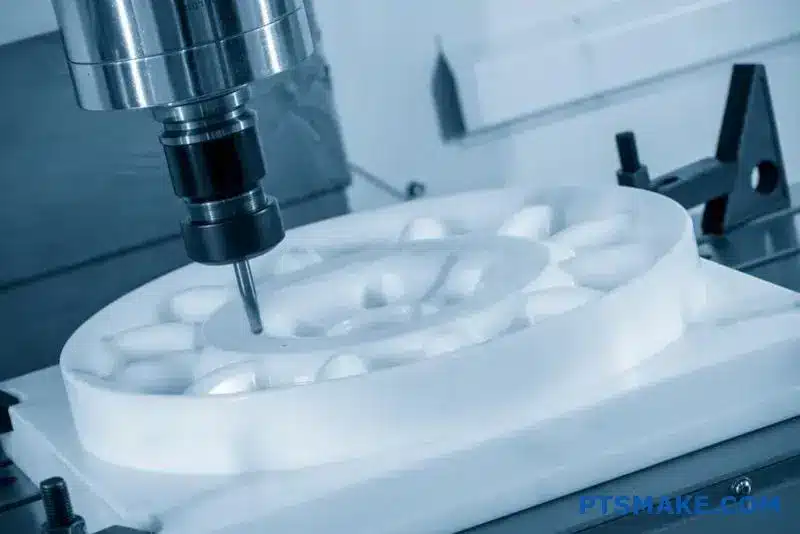
Finding the right LED heat sink manufacturer can make or break your lighting project. Poor thermal management leads to rapid LED degradation, color shifts, and costly field failures that damage your reputation.
Custom LED heat sinks require specialized manufacturing expertise to achieve optimal thermal performance while meeting your specific design, volume, and budget requirements. The right manufacturer combines advanced machining capabilities with deep thermal engineering knowledge.

I’ve worked with engineering teams who struggled with standard heat sink solutions that couldn’t meet their thermal targets or fit their unique form factors. Through my experience at PTSMAKE, I’ve seen how the right manufacturing partner transforms challenging LED thermal designs into reliable, cost-effective products.
Why is thermal management critical for LED performance and lifespan?
LEDs are champions of efficiency. But they have a critical weakness: heat. Excess heat silently destroys LED performance from the inside out.
The Impact of Heat
Unmanaged heat directly impacts how bright an LED is, what color it produces, and how long it lasts. It’s a chain reaction.
Performance Degradation
Higher temperatures mean lower light output and a shorter operational life. The relationship is direct and unforgiving.
| Temperature (Tj) | Lumen Output | Lifespan (L70) |
|---|---|---|
| Low | High | Long |
| High | Low | Short |
| Very High | Very Low | Failure |
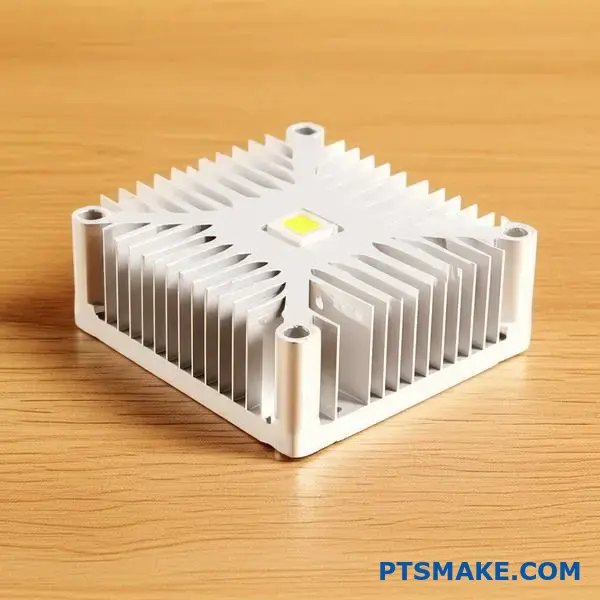

Heat is the primary cause of LED failure. The core of the problem lies at the semiconductor level. Managing this heat is not just an option; it’s essential for reliability.
How Heat Degrades an LED
Excess heat accelerates the natural aging process of the semiconductor materials within the LED chip. This is not just about getting hot to the touch. It’s about fundamental material damage. This process causes a gradual, irreversible decline in light output, known as Lumen Depreciation1.
Junction Temperature (Tj)
The temperature at the LED’s p-n junction is the most critical metric. Keeping this junction temperature low is the entire goal of thermal management. A quality led heat sink is designed specifically for this purpose.
In our past projects at PTSMAKE, we’ve seen how a well-engineered thermal solution can extend an LED’s useful life significantly. Small design improvements in the heat sink can make a huge difference.
Color Shift and Failure
Heat doesn’t just dim the light; it changes its color. This color shift, measured in CCT, is a clear sign of thermal stress.
| Thermal Stress | Visible Effect | Long-Term Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Stable Color | Expected Lifespan |
| High | Color Shift | Accelerated Dimming |
| Extreme | Major Shift | Catastrophic Failure |
Ultimately, uncontrolled heat leads to the breakdown of the materials, causing the LED to fail completely. It’s a simple path from hot to broken.
Effective thermal management is non-negotiable for reliable LED systems. It directly protects the semiconductor, ensuring consistent light output, stable color, and a long operational lifespan. A proper led heat sink is a critical part of this system.
What is the fundamental equation governing LED thermal design?
At the heart of LED thermal design is a beautifully simple formula. It acts as our guide for every project.
Tj = Ta + (P_heat × Rth_total)
This equation connects the LED chip’s temperature to its environment. It’s the foundation for creating reliable, long-lasting products.
Understanding each variable is the first step. Let’s break them down.
| Variable | Definition |
|---|---|
| Tj | Junction Temperature |
| Ta | Ambient Temperature |
| P_heat | Heat Power (Waste Heat) |
| Rth_total | Total Thermal Resistance |
This relationship dictates every engineering choice we make.

Let’s dig deeper into this core formula. Many engineers focus only on the heat sink, but that’s a limited view. The equation reveals a system-level challenge.
The real goal is to control Tj, the junction temperature. If this gets too high, the LED’s brightness fades and its lifespan shortens dramatically. It’s the critical performance limit.
Ta, the ambient temperature, is your baseline. It’s the temperature of the air surrounding the device. You usually can’t control this factor, so you must design for it.
P_heat is the waste heat generated by the LED. It’s the input power that isn’t converted into light. More efficient LEDs produce less heat, easing the thermal burden.
Finally, Rth_total is where designers can make the biggest impact. It measures how difficult it is for heat to escape. This resistance is the sum of every barrier from the chip to the air. The main process here is conduction2, as heat moves through the solid materials. A well-designed led heat sink is crucial for minimizing this value.
| Resistance Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Rth (j-c) | Junction-to-Case |
| Rth (c-s) | Case-to-Sink (TIM) |
| Rth (s-a) | Sink-to-Ambient |
At PTSMAKE, our precision machining processes are designed to optimize the sink-to-ambient path, ensuring efficient heat dissipation.
The fundamental equation, Tj = Ta + (P_heat × Rth_total), is your roadmap. It shows that managing junction temperature requires a holistic approach, considering the environment, LED efficiency, and the entire thermal path from chip to air.
How do manufacturing methods influence heat sink design and cost?
Choosing the right manufacturing process is a critical first step. It directly impacts your heat sink’s shape, performance, and final cost. There is no single "best" method.
Each technique has its own strengths and weaknesses. It’s a balance of design complexity, material choice, and production volume.
Let’s explore the most common options.
Key Manufacturing Processes
We will look at extrusion, die casting, forging, and CNC machining. Understanding these helps you make an informed decision for your project.
| Method | Best For | Relative Cost (High Volume) |
|---|---|---|
| Extrusion | Simple, linear fins | Low |
| Die Casting | Complex 3D shapes | Medium |
| CNC Machining | Prototypes, high performance | High |
This table provides a quick overview. Now, we will dive deeper into the details of each process.
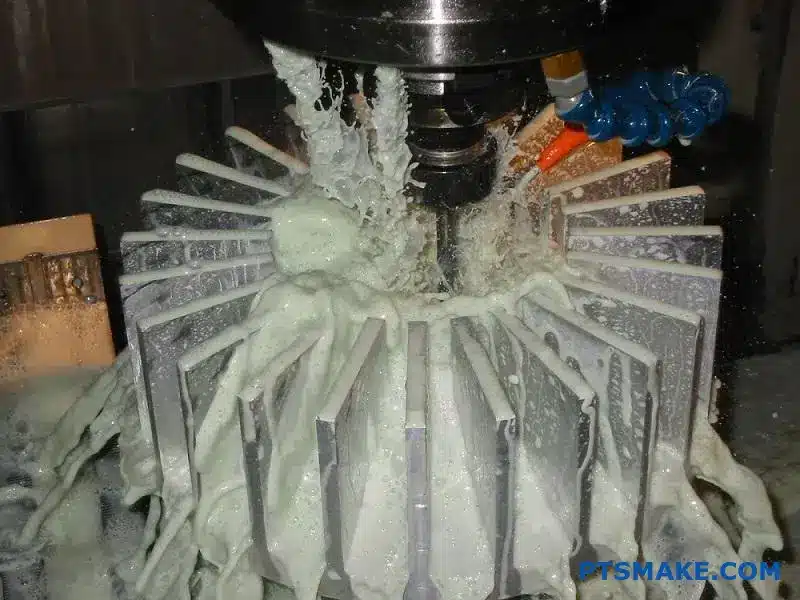

The manufacturing method sets the boundaries for your design. What is possible with one process might be impossible with another. This link between method and design is fundamental.
Extrusion: The Volume King
Extrusion is very cost-effective for large quantities. It involves pushing a block of aluminum through a die. This creates long sections with a constant cross-section.
This process is great for standard fin designs. However, the material properties are often anisotropic3. Heat travels better along the length of the extrusion than across it.
Die Casting: Complex Shapes
Die casting injects molten metal into a mold. This allows for complex, three-dimensional shapes. It’s ideal for integrating features like mounting points or housings. This is common for custom led heat sink applications.
The downside is lower thermal conductivity compared to extruded or machined parts. The tooling costs are also high.
CNC Machining: Ultimate Precision
At PTSMAKE, CNC machining is one of our core services. It offers unmatched design freedom and the tightest tolerances. It is perfect for prototypes or high-performance heat sinks with intricate features.
| Feature | Extrusion | Die Casting | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tooling Cost | Medium | High | Low/None |
| Design Freedom | Low | High | Very High |
| Part Cost | Low | Medium | High |
| Best For | High Volume | Complex Parts | Prototypes/Performance |
We often use CNC machining to create complex prototypes for clients before they commit to high-cost tooling for other methods.
Choosing a process involves balancing cost, volume, and performance. Extrusion offers low-cost volume production. Die casting enables complex shapes. CNC machining delivers the highest precision and design flexibility, which is ideal for demanding applications and prototypes.
What are the primary goals of an effective LED heat sink?
The primary goal is simple. An effective LED heat sink must keep the LED’s core temperature in check. This means staying below the manufacturer’s maximum limit.
It’s not just about preventing a catastrophic failure. It’s about ensuring reliability and consistent performance over thousands of hours. A well-designed led heat sink is the key to unlocking the full potential and lifespan of any high-power LED system.
| Core Objective | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Temperature Regulation | Prevents overheating and damage to the LED chip. |
| Performance Consistency | Maintains stable light output and color quality. |
| Extended Lifespan | Maximizes the operational life of the LED. |
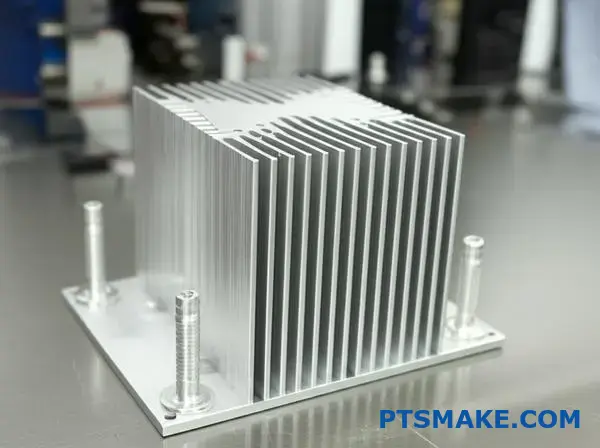

The phrase "under all operating conditions" is where the real engineering challenge lies. A heat sink isn’t just designed for a perfect lab environment. It must perform reliably in the real world.
This includes high ambient temperatures, cramped enclosures with poor airflow, or continuous 24/7 operation. Each scenario presents a unique thermal challenge. At PTSMAKE, we don’t just design for the average case. We stress-test our designs for the worst-case scenarios.
This ensures the Junction Temperature4 never exceeds the safe limit. A heat sink that works well on an open bench might fail inside a sealed lighting fixture. In our experience, accounting for these variables is what separates a good design from a great one.
Here is how different conditions impact design choices:
| Operating Condition | Heat Sink Design Consideration |
|---|---|
| High Ambient Heat | Requires larger surface area or active cooling. |
| Enclosed Fixture | Focus on efficient passive radiation and convection. |
| 24/7 Operation | Material selection for long-term thermal stability. |
| High Humidity | Corrosion-resistant materials and coatings are vital. |
The main goal of a heat sink is to keep the LED’s junction temperature below its specified maximum. This ensures the LED performs reliably and lasts as long as intended, no matter the operating environment. This is the cornerstone of effective thermal management.
What are the main materials used for LED heat sinks?
Choosing the right material is critical. It directly impacts LED performance and lifespan. The most common choices are aluminum, copper, and composites. Each has unique strengths.
Aluminum is the go-to for its balance. Copper offers superior heat transfer. Composites provide modern, lightweight solutions.
Quick Material Comparison
| Material | Key Feature | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Balanced cost & performance | General applications |
| Copper | Highest conductivity | High-power LEDs |
| Composites | Lightweight & versatile | Specialized designs |
This balance of properties is why most led heat sink designs start with aluminum.
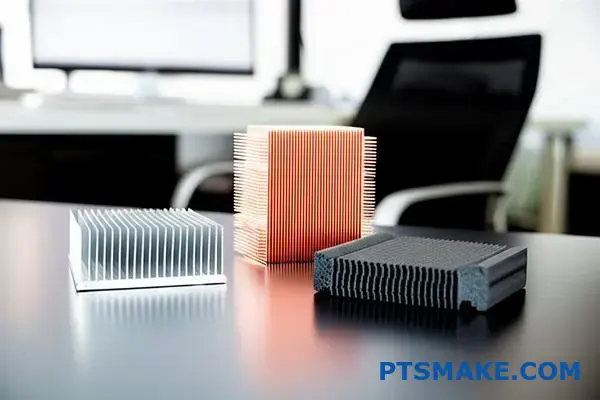

A Deeper Dive into Material Trade-offs
Selecting the ideal material requires a closer look. You must weigh performance against practical constraints like cost and weight. It’s a balancing act we manage daily at PTSMAKE.
Aluminum Alloys: The Workhorse
Aluminum is popular for good reason. Alloys like 6063 are excellent for extrusion. They offer good thermal performance and are easily machined. This makes them cost-effective for most projects. 1050 aluminum has higher purity. This gives it better thermal conductivity. However, it is softer and less durable.
Copper: The High-Performer
When performance is non-negotiable, we use copper. Its thermal conductivity is nearly double that of aluminum. But this power comes at a price. Copper is heavier and more expensive. It also requires more care to prevent corrosion.
Composites: The Innovator
Advanced composites are changing the game. These materials, like graphite composites, can be engineered. They offer excellent heat dissipation with very low weight. Their thermal properties can even be Anisotropic5, directing heat in specific paths. This offers incredible design freedom for complex applications.
| Feature | Aluminum (6063) | Copper (C110) | Composites |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | ~200 W/mK | ~390 W/mK | Variable (can be >500) |
| Weight | Low | High | Very Low |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (with anodizing) | Fair | Excellent |
| Relative Cost | Low | High | Very High |
The final choice depends entirely on your specific LED application, budget, and performance goals.
The right material for your LED heat sink depends on balancing thermal needs, weight, and budget. Aluminum is a great all-rounder, copper excels in performance, and composites offer lightweight, specialized solutions. The best choice is application-specific.
When should you use a standard versus a custom heat sink?
Choosing between a standard or custom heat sink is a critical decision. It directly impacts your project’s performance, budget, and timeline. There is no single right answer.
The best choice depends entirely on your specific needs. I’ve developed a simple framework to help guide you. It is based on five key factors. Let’s break them down.
Key Decision Factors
| Factor | Standard Heat Sink | Custom Heat Sink |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Needs | Low to Moderate | High / Specific |
| Production Volume | Low to High | Medium to High |
| Budget | Low (No NRE Cost) | Higher (Includes NRE) |
| Time-to-Market | Fast | Slower |
| Form Factor | Flexible | Restricted / Unique |

Deciding requires a deeper look at the trade-offs. It’s about balancing engineering requirements with business goals. At PTSMAKE, we guide clients through this process daily.
Analyzing Your Project’s Needs
Thermal Performance
First, assess your thermal load. For devices with low power dissipation, a standard heat sink is often sufficient. But for high-performance components or a compact led heat sink design, you need a custom solution. A custom design optimizes fin density, material, and airflow for maximum heat transfer. The lower a heat sink’s thermal resistance6, the better it performs.
Production Volume and Budget
Your budget is a major driver. Standard heat sinks have no tooling costs, making them ideal for prototypes and small runs. Custom heat sinks require an initial investment in tooling (NRE). However, for high-volume production, the per-unit cost can become much lower, justifying the initial expense.
Time and Aesthetics
Time-to-market is often critical. Standard parts are available off-the-shelf. Custom fabrication, from design to production, takes weeks or months. Finally, consider the physical space and look. If your product has a unique shape or specific branding needs, a custom heat sink is the only way to go.
| Scenario | Recommended Choice | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Early-stage Prototype | Standard | Fast, low-cost validation of a concept. |
| High-Volume Consumer Device | Custom | Optimized performance and lower per-unit cost. |
| Space-Constrained Equipment | Custom | Fits unique geometry where standard parts cannot. |
This framework helps you weigh the key factors: thermal needs, volume, budget, and design constraints. Using it ensures you choose the most effective and economical heat sink solution, whether it’s a standard part or a custom-engineered one from partners like us at PTSMAKE.
Case Study: Design a heat sink for a 150W high-bay light.
Designing a heat sink for a 150W high-bay light presents unique challenges. It is not just about dissipating heat.
We must balance thermal performance with strict physical constraints. The environment also plays a huge role.
This case study walks you through our process. We focus on the key decisions for this high-power industrial application.
| Design Challenge | Primary Goal |
|---|---|
| High Heat Flux | Rapidly move heat away from the LED source. |
| Weight Limitation | Ensure structural safety for ceiling mounting. |
| Reliability | Withstand dust, vibration, and long operating hours. |

Breaking Down the Design Process
Our first step is always thermal analysis. For a 150W light, a significant portion becomes waste heat. We need to manage this effectively to protect the LED’s lifespan.
The concentrated Heat Flux7 from the LED chip is the main problem. An efficient design must spread this thermal load quickly across a large surface area. This is where fin design becomes critical.
Weight is a major concern. High-bay lights are suspended overhead, so every gram matters. While copper is a better conductor, aluminum alloys like 6061 or 6063 offer an excellent balance of thermal conductivity and low weight. This is a common trade-off in led heat sink design.
In past projects at PTSMAKE, we’ve found CNC machining provides the best solution. It allows us to create complex fin geometries and remove unnecessary material, reducing weight without sacrificing performance.
Ensuring Long-Term Reliability
Reliability in a factory is non-negotiable. The design must resist dust accumulation, which can insulate the heat sink and reduce its effectiveness.
We tested several fin designs. Wider spacing between fins performs better in dusty environments, though it slightly reduces the total surface area.
| Fin Type | Pro | Con |
|---|---|---|
| Stamped | Low Cost | Lower Performance |
| Extruded | Good Balance | Design Limitations |
| CNC Machined | High Performance | Higher Initial Cost |
Ultimately, a custom CNC-machined solution offers the control needed to meet all performance, weight, and reliability targets for demanding applications.
Designing an effective heat sink requires balancing thermal needs with physical constraints like weight and environmental toughness. Precise manufacturing is key to achieving this balance, ensuring both performance and long-term reliability for the high-bay light.
Case Study: Manage heat in a sealed, compact 10W downlight.
A sealed 10W downlight presents a unique thermal challenge. With zero airflow, traditional convection cooling is off the table.
We must rely entirely on conduction and radiation. This forces a clever approach to design. The led heat sink isn’t just an add-on; it’s the core of the product’s structure.
The Zero-Airflow Challenge
Our goal is to move heat away from the LED chip efficiently. This requires careful material selection and an integrated design.
Heat Transfer Focus
Here’s how heat transfer works in this sealed system:
| Method | Relevance in Sealed Unit | Key Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Convection | Negligible (No Airflow) | N/A |
| Conduction | Critical | Material, Path |
| Radiation | Critical | Surface Area, Finish |
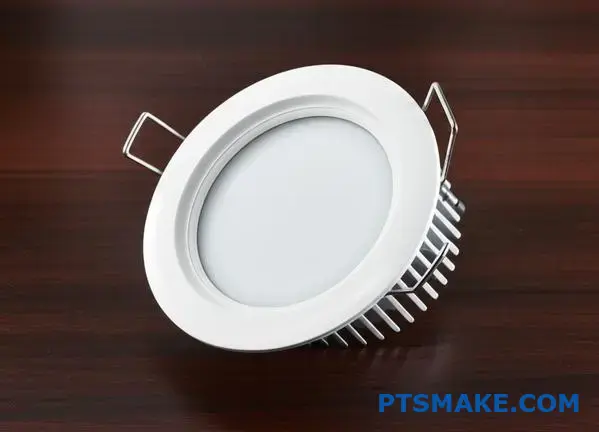

Designing an Integrated Heat Sink
In past projects at PTSMAKE, we often start with the material. Aluminum is the go-to choice for its properties and cost-effectiveness.
But not all aluminum is the same. The alloy choice matters greatly for thermal performance and how we can machine it.
Enhancing Conduction
The primary goal is creating an unbroken path for heat. This path starts at the LED board and ends at the outermost surface of the downlight.
We use CNC machining to create a single, integrated housing. This eliminates thermal resistance that you would find in assembled parts. Good Thermal conductivity8 is absolutely essential here.
We also ensure a perfect, flat interface between the LED module and the heat sink.
Boosting Radiation
Once heat reaches the outer surface, it must radiate away. We can increase the surface area with fins, even within a compact design.
Surface finish is also crucial. A matte black anodized finish can significantly improve heat radiation compared to a bare, polished surface.
Here’s a quick comparison of common aluminum alloys:
| Alloy | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| 6061 | ~167 | Structural, good balance |
| 6063 | ~201 | Extrusions, heat sinks |
| 1050A | ~229 | Pure, high conductivity |
For a sealed, fanless downlight, thermal management hinges on maximizing conduction and radiation. An integrated led heat sink design, crafted from the right materials with an optimized surface finish, is not just an option—it’s essential for reliability and performance.
Case Study: Design a thermal solution for an outdoor street light.
Designing for the outdoors is a different game. An outdoor luminaire faces constant environmental attacks. It’s not just about dissipating heat.
The thermal solution must also protect against water, dust, and sun.
Key Environmental Factors
Water and Dust (IP Rating)
A high IP rating is essential. It prevents water and dust from damaging the electronics inside. This sealing, however, can trap heat.
Solar Loading
Direct sunlight adds a significant heat load. The design must handle both internal heat from the LEDs and external heat from the sun.
Temperature and Corrosion
Wide temperature swings and humidity demand robust materials. Corrosion is a major enemy.
| Factor | Indoor Requirement | Outdoor Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| IP Rating | Low (e.g., IP20) | High (e.g., IP65+) |
| Solar Load | None | High |
| Temp. Swing | Stable | Wide (-40°C to 50°C) |
| Corrosion | Low Risk | High Risk |
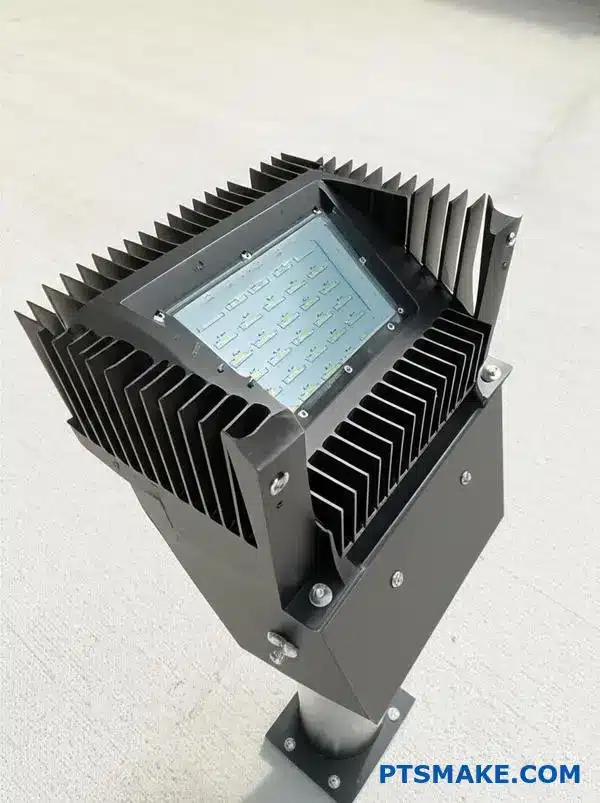

An effective outdoor thermal design is a balancing act. You need to keep electronics cool while completely sealing them from the elements. This is a core challenge.
Designing for Durability
Achieving a High IP Rating
To get an IP65 or higher rating, we use gaskets and precision-machined surfaces. At PTSMAKE, we ensure our CNC machining creates perfect sealing faces. This prevents any leaks.
A sealed housing, however, limits airflow. This makes the external led heat sink fins even more critical for heat dissipation. They are the only way for heat to escape.
Managing Solar Load and Temperature
The color and finish of the housing matter. A lighter-colored, reflective coating can reduce solar heat absorption by up to 15%, based on our testing.
The design must also accommodate material expansion and contraction due to temperature swings without compromising the seals.
Material Selection Against Corrosion
Corrosion can degrade thermal performance and cause structural failure. Choosing the right material and finish is crucial. We must prevent issues like Galvanic corrosion9.
| Material | Coating/Finish | Corrosion Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| ADC12 Aluminum | Powder Coating | Good |
| A380 Aluminum | Anodizing | Very Good |
| AL6061 | Anodizing + Coating | Excellent |
At PTSMAKE, we often recommend AL6061 with a two-step finish for coastal or highly corrosive environments. This ensures long-term reliability.
Designing a thermal solution for outdoor use is a complex task. It requires balancing heat dissipation with robust protection against sun, water, dust, and corrosion. The entire system, not just the heat sink, must be engineered for survival.
Failure Analysis: A fixture’s LEDs are failing prematurely. Why?
When LEDs fail, the heat sink is often the prime suspect. To find the root cause, you need a systematic approach. I’ve developed a simple diagnostic checklist over the years. This helps you quickly identify if the led heat sink is the problem.
This process saves time and prevents repeat failures. It focuses on three main failure points.
Key Diagnostic Areas
| Failure Mode | Inspection Point | Common Signs |
|---|---|---|
| TIM | Thermal Interface Material | Uneven spread, gaps, contamination |
| Design | Heat Sink Size & Shape | Too small for the power output |
| Environment | Airflow | Dust buildup, blocked vents |
This structured check is the first step. It guides you directly to the potential issue.

Let’s dive deeper into this checklist. It’s a practical tool we use at PTSMAKE when helping clients troubleshoot thermal issues. By breaking down the problem, we can isolate the exact cause of the premature failure.
Digging into the Details: A Step-by-Step Guide
First, carefully disassemble the fixture to access the LED module and its heat sink. A visual inspection is powerful. Look for discoloration on the PCB or the LED itself, which indicates extreme heat.
Thermal Interface Material (TIM) Problems
Poor TIM application is a very common failure source. You should check for an even, thin layer connecting the LED board to the heat sink. Too little or too much TIM creates high Thermal Resistance10, trapping heat.
| TIM Condition | Indication |
|---|---|
| Dry or Cracked | Material has degraded over time. |
| Gaps or Bubbles | Poor initial application. |
| Too Thick | Increases thermal path, less effective. |
| Contaminated | Dust or oils reduce performance. |
Undersized Heat Sink Design
Next, evaluate the led heat sink itself. Does it feel inadequate for the fixture’s size and power? An undersized sink simply cannot dissipate heat fast enough. At PTSMAKE, we often see designs that prioritize aesthetics over thermal performance. A proper design, often achieved through precision CNC machining, ensures sufficient surface area.
Blocked Airflow
Finally, check for environmental factors. Is the fixture clogged with dust or debris? Are vents blocked? Poor airflow turns even a well-designed heat sink into a heat trap. This is especially critical in compact or enclosed fixtures.
This methodical checklist helps you diagnose heat sink related failures accurately. By examining the TIM, the design, and airflow, you can pinpoint the root cause and implement a reliable solution, preventing future LED burnouts.
Cost Reduction: Your heat sink is over budget. What now?
Your heat sink design is complete. But the quote comes back much higher than expected. This is a common problem. Don’t panic.
There are practical ways to lower the cost. We can look at four key areas. These are material, manufacturing process, design simplicity, and thermal materials.
Key Cost-Down Levers
| Strategy | Primary Focus | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Material Change | Cost vs. Performance | Non-critical thermal needs |
| Process Change | Unit Cost at Scale | High-volume production |
| Simplification | Machining Time | Complex initial designs |
| Alternative TIMs | Component Cost | Overall system optimization |
Let’s explore how to make smart adjustments.
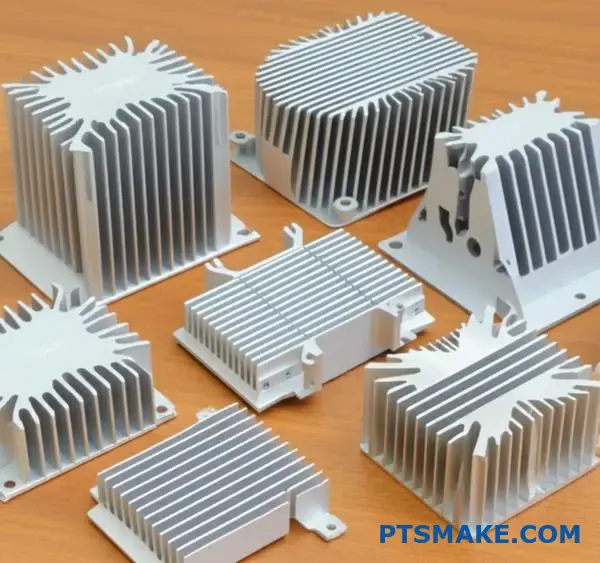

When your budget is tight, every decision matters. We need to evaluate the trade-offs carefully. It’s not just about cutting costs. It’s about reducing cost without hurting performance too much.
Rethinking Material and Process
Changing from copper to aluminum is often the first step. Aluminum is less expensive and lighter. Its thermal performance is lower than copper’s, but it’s often good enough for many applications, like a standard led heat sink.
For high-volume production, switching the process is key. CNC machining offers great precision but is costly for large quantities. Die casting or extrusion can drastically cut the price per unit. However, they require a high upfront investment in tooling.
| Manufacturing Method | Tooling Cost | Unit Cost | Ideal Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | None | High | Low to Medium |
| Die Casting | High | Low | High |
| Extrusion | Medium | Very Low | High |
Simplifying Design and Components
Look at your heat sink’s geometry. Can you reduce the number of fins? Or make them thicker and farther apart? These changes reduce complex machining operations and slash cycle times.
Also, examine your Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs). A high-performance TIM is great, but a slightly less effective one might save significant money. The key is whether the system’s thermal conductivity11 remains within your required operating range. This is a balance we help clients at PTSMAKE find regularly.
These four strategies provide a clear framework for reducing heat sink costs. By evaluating materials, manufacturing processes, and design complexity, you can find significant savings without compromising the essential performance of your product.
How do you balance thermal performance with industrial design?
Balancing aesthetics with function is a primary challenge. A beautiful luminaire that overheats is a failed product. This is where smart integration comes in. We can make the product’s housing do the cooling work.
The Housing as a Heatsink
The concept is simple but very effective. The external housing itself becomes the led heat sink. This approach removes the need for separate, often bulky, thermal components. It results in a cleaner, more unified design.
Manufacturing for Integration
Achieving this requires high precision. At PTSMAKE, we leverage CNC machining to create intricate fin geometries directly on the housing. These features are both visually appealing and thermally efficient.
| Feature | Traditional Design | Integrated Design |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling | Separate heat sink | Housing is the heat sink |
| Aesthetics | Bulky, added parts | Sleek, minimalist |
| Assembly | More components | Fewer components |
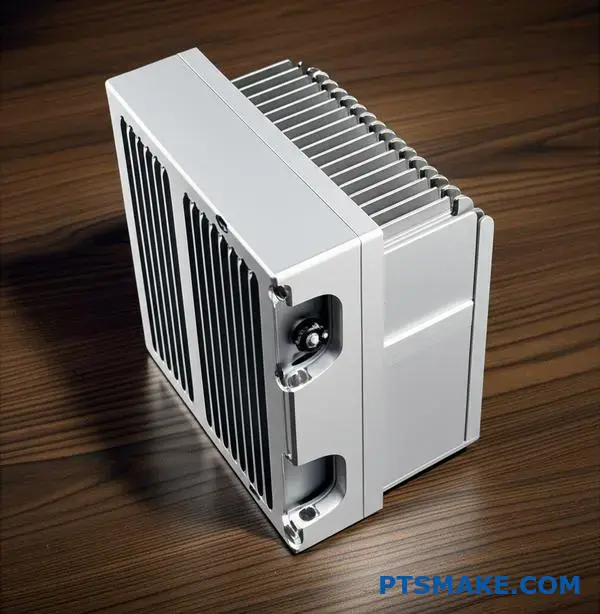

This integration strategy goes beyond just shape. It demands a solid understanding of materials and thermal dynamics. The process always begins with selecting the right material.
Choosing Materials and Finishes
Aluminum alloys, like 6061 or 6063, are excellent choices. They provide great thermal conductivity and are easily machined. But the surface finish is just as important. Anodizing not only adds protection but can also improve radiative cooling.
Based on our tests, a matte black anodized finish often performs best. It maximizes heat emission far better than a polished surface. This small detail yields a significant impact.
Designing for Airflow
The main goal is maximizing the surface area exposed to air. This greatly improves the efficiency of convective heat transfer12. We design fins that are not just decorative patterns but are engineered for function.
The specific shape, spacing, and orientation of these fins direct airflow. This process effectively pulls heat away from the core LED components, ensuring longevity.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum 6061 | ~167 | Great balance of strength & conductivity |
| Aluminum 6063 | ~201 | Excellent for extrusion, good conductivity |
| Copper | ~401 | Superior conductivity, higher cost/weight |
We use simulation tools early in the design phase. This allows us to predict thermal performance before any material is cut. It saves our clients both time and money. Prototypes then help validate the simulation results.
By designing the luminaire housing to act as the heat sink, you achieve a sleek aesthetic. This approach, enabled by precision CNC machining and smart material selection, perfectly merges form with essential thermal function, creating a superior final product.
How are new technologies like COB LEDs changing heat sink design?
Chip-on-Board (COB) LEDs are a game-changer. They pack immense power into a small area. This creates intense, concentrated heat.
The Challenge of COB LEDs
Traditional LEDs spread heat over a larger surface. COB arrays, however, create hotspots. This high heat flux density is the core problem for thermal management.
Why Traditional Designs Fall Short
A simple aluminum extrusion is often not enough. The heat is too concentrated for it to dissipate effectively. This demands a smarter approach for a modern led heat sink.
| LED Type | Typical Heat Flux (W/cm²) |
|---|---|
| Standard SMD LED | 5-15 |
| COB LED Array | 50-200+ |
This shift requires rethinking heat sink design from the ground up.
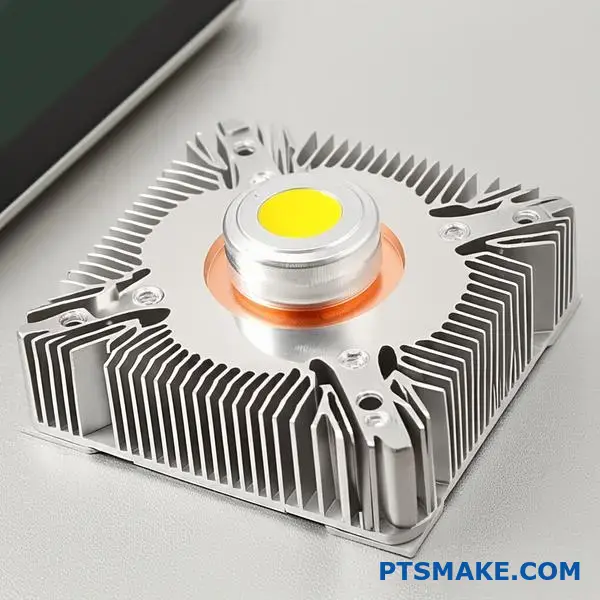

COB technology fundamentally alters the thermal challenge. It’s not just about the total amount of heat, but its extreme concentration. A tiny, super-hot point is much harder to cool than a larger, warm area.
Moving Beyond Simple Extrusions
In past projects at PTSMAKE, we’ve seen this firsthand. Simply making a larger passive led heat sink provides diminishing returns. The real bottleneck is how quickly heat can move away from the tiny COB source.
The efficiency of this heat transfer is key. A low thermal resistance13 path is crucial. Without it, heat builds up at the source, drastically shortening the LED’s lifespan and affecting performance.
Advanced Cooling Strategies
This drives the need for more sophisticated solutions. These methods are specifically designed to handle high heat flux. They pull heat away from the chip far more effectively than a block of solid metal.
Phase-Change Technology
Heat pipes and vapor chambers are excellent examples. They use a liquid-to-vapor cycle inside a sealed container. This process transfers thermal energy with incredible speed.
Active Cooling Systems
Sometimes, a fan or even a liquid cooling loop is necessary. These are common in high-power industrial or commercial fixtures where reliability is paramount.
| Cooling Solution | Typical Heat Flux Capacity (W/cm²) | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Extrusion | < 50 | General purpose, low-power |
| Heat Pipes | 50 – 150 | High-power spotlights, downlights |
| Vapor Chambers | 100 – 300+ | Compact, high-intensity fixtures |
| Active (Fan) Cooling | Variable | Enclosed systems, stage lighting |
Choosing the right technology requires careful analysis of the specific product requirements.
COB LEDs create intense, localized heat, overwhelming traditional passive heat sinks. This high heat flux density necessitates advanced thermal solutions like heat pipes, vapor chambers, or active cooling to maintain LED performance and ensure long-term reliability in demanding applications.
How does the heat sink interact with optical and driver components?
A heat sink is never an island. It’s a critical team player in any lighting or electronic system. Its performance directly impacts other key components.
Poor thermal management doesn’t just mean a hot LED. It can drastically shorten the life of the driver electronics nearby.
Impact on System Components
The shape of an led heat sink is also crucial. A bulky or poorly designed fin can block light. This creates unwanted shadows and ruins the intended optical distribution.
| Component | Heat Sink Interaction | Potential Negative Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Driver Electronics | Thermal Proximity | Reduced lifespan, performance issues |
| Optical Lens | Physical Obstruction | Uneven light, shadows |
This is why we view heat sink design as part of a complete system puzzle.

Thinking of a heat sink in isolation is a common pitfall. In past projects at PTSMAKE, we’ve seen how this thinking leads to system-level failures. Heat is a relentless enemy of electronic components, especially capacitors and ICs in the driver.
The Ripple Effect of Heat
Excessive heat from the LED, poorly managed by the heat sink, radiates to the driver board. This elevated temperature accelerates the aging of its components. It’s a primary cause of premature driver failure and flickering lights. We often advise clients on specific Derating14 strategies to mitigate this.
Shape and Light Distribution
The physical design of the led heat sink is equally important. We can’t just focus on thermal performance. Its geometry must complement the optical design.
| Fin Design Factor | Impact on Optics |
|---|---|
| Height | Can cast long shadows |
| Density | May block light at wide angles |
| Overall Shape | Can interfere with beam patterns |
Working with clients, we use co-simulation. This allows us to balance thermal needs with optical requirements. We ensure the heat sink cools effectively without compromising the quality of light. This holistic approach avoids costly redesigns later.
A heat sink’s design has a direct and significant impact on both electronic longevity and light quality. Treating it as an integral part of the overall system, not an afterthought, is crucial for creating a reliable and high-performing product.
Unlock Superior LED Heat Sink Solutions with PTSMAKE
Ready to optimize your LED thermal management? Partner with PTSMAKE for custom, high-precision heat sink manufacturing tailored to your project’s unique requirements. Contact us now for a quote and experience trusted quality, speed, and engineering expertise—your next-generation thermal solutions start here!
Understand the science behind why LEDs dim over time and how to prevent it. ↩
Learn how heat transfer mechanisms like conduction influence material choice and design for effective thermal management. ↩
Learn how this property affects heat transfer and your design choices. ↩
Learn what this critical temperature means for your LED’s health and how to manage it effectively. ↩
Discover how a material’s directional properties can revolutionize your thermal management strategy. ↩
Understand this critical thermal metric to see how it directly impacts your heat sink’s performance. ↩
Learn how this critical metric influences the design and efficiency of your thermal management system. ↩
Understand how material choice directly impacts your product’s thermal performance and lifespan. ↩
Learn why material selection is critical to prevent premature failure in outdoor products. ↩
Understand how this key metric governs heat transfer efficiency in your designs. ↩
Understand how this property impacts your heat sink’s performance and material choice. ↩
Learn how airflow design principles can significantly improve your product’s cooling efficiency and lifespan. ↩
Understand how this crucial property affects the performance and longevity of your electronic components. ↩
Learn how derating improves the long-term reliability of electronic components. ↩