You’re designing precision parts that need both protection and performance. Standard chrome might offer corrosion resistance, but it creates unwanted glare and reflection that can interfere with sensors, optics, and the sleek aesthetics your clients expect.
Black chrome plating provides superior corrosion protection while eliminating reflective surfaces, making it ideal for precision CNC machined parts in aerospace, medical, robotics, and optical applications where both function and form matter.

I’ve worked with many engineers who initially dismissed black chrome as purely decorative. They discovered it offers real functional advantages – from reducing light interference in sensor housings to providing EMI shielding in electronic enclosures. The choice between black chrome and traditional chrome goes beyond aesthetics.
Black Chrome Vs. Traditional Chrome: Critical Differences Engineers Must Consider
Choosing the right surface finish is a critical engineering decision. It goes far beyond simple aesthetics. Your choice impacts performance, longevity, and overall component reliability.
Let’s break down the key differences between traditional chrome and black chrome plating. Each has unique properties that make it suitable for specific applications.
Key Performance Metrics at a Glance
This table provides a quick overview. We’ll explore these points in more detail.
| Property | Traditional Chrome | Black Chrome |
|---|---|---|
| Reflectivity | High (Mirror-like) | Low (Matte/Satin) |
| Durability | Very High | Good to High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Thermal Properties | Low Emissivity | High Emissivity |
Understanding these distinctions is the first step in selecting the optimal coating.
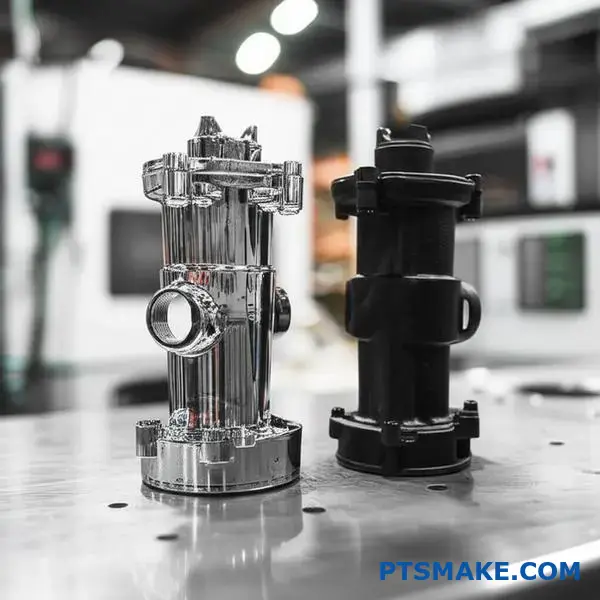

The choice between these two finishes is not always straightforward. While both are excellent corrosion-resistant coatings, their functional differences are significant. At PTSMAKE, we often guide clients through this decision by focusing on the end-use application.
Functional Differences Beyond the Finish
Reflectivity and Thermal Management
Traditional chrome is highly reflective. This is ideal for decorative parts or surfaces where high light reflection is desired.
Black chrome, however, has very low reflectivity. This makes it perfect for optical components, firearm parts, or automotive trim where glare reduction is essential. This property also gives it high thermal emissivity, allowing it to radiate heat more effectively than traditional chrome. This can be a major advantage in thermal management applications.
Durability and Hardness
Hard chrome is known for its extreme hardness and wear resistance. Decorative bright chrome is thinner but still quite durable.
The durability of black chrome plating can vary. It depends heavily on the specific plating process used. While it offers strong protection, its tribological properties1 may differ from hard chrome in high-wear scenarios. As a chrome plating alternative, its performance must be carefully matched to the component’s operational stresses.
The right choice between black and traditional chrome depends entirely on your application’s functional needs. Consider factors like light control, thermal performance, and wear resistance, not just the final look. This ensures the component performs as designed.
Can Black Chrome Stand Up to Harsh Environments? A Durability Guide
How do we prove the toughness of black chrome plating? We can’t just rely on looks. We put it through rigorous testing. This is a crucial black chrome durability test.
These tests simulate years of harsh use. They expose the finish to extreme conditions. This shows us its true limits.
Salt Spray Testing
This is the classic corrosion test. We expose parts to a dense saltwater fog. It mimics coastal or winter road conditions. We measure how long until corrosion appears.
High-Temperature and Chemical Exposure
Other tests check performance under heat and chemicals. We see if the finish cracks, peels, or discolors. This is vital for industrial or automotive parts.
A summary of key durability tests:
| Test Type | Purpose | Key Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Salt Spray | Evaluates corrosion resistance | Hours to first sign of rust |
| High Temp | Checks thermal stability | No cracking or discoloration |
| Chemical | Measures resistance to solvents | No etching or softening |

Simply listing tests isn’t enough. We need to understand the results. The performance of black chrome plating can vary. This often depends on the specific process used.
Interpreting Durability Test Results
A standard black chrome finish might last 100-200 hours in a salt spray test. At PTSMAKE, we work with clients to enhance this. By refining the underlying plating layers, we can significantly boost corrosion resistance.
The substrate material is also critical. Black chrome on stainless steel performs differently than on aluminum. You must consider the entire system.
True durability comes from controlling the entire process. A quality black chrome durability test confirms this. It ensures the part meets specs. This is crucial for applications where failure is not an option.
We ran a comparative ASTM B1172 test for a client in the marine industry. It showed our enhanced process doubled the corrosion-free lifespan. This is the kind of data that builds trust.
Here’s how different factors impact performance.
| Influencing Factor | Impact on Durability | Our Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate Prep | High | Multi-stage cleaning and activation |
| Underplating | High | Optimized nickel or copper layers |
| Plating Thickness | Medium | Tightly controlled per specification |
| Sealing Process | High | Application-specific top coats |
This level of detail ensures the finish is genuinely chemical-resistant chrome when needed.
Black chrome’s durability is proven through specific tests. These include salt spray, high-temperature, and chemical exposure. The quality of the plating process and the substrate material are critical factors that determine its real-world performance and resistance.
How Black Chrome Enhances Aesthetics Without Compromising Function
The true beauty of black chrome plating lies in its versatility. It is not a single look. It is a spectrum of finishes. This allows us to tailor the part’s appearance to precise design requirements.
Achieving the Perfect Finish
Achieving a consistent color is crucial. Any variation can disrupt the product’s overall aesthetic. We focus on tight process control. This ensures every part has a uniform, deep black finish. The choice between matte and gloss then defines the character.
| Finish Type | Primary Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Matte | Non-reflective, soft |
| Gloss | Highly reflective, deep |
This decision impacts both the look and feel. It creates a specific user experience.

The choice between a matte or gloss finish goes beyond simple preference. It fundamentally changes how a component interacts with light and its environment. This choice influences the final product’s perceived value and style.
Matte vs. Gloss: A Deeper Look
Matte chrome parts excel at diffusing light. This creates a subtle, modern, and high-tech appearance. It’s excellent for hiding fingerprints. This makes it ideal for components that are frequently handled. The non-reflective surface has an industrial, yet sophisticated feel.
Gloss black chrome offers a classic, luxurious look. Its mirror-like finish reflects light sharply. This is often associated with high-end automotive trim and premium electronics. While visually striking, it requires more care. It shows fingerprints and smudges more easily. The key is understanding the end-use.
The process control for aesthetic black chrome is demanding. It involves managing the plating bath chemistry and electrical current with high precision. This ensures the desired level of specular reflection3 is consistently achieved.
Finish Application Comparison
Here is how I guide clients on choosing a finish.
| Attribute | Matte Black Chrome | Gloss Black Chrome |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Appeal | Understated, modern, industrial | Luxurious, classic, bold |
| Maintenance | Excellent fingerprint-resistant coating, low-main. | Shows smudges, requires regular cleaning |
| Best For | High-touch surfaces, tactical gear, electronics | Decorative trim, luxury goods, automotive parts |
| Durability | Hides minor scratches well | Can show micro-scratches more easily |
This structured choice ensures the finish enhances the product as intended.
Black chrome plating offers a range of aesthetic options. The choice between matte and gloss affects the look, feel, and practicality. It impacts everything from fingerprint resistance to the perception of luxury, blending visual appeal with functional performance.
Black Chrome for Optics and Sensors: Why Engineers Choose It
In high-stakes applications like optics and sensors, control is everything. Unwanted light and electronic noise can ruin data integrity. This is where black chrome plating becomes essential.
This finish isn’t just for looks. It’s a high-performance solution. Its unique structure provides an excellent non-reflective chrome coating. This helps engineers manage light and electromagnetic interference effectively, ensuring precision.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Coating Type | Typical Reflectivity | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Chrome | > 60% | High Durability |
| Black Oxide | 5-10% | Corrosion Resistance |
| Black Chrome | < 1% | Light Absorption |
This low reflectivity is why so many optical engineers choose it.

The true value of black chrome lies in its multifunctional performance. Engineers don’t have to choose between optical clarity and electronic protection. They get both from a single, reliable finish.
Superior Light Absorption
The primary function of black chrome in optical systems is to absorb stray light. The finish has a porous, dendritic structure. This traps photons instead of reflecting them.
This minimizes internal reflections that cause glare or ghosting. For sensitive equipment, preventing even minor light scatter is critical. This is crucial for an optical-grade chrome finish. The surface effectively acts as a light sink, improving signal-to-noise ratio in detectors. This makes it a top choice for components inside cameras, telescopes, and laser systems. The lack of Specular Reflection4 is a key factor.
Effective EMI Shielding
Beyond optics, black chrome plating provides excellent EMI shielding. Chrome is naturally conductive. The plating creates a thin, conductive layer over the component.
This layer acts like a Faraday cage. It grounds out electromagnetic interference. This protects sensitive electronics within sensors from external noise. For applications combining optical and electronic components, such as advanced sensor modules, this dual benefit is invaluable. It simplifies design and enhances reliability.
| Property | Benefit for Optics | Benefit for Sensors |
|---|---|---|
| Light Absorption | Reduces internal reflections, glare. | Improves signal accuracy. |
| Low Reflectivity | Enhances image contrast. | Prevents false readings from stray light. |
| EMI Shielding | Not applicable. | Protects electronics from interference. |
Black chrome plating offers a unique combination of low reflectivity, excellent light absorption, and effective EMI shielding. These properties make it an indispensable non-reflective chrome coating for high-performance optics and sensors, ensuring signal integrity and accuracy.
Black Chrome Thickness: Why It Matters in Precision Applications
Managing black chrome plating thickness is not just a quality check. It is a fundamental part of precision engineering. The thickness directly impacts a part’s final dimensions, performance, and fit.
For projects with tight tolerances, this control is absolutely critical. Even a few extra microns can turn a perfect-fit component into scrap.
Standard Thickness Ranges
Black chrome thickness specs vary by application. We typically classify them into three main categories.
| Application Type | Typical Thickness Range (microns) | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Decorative | 1-3 µm | Appearance, light wear |
| Functional | 3-8 µm | Durability, corrosion resistance |
| Precision Fit | 2-5 µm | Dimensional accuracy |
Choosing the right specification is the first step. It ensures the part meets its design intent without costly rework.

Measuring Plating Thickness Accurately
You can’t control what you can’t measure. For precision work, we rely on non-destructive methods to verify coating thickness. This ensures every part meets its required specification without damage. The choice of method depends on the part’s geometry and the required accuracy.
One of the most reliable methods is X-ray fluorescence5. This technique allows us to get fast and accurate readings. It’s essential for verifying the plating thickness for tight tolerance parts. At PTSMAKE, we integrate this measurement step directly into our quality control process.
How Thickness Affects Final Part Fits
For precision components, every micron counts. The applied black chrome plating adds to the part’s final dimensions. Engineers must account for this during the initial design phase. Failing to do so leads to assembly issues.
Consider how plating impacts a shaft designed to fit into a bearing.
| Component | Initial Dimension | Plating Thickness | Final Dimension | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaft OD | 10.000 mm | +0.005 mm (5µm) | 10.005 mm | Too tight for bearing |
| Shaft OD | 10.000 mm | +0.002 mm (2µm) | 10.002 mm | Correct fit |
This shows why precise control over black chrome plating is non-negotiable. It’s the difference between a functional assembly and a failed one. We work with clients to define these specs early on.
Controlling black chrome thickness is essential for precision applications. Standard specs guide the process, while accurate measurement ensures compliance. This layer directly impacts final dimensions, making it critical for parts requiring tight tolerance fits.
Eco-Friendly Chrome Alternatives: Where Black Chrome Stands
Navigating the world of chrome plating means understanding regulations. Global standards like REACH and RoHS are pushing for greener solutions.
This shift directly impacts material choices. The focus is now on sustainable options that don’t sacrifice quality.
Hexavalent vs. Trivalent Chrome
The primary debate is between hexavalent and trivalent chrome. Hexavalent chrome is a known carcinogen and is heavily regulated.
Trivalent chrome emerges as a safer, more eco-friendly alternative. It’s a key player in RoHS compliant plating.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Hexavalent Chrome | Trivalent Chrome |
|---|---|---|
| Toxicity | High (Carcinogenic) | Low |
| Regulation | Heavily Restricted (REACH) | Compliant |
| Eco-Impact | Negative | Positive |

The Drive Towards Green Chrome Alternatives
The industry’s move away from hexavalent chromium isn’t just about compliance. It’s a fundamental shift towards sustainable manufacturing.
At PTSMAKE, we’ve seen clients increasingly request finishes that meet strict environmental standards without compromising performance. This is where trivalent-based eco black chrome plating excels.
Why Trivalent Black Chrome Wins on Sustainability
Trivalent chromium processes use less hazardous chemicals. The waste treatment is also simpler and less costly compared to hexavalent systems.
This process forms a stable passivation layer6 that provides excellent corrosion resistance. The result is a durable, safe, and visually appealing finish. It meets the demands of modern product design.
We’ve found through our testing that trivalent solutions can match the deep, rich black color that designers want. It proves that sustainability doesn’t mean a compromise on aesthetics or function.
Let’s break down the sustainability factors:
| Sustainability Factor | Hexavalent Chrome | Trivalent Black Chrome |
|---|---|---|
| Worker Safety | High Risk | Low Risk |
| Waste Treatment | Complex & Costly | Simpler & Cheaper |
| Energy Consumption | High | Lower |
| Regulatory Burden | High & Increasing | Low & Stable |
Regulations like REACH and RoHS are driving the shift to safer materials. Trivalent black chrome stands out as a sustainable, compliant alternative to hazardous hexavalent chrome, offering excellent performance and aesthetics without the environmental or health risks.
Black Chrome in Robotics: Case Studies & Real-world Benefits
Theory is useful, but results are what truly matter. I’ve seen how black chrome plating transforms robotic components from simple parts into high-performance assets.
This finish is not just for looks. It provides critical functional advantages.
Key Benefits in Action
Enhanced Durability
In demanding industrial settings, a robot’s longevity is key. Black chrome adds a hard, protective layer. This shields parts from corrosion and wear.
Improved Sensor Accuracy
The matte-like surface of black chrome is crucial. It minimizes light reflection, which helps optical sensors get cleaner, more accurate readings.
| Feature | Standard Chrome | Black Chrome |
|---|---|---|
| Reflectivity | High | Low |
| Wear Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Aesthetics | Bright, Mirror-like | Sleek, Matte/Satin |

A Closer Look at Application Scenarios
Let’s consider a real-world example. An automated optical inspection (AOI) system on a production line. The robotic arm positions a high-resolution camera to check for defects.
Originally, the client used components with a standard anodized finish. They faced issues with light from overhead fixtures creating glare. This glare caused false readings and system errors.
We recommended switching to a black chrome finish for the camera mounts and arm segments near the lens. This specific black finish for robotic components drastically reduced unwanted specular reflection7. It absorbed stray light instead of bouncing it into the camera.
The result was an immediate increase in inspection accuracy and a reduction in false positives. This simple change in surface finish directly improved the robot’s core function.
From the Factory to the Field
This principle applies beyond factory floors. For surgical or collaborative robots, aesthetics become vital. A non-reflective, black finish looks professional and clean. It conveys precision and quality, building user trust. The durability of chrome plating for robots ensures this look lasts, even through repeated sterilization cycles.
| Problem | Black Chrome Plating Solution |
|---|---|
| Sensor Glare & Inaccuracy | Low reflectivity for clean data capture. |
| Component Wear & Tear | Hard surface that resists abrasion. |
| Corrosion from Fluids | Creates a non-porous protective barrier. |
| Perceived Low Quality | Provides a premium, high-tech aesthetic. |
Black chrome plating offers a trifecta of benefits. It boosts durability against harsh environments, enhances sensor performance by reducing glare, and provides a professional aesthetic. It’s a smart, functional upgrade for any advanced robotic system, a key service we provide at PTSMAKE.
How Black Chrome Affects Electrical Conductivity in Precision Parts
When choosing a finish, you must balance aesthetics and function. Black chrome plating is prized for its look, but it poses challenges for electrical conductivity.
The Conductivity Dilemma
This finish is inherently more resistive than standard chrome. The black color comes from contaminants that impede electron flow. This is a critical factor in electronics.
Insulating vs. Conductive Finishes
For parts requiring electrical contact, understanding this trade-off is key. We often need to engineer solutions.
A quick comparison highlights the issue:
| Finish Type | Relative Conductivity | Common Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Bare Copper | Very High | Electrical Wiring |
| Silver Plating | High | High-Frequency Contacts |
| Standard Chrome | Moderate | Wear Resistance, Some Contact |
| Black Chrome | Low to Very Low | Decorative, Non-Conductive Areas |

The low conductivity of black chrome plating isn’t always a deal-breaker. We have developed effective workarounds to get the best of both worlds: premium aesthetics and reliable electrical performance. It just requires careful planning during the design phase.
Strategies for Electrical Contacts
The most common strategy is selective plating. This involves masking areas that need to remain conductive before applying the black chrome. This ensures critical contact points are unaffected.
Masking Techniques
We use precise masking methods. This can be done with special tapes, lacquers, or custom fixtures. The goal is to create sharp, clean lines between the plated and unplated surfaces. A poor masking job leads to part failure.
Exploring Conductive Chrome Alternatives
Sometimes, a different finish is a better solution. If conductivity is the top priority, other coatings might be more suitable. However, they may not offer the same appearance. At PTSMAKE, we help clients evaluate these options.
| Strategy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Masking | Maintains conductivity; uses desired finish | Adds labor cost; complex geometries are difficult |
| Conductive Underlayer | Better conductivity than black chrome alone | May alter final appearance; adds process steps |
| Alternative Finishes | Superior conductivity; simpler process | Different aesthetic; may lack wear resistance |
The chromium oxide within the finish forms a natural passivation layer8 which contributes significantly to its insulating properties. Understanding this helps in engineering effective solutions for electrical components that require this specific aesthetic.
Black chrome plating offers a sleek look but has low conductivity. By using strategies like selective masking or considering conductive chrome alternatives, you can achieve both the desired appearance and necessary electrical performance for your precision parts.
Black Chrome for Aluminum vs. Steel: What Product Designers Must Know
When choosing black chrome plating, the substrate is everything. Your choice between aluminum and steel directly impacts the final product’s performance. It affects adhesion, wear resistance, and visual appearance.
A common mistake is assuming the process is identical for both metals.
Substrate Impact on Adhesion
Black chrome on aluminum requires more complex pre-treatment. Without a proper underplate, adhesion will fail. Steel, being more receptive, offers a more direct bonding process.
Wear and Durability Comparison
Steel’s hardness provides a stronger foundation for the chrome layer. This makes the coating more resistant to scratches and impacts. Aluminum is softer, so the coating can be more prone to damage.
Finish Appearance Differences
The final look can vary slightly. A well-prepared steel part often yields a deeper, more uniform black. Aluminum can achieve a great finish, but surface prep is absolutely critical.
| Feature | Black Chrome on Aluminum | Black Chrome on Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Adhesion | Requires underplating (e.g., nickel) | Strong, direct bond possible |
| Wear Resistance | Good, but substrate is softer | Excellent, due to hard substrate |
| Appearance | Excellent, very prep-dependent | Excellent, often deeper black |

The steel chrome coating comparison reveals key process differences. These differences are vital for product designers to understand. They influence both cost and final performance.
The Role of Underplating
For aluminum, a multi-layer approach is not optional; it’s necessary. We typically apply a layer of nickel before the black chrome. This barrier layer ensures strong interfacial adhesion9 and prevents issues like blistering or peeling down the line. Without it, the plating will not last.
For steel, while underplating can enhance corrosion resistance, it’s not always required for adhesion itself. This can simplify the process.
Long-Term Performance Considerations
Think about your product’s lifecycle. A steel part with black chrome plating will generally handle abrasion better than an aluminum one. If your component faces constant handling or mechanical stress, steel is often the more durable choice.
However, for applications where weight is a primary concern, black chrome on aluminum is an excellent solution. You just have to design with its limitations in mind. Proper engineering and plating specifications are key.
| Substrate | Key Advantage | Main Challenge | Best Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Lightweight | Complex pre-treatment | Aerospace, electronics, consumer goods |
| Steel | Durability, Hardness | Heavier weight | Automotive, industrial hardware |
Choosing between aluminum and steel for black chrome plating involves trade-offs. Steel offers superior durability and simpler adhesion. Aluminum provides a lightweight alternative but requires careful and complex surface preparation to ensure the coating lasts. The application dictates the best choice.
Black Chrome In Medical Electronics: Functional and Aesthetic Wins
In medical electronics, functionality is paramount. Black chrome plating delivers distinct advantages that go beyond just looks. Its properties are uniquely suited for demanding medical applications.
Low Reflectivity in Surgical Settings
Glare can be a significant issue in operating rooms. Black chrome’s matte finish minimizes light reflection. This helps surgeons maintain clear visibility. Better visibility reduces eye strain and improves precision during procedures.
Biocompatibility and Patient Safety
Patient safety is always the top priority. Medical chrome finishes must be inert. Black chrome provides a stable, non-reactive surface. This makes it a safe choice for instruments and device components that may have patient contact.
Coating for Small Volume Components
Modern medical devices feature incredibly small parts. Applying a uniform coating is a challenge. Black chrome plating excels here. It provides a consistent, durable finish on even the most intricate, small-volume components.
| Feature | Black Chrome | Standard Chrome | Stainless Steel |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reflectivity | Low | High | Medium-High |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Small Part Uniformity | Excellent | Good | N/A |

When we discuss chrome coating for medical parts, we must go deeper than surface-level benefits. The process control and material science behind the finish are what truly ensure performance and safety in the field.
Ensuring True Biocompatibility
A finish is only as good as its composition. For medical applications, this means preventing any harmful materials from interacting with the body. We focus heavily on minimizing potential leachables10 during our plating process. Our tests confirm the stability of the coating under various conditions. This ensures the black chrome plating remains inert and safe over the device’s entire lifecycle. It’s a commitment to safety that defines our approach to medical components.
The Challenge of Uniformity
Coating small, complex parts presents a unique engineering challenge. An uneven finish can compromise both function and safety. At PTSMAKE, we’ve refined our black chrome plating process for micro-components. This involves precise current control and specialized bath chemistry. The result is a perfectly uniform coating that adheres to the tightest tolerances required in medical electronics.
Quality Control for Medical Finishes
We implement a multi-stage quality control process. Each step verifies the integrity and consistency of the coating.
| QC Stage | Key Metric | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Surface Prep | Surface Roughness | < 0.8 µm Ra |
| 2. Plating | Thickness Uniformity | ±5% Variation |
| 3. Final Inspection | Adhesion Test (ASTM D3359) | 5B Rating |
| 4. Purity Analysis | XRF Spectroscopy | No prohibited elements |
This rigorous process ensures every part meets the exacting standards of the medical industry.
Black chrome plating offers a trifecta of benefits for medical electronics: reduced glare, proven biocompatibility, and flawless coating on small components. This makes it a superior choice for high-performance medical chrome finishes where safety and precision are non-negotiable.
Meeting Aerospace Standards With Black Chrome: What to Know
Aerospace components demand finishes that meet strict military specifications. This is where MIL-SPEC plating is critical. Black chrome plating is a top choice.
Why Choose Black Chrome?
It offers more than a non-reflective finish. This aircraft-grade chrome coating provides exceptional durability. It also enhances corrosion and abrasion resistance for parts in harsh environments.
Meeting Key Requirements
Compliance is non-negotiable. The right aerospace chrome finish ensures parts perform reliably under extreme stress, contributing to mission success and safety.

Navigating MIL-SPEC Plating Standards
Meeting military specifications for plating is a precise science. It is not just about applying a coating. It involves rigorous process control and documentation. A key standard for this finish is MIL-DTL-14538.
This specification outlines exact requirements. It covers coating thickness, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability. In our work with clients, we’ve found that black chrome consistently meets these benchmarks. The process involves a controlled cathodic deposition11, ensuring a uniform and strongly bonded layer.
Key Performance Metrics
Achieving the right balance of properties is crucial. The aircraft-grade chrome coating must adhere perfectly. It cannot flake or peel, even under severe vibration or temperature shifts. This is a baseline requirement for any component we handle at PTSMAKE.
Here is a simple breakdown of how black chrome addresses key MIL-SPEC criteria:
| MIL-SPEC Requirement | Black Chrome Performance |
|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Exceeds salt spray test standards |
| Coating Adhesion | Excellent bond, no flaking or peeling |
| Light Absorbance | High; reduces glare and reflection |
| Surface Hardness | Provides a durable, wear-resistant surface |
Managing every step of the process ensures the final black chrome plating on your components is fully compliant. It must be ready for demanding aerospace applications where failure is not an option.
Black chrome plating is a proven solution for meeting stringent MIL-SPEC aerospace standards. Its durability, corrosion resistance, and non-reflective properties make it ideal. Partnering with an experienced supplier ensures full compliance and optimal performance for critical components.
The Role of Fixturing and Masking in Black Chrome Quality
When discussing black chrome plating, chemistry often takes center stage. However, the physical setup is equally crucial for a flawless finish. This is where fixturing and masking are essential.
Proper jigging for chrome plating ensures parts are stable. It also guarantees optimal electrical contact and current distribution. Masking techniques protect specific areas from the plating process. Both are fundamental to achieving precise, high-quality results.
| Aspect | Custom Fixturing | Standard Fixturing |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | High, for specific parts | Moderate, for general use |
| Part Stability | Excellent | Varies with geometry |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |

The Art of Precision Masking and Jigging
Precision is the core of effective masking for black chrome plating. It’s about more than just covering a section. It’s about creating razor-sharp demarcation lines and protecting critical features like threads or mating surfaces.
At PTSMAKE, we use a variety of techniques. These range from high-temperature tapes to custom-molded silicone plugs and liquid maskants. The choice depends entirely on the part’s geometry and the specific requirements of the project.
Proper jigging goes hand-in-hand with masking. A well-designed jig holds the part securely. It also minimizes contact points that could leave marks on the finished surface. This careful planning helps prevent issues like uneven plating thickness caused by the Faraday cage effect12. The right setup ensures a consistent, uniform coating across even the most complex shapes.
| Masking Technique | Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High-Temp Tape | Flat surfaces, straight lines | Crisp, clean edges |
| Liquid Maskant | Complex curves, irregular shapes | Conforms perfectly to surfaces |
| Custom Plugs/Caps | Threads, holes, and ports | Reusable and highly accurate |
Effective fixturing and precise masking are non-negotiable for superior black chrome plating. These steps ensure coating uniformity, protect critical features, and deliver the exact finish your design requires. They are foundational to achieving a successful outcome.
How Tightly Can You Tolerate? Understanding Plating Stack-Up
Predicting dimensional changes after plating isn’t guesswork. It’s about understanding the physics. Especially for complex features like gaps, holes, and threads.
The plating thickness you specify is just an average. The actual buildup varies across the part’s geometry. This is vital for avoiding tolerance issues.
Plating Build-Up on Different Features
How does a layer of black chrome plating affect your design? It depends on the feature. External surfaces plate differently than internal ones.
Common Plating Thickness Variations
| Feature Type | Expected Plating Buildup |
|---|---|
| External Corner | Thicker |
| Internal Corner | Thinner |
| Flat Surface | As Specified |
| Small Hole ID | Very Thin / None |
This variation leads to chrome plating tolerance accumulation.

The Challenge of Internal and External Features
Predicting plating behavior is crucial for parts that need to assemble perfectly. A few microns can make all the difference between a snug fit and a scrapped part.
Plating Dynamics in Holes
For through-holes, plating builds up more at the entry and exit points. The center receives significantly less. Blind holes are even trickier, with the bottom getting almost no coverage unless special anodes are used. This is due to the principles of Current Density Distribution13.
Navigating Threaded Components
Threads present a unique challenge. The peaks (crests) attract more plating material, while the valleys (roots) receive less. This alters the pitch diameter and can cause binding if not accounted for. Managing dimensional changes after plating threads is a core part of our process at PTSMAKE.
We model this behavior to adjust pre-plating dimensions. This ensures that after a finish like black chrome plating, the final part is perfectly within spec.
| Thread Feature | Plating Buildup | Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Crest (Peak) | High | Increases major/minor diameter |
| Root (Valley) | Low | Can cause interference |
| Flank | Moderate | Affects pitch diameter |
Understanding these nuances prevents costly assembly failures.
Predicting plating buildup, especially on complex features, is critical for maintaining tight tolerances. Understanding how factors like current distribution affect holes and threads ensures functional, in-spec parts and avoids assembly issues after finishing.
Avoiding Fatigue Failures with Black Chrome on Moving Assemblies
When components are in motion, they experience cyclical loads. This creates a significant challenge for any surface coating, including black chrome plating.
The primary concern is stress concentration. This often occurs at the transition points where the coating begins and ends.
These zones can become failure points under repeated stress. A component’s fatigue life can be drastically reduced if this is not managed.
Let’s examine the critical areas to watch.
| Stress Point Area | Fatigue Risk Level | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Edge | High | Blend or feather the edge |
| Internal Corners | High | Apply a radius before plating |
| Fastener Holes | Medium | Chamfer and de-burr holes |

The Challenge of Cyclical Loads
Moving assemblies subject parts to continuous stress cycles. This is a far more demanding environment than a static one. For chrome under dynamic load, this can be problematic.
Micro-cracks, inherent to many chrome plating processes, can act as initiation sites. Over time, these cracks can propagate from the coating into the base material. This directly compromises the part’s structural integrity.
Stress Points at Coating Transitions
The boundary where the black chrome plating stops is a major stress riser. An abrupt coating edge acts like a small notch, concentrating stress.
This is where fatigue cracks love to start. At PTSMAKE, we often work with clients to design a smoother transition, like a gentle radius. This helps distribute the load more effectively. It is a key detail for a durable fatigue chrome coating. The plating process can also introduce risks like hydrogen embrittlement14, which weakens the substrate, especially under dynamic loads.
Key Process Controls for Fatigue Resistance
| Control Step | Purpose | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Stress Relief Bake (Pre) | Removes residual stress from machining | High |
| Shot Peening | Induces compressive surface stress | High |
| De-embrittlement Bake (Post) | Removes absorbed hydrogen | Critical |
Managing cyclical loads and stress points is crucial for black chrome on dynamic parts. Proper design of coating transitions and strict process controls are essential to prevent premature fatigue failures and ensure component reliability.
Unlock Precision With Black Chrome Plating – Choose PTSMAKE
Ready to enhance your CNC machined parts with advanced black chrome plating? Let PTSMAKE help you achieve unbeatable aesthetics, corrosion resistance, and tight tolerances. Contact us today for a fast, no-obligation quote—experience why industry leaders trust PTSMAKE for precision and reliability in every project!
Learn how surface properties impact friction, wear, and lubrication in mechanical systems. ↩
Understand the technical standard for operating salt spray apparatus. ↩
Learn how surface physics dictates the visual difference between matte and gloss finishes. ↩
Understand the difference between mirror-like and scattered light reflections and why it matters for optical design. ↩
Learn how this non-destructive method ensures precise coating thickness on your parts. ↩
Understand how this microscopic layer provides powerful corrosion protection for your parts. ↩
Understand how surface reflectivity directly affects the performance and reliability of robotic vision systems. ↩
Learn more about how this protective surface layer forms and impacts material properties. ↩
Understand the science behind coating failure to improve your product’s long-term reliability. ↩
Learn more about chemical compounds that can migrate from materials and their importance in medical device safety. ↩
Understand the science behind how this electrochemical process creates durable and compliant aerospace coatings. ↩
Discover how this electrical principle can impact plating uniformity and how proper design can mitigate it. ↩
See how electrical current variation impacts final plating thickness and part precision. ↩
Discover how trapped hydrogen can cause unexpected brittle failure in metals post-plating. ↩