is essential. This proactive approach ensures part integrity and overcomes the inherent limitations of working at the micron scale.
The Smart Buyer’s Guide To Micro CNC Tolerances & Specs
Understanding the Blueprint for Micro Parts
Interpreting technical drawings for micro dimensions can be challenging. A single misplaced symbol or an overly tight tolerance can inflate costs significantly.
This section serves as a basic micro CNC dimensioning guide. We’ll explore how to read these specifications accurately. The goal is to prevent unnecessary expenses from over-specification. Understanding how tight specs impact cost is crucial for any project’s success in micro CNC machining.
A Practical Guide to Reading Micro Tolerances
Learning how to read tolerances for micro parts is not just for engineers. Decision-makers need this skill to manage budgets effectively. Every line on a drawing has cost implications.
Key Elements on a Micro Part Drawing
A drawing communicates more than just shape. It details surface finish, material, and crucial tolerances that define function. Misunderstanding these details is a common pitfall.
Here is a simplified breakdown of common symbols:
| Símbolo | Significado | Implication for Micro CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Ø | Diámetro | Defines the size of a circular feature. |
| R | Radio | Specifies the curvature of an edge or surface. |
| +/- | Bilateral Tolerance | Allows variation in both positive and negative directions. |
| ⌖ | Tolerancia posicional | Controls the location of a feature. |
How Tight Specs Impact Cost
Over-specification is a frequent issue. For example, tightening a tolerance from ±0.01mm to ±0.005mm might seem small. However, this can easily double the machining time and cost.
At PTSMAKE, we often advise clients on their designs. We help them find a balance between functionality and manufacturability. This ensures the part works as intended without excessive cost. Understanding a system like Dimensionamiento geométrico y tolerancias13 is vital for this optimization process.
Correctly interpreting micro-dimension drawings is key to cost control. Over-specifying tolerances directly increases manufacturing complexity and expense. Clear communication with your manufacturing partner, like us at PTSMAKE, helps optimize design for both performance and budget.
Micro CNC Machining For Medical Devices: What You Need To Know
When producing parts for medical devices, precision goes beyond dimensions. Regulatory compliance and cleanliness are non-negotiable. For medical device engineers, understanding these requirements is critical.
This ensures patient safety and successful product launches. Let’s discuss the key standards.
Regulatory Standards in Medical Machining
The primary standard is ISO 13485. It governs the quality management system for medical device manufacturing. It’s a framework for consistency and safety.
The Role of Cleanliness
Contamination control is vital. Particles or residues can cause device failure or harm patients. This is where specialized environments come into play for any CNC micro machining for medical aplicaciones.
| Standard/Practice | Objetivo principal |
|---|---|
| ISO 13485 | Sistema de gestión de la calidad |
| Limpieza | Contamination Control |
| Trazabilidad | Part & Material History |

Navigating the regulatory landscape is a core challenge. It’s not just about making a part to print; it’s about proving how you made it, with what materials, and in what environment. This is where a partnership with an experienced manufacturer becomes invaluable.
ISO 13485: More Than a Certificate
ISO 13485 manufacturing micro parts requires a robust quality management system (QMS). This system mandates strict controls over every process. It covers everything from material sourcing to final inspection and documentation. Traceability is key here. We must be able to track every part back to its raw material batch.
Risk Mitigation and Validation
A major part of ISO 13485 is risk management. We analyze potential failure modes for each production step. We then implement controls to mitigate those risks. This systematic approach ensures reliability. It also involves rigorous Validación del proceso14 to confirm that our manufacturing steps consistently yield parts that meet specifications.
Cleanliness in Production
For many sensitive components, cleanroom micro machining is essential. This controlled environment minimizes airborne particulates, protecting parts from contamination.
| Risk Mitigation Strategy | Descripción |
|---|---|
| FMEA | Analyzing potential process failures. |
| Validation (IQ/OQ/PQ) | Verifying equipment and processes. |
| Trazabilidad de los materiales | Documenting material origins and batches. |
| Cleanroom Control | Managing environmental contaminants. |
For medical micro machining, success hinges on rigorous adherence to standards like ISO 13485. A controlled, clean environment and proactive risk management are not optional—they are essential for producing safe, reliable parts.
Avoid Communication Gaps: 7 Must-Have Details In Micro CNC RFQs
A Request for Quotation (RFQ) is your first, most critical communication with a manufacturer. For micro CNC machining, details are everything.
Vague RFQs often lead to guesswork. This results in misquotations, production delays, and parts that don’t meet your standards.
Providing clear, complete information is the only way to get accurate pricing. It also ensures the final components are exactly what you designed. This guide acts as your essential RFQ checklist. It helps you specify CNC micro features for a seamless process.

An RFQ for micro CNC machining needs more than just a 3D model. It must be a complete technical package. Missing information forces us to make assumptions about tolerances, finishes, or even materials. This creates risk for both you and the supplier. At PTSMAKE, we’ve found that the most successful projects begin with the most detailed RFQs.
Clear instructions remove ambiguity. They allow us to quote micro components accurately and plan the most efficient manufacturing path. This saves time and prevents costly rework later. Your goal should be to leave no room for interpretation. Every critical feature should be clearly defined.
Essential RFQ Checklist for Micro CNC
To avoid communication gaps, ensure your RFQ includes these crucial details. This information helps us understand your exact needs for any Metrología15 requirements and other specifications.
| RFQ Detail | Why It’s Crucial | Ejemplo |
|---|---|---|
| Calidad del material | Affects tool choice, speed, and cost. | Aluminum 6061-T6, not just "Aluminum" |
| Tolerancias críticas | Focuses effort on what matters most. | Highlight ±0.005mm on the 2D drawing. |
| Acabado superficial (Ra) | Dictates the final machining steps and cost. | Specify Ra 0.8 µm on sealing surfaces. |
| Quantity Breaks | Allows for accurate volume-based pricing. | Request pricing for 100, 500, and 1000 units. |
| Inspection Needs | Ensures quality standards are met and verified. | Request a CMM report for critical features. |
| Tratamiento posterior | Defines necessary secondary operations. | Anodizing Type II, Black; or Heat Treat to HRC 45. |
| CAD & 2D Drawings | Provides comprehensive geometric and tolerance data. | Submit both a STEP file and a PDF drawing. |
A well-prepared RFQ with specific details on materials, tolerances, and finishes is non-negotiable. It is the best way to prevent errors, get reliable quotes, and ensure your micro CNC machining project succeeds from the start.
Ready to Elevate Your Micro CNC Machining? Contact PTSMAKE Today!
Unlock ultra-precise micro CNC machining for high-precision parts—without the hassles of tolerance issues, supplier delays, or quality risks. Ready for zero-defect components and responsive, expert support? Send your RFQ to PTSMAKE now and move your project to the next level!
Learn how these components translate electrical energy into precise, sub-micron physical movements for ultimate machining accuracy. ↩
Learn how a material’s directional properties can impact micro-machining precision. ↩
Learn more about this statistical method for process control to understand its impact on manufacturing consistency. ↩
Learn how this physical phenomenon can impact precision and how our processes are designed to control it. ↩
Learn how this property can affect tool wear and precision in micro machining. ↩
Learn how friction, wear, and lubrication at a micro-level impact the lifespan of mechanical parts. ↩
Understand how tool bending affects micro-part accuracy and discover design strategies to prevent it. ↩
Learn how this statistical method ensures consistent quality in high-volume production. ↩
Learn how this data-driven methodology ensures every part meets spec, even in high-volume runs. ↩
Learn how precise surface finish control impacts component performance and functionality. ↩
Learn about the science of measurement and its critical role in precision manufacturing. ↩
Learn how internal material forces can affect your part’s accuracy and long-term stability. ↩
Explore our detailed guide on GD&T to better define part function and control manufacturing costs. ↩
Discover why this validation is critical for ensuring consistent quality and regulatory compliance for your medical parts. ↩
Learn how precise measurement science ensures your micro components meet exact specifications. ↩







