You’re spending valuable time dealing with inconsistent zinc plating results, dimensional tolerance issues, and quality problems that slow down your production cycles. These coating challenges create delays, increase costs, and strain relationships with downstream assembly teams.
Zinc plating is an electrochemical process that deposits a thin layer of zinc onto CNC machined parts to provide corrosion resistance, improve aesthetics, and extend part lifespan while maintaining cost-effectiveness for high-volume production.

This guide covers the technical details you need to make informed decisions about zinc plating specifications, quality control methods, and supplier selection. You’ll learn how to avoid common pitfalls that affect dimensional tolerances and discover proven strategies for achieving consistent results across different part geometries.
The Hidden Benefits Of Zinc Plating For Precision Parts
Many engineers see zinc plating as just a basic finish. But that view is too simple. The real zinc plating benefits go much deeper.
More Than a Simple Coating
It provides strong protection against rust. It also gives parts a clean, professional look. This makes it a smart choice for precision components.
Why Zinc Plating Matters
This finish is critical for both performance and appearance.
| 特徴 | Impact on Precision Parts |
|---|---|
| 腐食シールド | Extends the operational life of parts. |
| Aesthetic Finish | Offers a clean and consistent appearance. |
| コスト効率 | Reduces long-term replacement costs. |
Understanding these points reveals why zinc plating matters in manufacturing.

Zinc plating is a go-to choice for preventing rust. However, the way it works is more complex than a simple barrier. It’s an active protective system.
The Science of Protection
The zinc coating for CNC parts acts as a 犠牲陽極1 for the base metal, like steel. This means the zinc layer corrodes first. It sacrifices itself to protect the part underneath. This is a critical feature for parts used in harsh environments.
Aesthetics and Added Defense
The process doesn’t end with plating. We often apply a chromate conversion coating. This secondary layer adds color and boosts corrosion resistance significantly. It allows for functional and visual customization.
| Chromate Finish | ビジュアル・キュー | Performance Boost |
|---|---|---|
| クリア(青) | Bright Silver | Good Protection |
| イエロー | Iridescent Gold | Excellent Protection |
| ブラック | Deep Black | Very Good Protection |
A Smart Economic Decision
The true value of zinc plating is in its long-term performance. The initial cost is low, but the real savings come from reduced maintenance and replacement needs. At PTSMAKE, we often advise this finish for its excellent balance of cost, performance, and reliability.
Zinc plating provides an active sacrificial shield against corrosion, not just a passive one. It offers versatile aesthetic finishes that also enhance durability. This combination delivers exceptional long-term value and reliability for precision parts, making it a truly cost-effective solution.
Zinc Plating Vs. Hot-Dip Galvanizing: What’s The Better Fit For Your Project?
When comparing zinc plating vs galvanizing, performance is key. It’s not just about corrosion resistance. Surface finish and dimensional precision are equally important for a part’s function.
Corrosion Protection Levels
Hot-dip galvanizing creates a much thicker protective layer. This offers superior corrosion resistance in harsh environments. Zinc plating provides a thinner, yet effective, barrier.
表面仕上げの比較
Zinc plating results in a smooth, bright, and uniform surface. This makes it ideal for aesthetic applications. Galvanizing leaves a rougher, more utilitarian finish.
| 特徴 | 亜鉛メッキ | 溶融亜鉛メッキ |
|---|---|---|
| 終了 | Smooth, Bright | Rough, Matte Gray |
| 均一性 | 高い | Lower, can be uneven |
| 最適 | Aesthetics, Indoor Use | 過酷な環境 |
This table shows a fundamental difference between zinc plating and galvanizing.

The Critical Role of Dimensional Tolerance
The choice heavily impacts your part’s final dimensions. This is a crucial detail for precision components. Tolerances after plating can make or break an assembly.
Zinc plating adds a very thin coating. Typically, it is only 5-25 micrometers thick. This makes it perfect for parts with tight tolerances, like fasteners or mating components. The process ensures predictable results.
Hot-dip galvanizing is different. It creates a thick coating, often 50-100 micrometers or more. This layer is also less uniform. It can fill threads and alter critical dimensions, often requiring post-processing like re-tapping.
Understanding the Bond
The protection mechanism also differs. Galvanizing forms a metallurgical bond with the steel. This creates a durable, abrasion-resistant alloy layer.
Zinc plating, on the other hand, adheres through an electrochemical bond. The zinc layer acts as a 犠牲陽極2. It corrodes first to protect the underlying steel. This is a key difference between zinc plating and galvanizing. This method offers reliable protection for many applications.
Ultimately, the decision balances precision against protection. Zinc plating excels in dimensional control and offers a cosmetic finish. Hot-dip galvanizing provides robust, long-term corrosion resistance at the cost of surface uniformity and tight tolerances.
How To Avoid Thread Jamming After Zinc Plating
Zinc plating adds corrosion resistance. But it also adds thickness. This often causes thread jamming on fasteners and CNC parts.
Designers must plan for this added layer. It’s a common oversight that leads to assembly failures.
At PTSMAKE, we guide our clients on three key areas. These are masking, thread tolerances, and post-plating adjustments.
Proactive Design Choices
Proper planning is crucial. Addressing potential issues during the design phase saves time and cost later. This is key for zinc plating threaded parts.
Here’s a quick look at masking options:
| Masking Type | ベスト・ユースケース | 考察 |
|---|---|---|
| Caps/Plugs | External/Internal Threads | Reusable, consistent |
| テープ | Irregular Surfaces | 労働集約的 |
| ラッカー | 複雑な幾何学 | Requires clean removal |
Thinking ahead helps avoid thread fit issues plating.

To prevent thread fit issues, you must account for the plating thickness before manufacturing. It’s not something to fix later.
高度なマスキング戦略
For effective masking threaded CNC parts, select the right method. Silicone caps and plugs offer a clean, reusable solution for standard threads. They provide a sharp plating line.
For more complex areas, high-temperature tapes work well. However, they demand precise application and can be labor-intensive. Liquid masking is another option, but removal must be thorough to avoid contamination.
Adjusting Thread Tolerances
The most critical step is adjusting thread tolerances. You must specify threads to be cut undersize to accommodate the zinc layer.
For example, if you plan for a 0.0003-inch (8µm) zinc plating thickness, the pre-plating thread dimensions must be reduced accordingly. This prevents the final part from being oversized. Failure to do so can cause issues like 凛々しい3 組み立て中に。.
We often recommend specific adjustments based on the plating class.
Plating Thickness and Tolerance
| Plating Class | 典型的な厚さ | 推奨される措置 |
|---|---|---|
| Class 1 (5µm) | ~0.0002" | Undersize internal threads |
| Class 2 (8µm) | ~0.0003" | Significant undersizing |
| Class 3 (12µm) | ~0.0005" | Requires special tooling |
Post-Plating Adjustments
Sometimes, post-plating work is needed. Lightly chasing the threads with a die or tap can clear minor buildups. Baking parts after plating is also crucial to prevent hydrogen embrittlement. This process can sometimes affect the final fit.
Proper design is key to avoiding thread jamming. This includes selecting the right masking technique, accurately specifying pre-plating thread tolerances, and planning for any necessary post-plating adjustments. This ensures a successful outcome for zinc plating projects.
How Zinc Plating Impacts Dimensional Tolerances In Tight-Fit Assemblies
Zinc plating adds a protective layer, but it also adds material. This is a critical detail for tight-fit assemblies. The zinc plating tolerance impact can be significant.
Every dimension on a part will change after plating. It’s not just a coating; it’s a dimensional shift.
Understanding Plating Buildup
The added zinc thickness typically ranges from 5 to 25 micrometers (µm). This seems small, but it can easily push a precise part out of tolerance.
均一性の課題
The thickness isn’t perfectly even. Plating tends to build up more on sharp external corners and edges. This is a key concern for zinc build-up CNC parts.
| フィーチャー・タイプ | Expected Buildup |
|---|---|
| 平面 | Nominal Thickness |
| 外部コーナー | 1.5x – 2.0x Nominal |
| 内部コーナー | 0.5x – 0.75x Nominal |
| 穴/ボア | Reduced Thickness |
This uneven buildup means a simple offset isn’t enough. We must account for geometric effects.

Zinc plating is more than one layer. After the zinc is applied, a chromate conversion coating is added for extra corrosion resistance and color. This film also adds to the total thickness.
The Role of Chromate Conversion Films
While the chromate layer is very thin, often just 0.1 to 0.5 µm, it’s part of the final dimension. For extremely tight tolerances, even this minuscule addition matters. The total dimension change after plating is the sum of the zinc and chromate layers.
Strategies for Dimensional Control
At PTSMAKE, we manage this by planning ahead. We often machine parts slightly undersized. This compensates for the material added during the zinc plating process.
This requires precise calculation and clear communication between our machining team and our plating partners. The process of 電気化学蒸着4 is controllable, but it demands expertise. We specify not just the final dimension, but also the target plating thickness.
For example, a shaft designed to be 20.00mm after plating might be machined to 19.98mm beforehand. This accounts for a target plating thickness of 10 µm on the radius.
| 寸法 | 仕様 | Pre-Plating (Target) | Post-Plating (Result) |
|---|---|---|---|
| シャフト径 | 20.00 mm ±0.01 | 19.98 mm | 20.00 mm |
| 穴径 | 15.00 mm ±0.01 | 15.02 mm | 15.00 mm |
This proactive approach is essential for ensuring that zinc build-up CNC parts fit perfectly in their final assembly.
Zinc plating adds a predictable but variable thickness. This buildup, plus the chromate film, directly affects final dimensions. Success in tight-fit assemblies requires carefully engineering the pre-plating dimensions to compensate for this addition, a core part of our process at PTSMAKE.
Design Secrets For Maximizing Zinc Plating Uniformity On Complex Parts
Achieving a uniform zinc plating finish on complex CNC parts is a common challenge. The part’s geometry directly influences the outcome.
Certain features can block the electrical current needed for plating. This creates uneven coating thickness.
Key Geometry Considerations
Thinking about plating during the design phase is crucial. Small changes can make a huge difference in the final quality and consistency.
| 特徴 | めっきへの影響 | 推薦 |
|---|---|---|
| シャープな内角 | 接着不良 | Use Radii/Fillets |
| Deep, Narrow Holes | Thin or No Coating | Widen or Re-evaluate |
| 大きな平面 | Prone to Buildup | Add Slight Crown |
Proper racking is just as important as the design itself. It ensures optimal current flow.
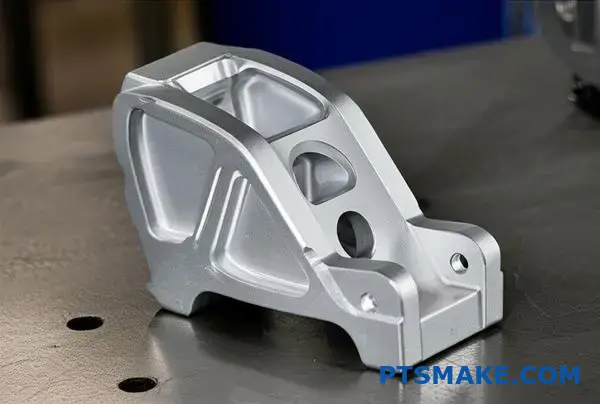

Deeper Dive into Plating Challenges
The core issue with coating complex CNC geometry is managing current density. High-current areas get thick plating, while low-current areas are left thin.
This is especially true for parts with holes and recesses. These areas often suffer from what is known as the ファラデーケージ効果5, where the exterior of a feature shields the interior from the electrical field.
Racking: More Than Just Holding a Part
Effective racking is a science. At PTSMAKE, we design custom fixtures. These fixtures ensure every critical surface is properly exposed to the plating solution and electrical current.
We also consider drainage. Trapped solutions can cause staining and corrosion post-plating. Racking orientation must allow for complete drainage.
Common Problem Zones and Solutions
Understanding where failures occur is the first step. After reviewing numerous client parts, we’ve found consistent patterns.
| 問題領域 | Plating Issue | 緩和戦略 |
|---|---|---|
| ブラインドホール | No plating inside | Use auxiliary anodes |
| Recessed Pockets | Thin coating | Adjust rack angle, use current thieves |
| Threaded Sections | Buildup on crests | Masking or post-plate chasing |
By addressing these zinc plating uniform coating tips early, we prevent costly rework. It’s about designing for manufacturability, which includes the finishing process.
Effective zinc plating on complex parts requires a dual focus. You must consider the part’s geometry during the design phase and use intelligent racking methods. This combined strategy prevents common adhesion and uniformity issues, ensuring a high-quality, consistent finish.
The Ultimate Guide To Zinc Chromate Conversion Options
When choosing a zinc chromate conversion coating, the color is your first clue to its properties. It’s not just about aesthetics. Each color—blue, yellow, and black—indicates a different level of corrosion protection.
This choice directly impacts your part’s durability and performance. Understanding these differences is key.
Quick Guide to Chromate Colors
We can break down the primary types by their key features. This helps in making a quick, informed decision for your project.
| 特徴 | Blue (Clear) Chromate | Yellow Chromate | Black Chromate |
|---|---|---|---|
| 外観 | Bright, slight blue tint | Iridescent, yellowish | マットと光沢のある黒 |
| 耐食性 | Basic (24-48 hrs) | Moderate (96-150 hrs) | High (150-250+ hrs) |
| 一般的な使用 | Decorative, indoor | General industrial | Automotive, exterior |

Diving Deeper: Properties and Applications
Beyond the basic color chart, each zinc chromate conversion coating has specific strengths. Selecting the right one is crucial for the longevity and reliability of your components. The choice affects not just corrosion resistance but also paint adhesion and electrical conductivity.
Yellow Chromate Properties
Yellow chromate is often the default choice for general industrial use. It provides a great balance between cost and performance. The yellow chromate properties include excellent paint adhesion, making it a reliable primer base. We often recommend it for parts that need both protection and a subsequent coating.
The Superior Black Zinc Finish
The black zinc finish offers the highest level of corrosion resistance. This makes it ideal for parts exposed to harsh weather or corrosive agents. It’s a common choice for automotive components, military hardware, and outdoor equipment. Its decorative black appearance is an added bonus.
When to Use Blue (Clear) Chromate
Blue or clear chromate provides minimal protection. Its primary role is to prevent oxidation on the zinc plating during storage. It’s used when the part’s metallic appearance is important and the environment is not demanding. The process creates a protective layer through 不動態化6, which keeps the surface bright.
Choosing between blue, yellow, and black chromate involves balancing corrosion resistance, appearance, and cost. Black offers maximum protection, yellow provides a versatile mid-range solution, and blue is ideal for basic protection where aesthetics are key. Your application dictates the best option.
Boost First-Pass Yield With These Zinc Plating Quality Standards
Achieving consistent zinc plating quality control isn’t magic. It relies on established industry standards. These frameworks ensure everyone speaks the same language.
They provide clear guidelines for success. This alignment prevents misunderstandings between you and your supplier.
主要業界標準
For most commercial parts, the ASTM B633 standard is crucial. It details thickness, types, and classes for electrodeposited zinc on iron and steel. It’s our primary reference at PTSMAKE.
Here’s a quick comparison of common standards:
| スタンダード | フォーカス・エリア | 主要用途 |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM B633 | コマーシャル | General industrial, automotive, consumer goods |
| MIL-STD-870 | ミリタリー | Aerospace, defense, high-reliability applications |
| ISO 2081 | インターナショナル | Global commerce, European markets |
These standards are the foundation for a successful project.

Knowing the standards is only half the battle. The real key to first-pass yield is proactive, in-process quality control. You can’t just inspect the final product. You have to monitor the entire process. This is how to inspect zinc plating effectively.
In-Process Quality Control Checks
At PTSMAKE, we build quality checks into every step. We monitor bath chemistry, temperature, and current density in real-time. This prevents defects before they happen. It’s far more efficient than finding a problem at final inspection. This approach ensures the zinc coating provides consistent cathodic protection7 ベースメタル用。.
We use several methods to verify quality during and after plating. Our findings show that a combination of tests provides the most reliable results.
| 検査方法 | 目的 | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| 蛍光X線 (XRF) | Measures plating thickness | In-process & final |
| 接着試験 | Checks coating bond | Post-plating |
| 塩水噴霧試験 | Verifies corrosion resistance | Final qualification |
| 目視検査 | Finds surface defects | プロセス全体を通じて |
Beyond the Standards
While standards provide a baseline, experience matters. A good supplier knows how part geometry affects plating distribution. They adjust parameters to ensure even coverage on complex shapes. This expertise is what truly boosts quality.
Adhering to standards like ASTM B633 and implementing rigorous in-process checks are non-negotiable. This proactive approach to zinc plating quality control ensures parts meet spec, reducing rework and improving your first-pass yield significantly.
How Long Does Zinc Plating Last? Real-World Durability Tests Explained
How do we predict zinc plating lifespan? The industry relies heavily on standardized tests. The most common is the salt spray test.
This test provides a crucial baseline for corrosion test performance. It helps us compare different plating finishes under controlled conditions.
Salt Spray Test Benchmarks
In this accelerated test, parts are exposed to a salt fog. We measure the hours until white rust (zinc corrosion) and red rust (steel corrosion) appear. The results vary based on the passivation type.
| Passivation Type | Hours to White Rust (ASTM B633) | 赤錆へ至る時間 |
|---|---|---|
| クリア(三価) | 12 – 24 hours | 72 – 120 hours |
| 黄色(三価) | 72 – 96 hours | 150 – 200 hours |
| Black (Trivalent) | 48 – 72 hours | 120 – 180 hours |
These numbers provide a standardized measure of performance.

While salt spray tests are essential, they don’t tell the whole story. They represent a "worst-case" scenario. Real-world zinc durability depends on many other factors that these tests cannot fully simulate.
Lab Data vs. Environmental Reality
A constant salt fog is very different from daily environmental exposure. Real-world conditions include fluctuating humidity, temperature cycles, and UV radiation. These variables significantly influence the actual zinc plating lifespan.
The primary protective mechanism of zinc is through ガルバニック腐食8, where the zinc sacrifices itself to protect the underlying steel. The rate of this sacrifice changes dramatically based on the environment.
さまざまな環境における性能
A part’s location is the biggest factor in its longevity. Our experience shows that the environment dictates performance more than a lab test.
| 環境 | Typical Conditions | Expected Lifespan (with proper passivation) |
|---|---|---|
| Mild / Indoor | Controlled temperature, low humidity | 15+ years |
| Moderate / Urban | Moderate humidity, some pollutants | 5 – 10 years |
| Severe / Marine | High humidity, salt exposure, industrial | 1 – 5 years |
At PTSMAKE, we help clients select the right finish. We focus on the part’s final application, ensuring the specification meets real-world demands, not just a test certificate.
Salt spray tests provide a standardized benchmark for corrosion resistance. However, true real-world zinc durability is ultimately determined by the specific operating environment. Matching the plating specification to the application is critical for achieving the desired product lifespan.
Ultimate Comparison: Rack Vs. Barrel Zinc Plating For B2B Parts
Choosing between rack and barrel zinc plating directly impacts your bottom line. It’s a classic trade-off between volume and precision.
Barrel plating processes huge batches at once. This makes it incredibly cost-effective for the right parts.
Rack plating handles parts individually. This process costs more per piece but offers unmatched quality for specific needs. Understanding this is key for successful outcomes.
| ファクター | バレルめっき | ラックめっき |
|---|---|---|
| 人件費 | 低い | 高い |
| スループット | 大量 | 少量 |
| 単価 | 非常に低い | より高い |

Best Uses and Cost-Effectiveness
The best choice depends entirely on the part’s design and final application. There is no single "better" method for zinc plating.
The Workhorse: Barrel Plating
For bulk processing, nothing beats barrel plating. It’s the ideal small parts zinc coating method. Think fasteners, nuts, and stamped brackets.
We often use barrel plating CNC parts when the components are small and don’t have critical cosmetic surfaces. The parts tumble together, which is highly efficient. This can cause minor surface marks, a trade-off many clients accept for non-visible components where corrosion resistance is the main goal.
The Specialist: Rack Plating
The key rack zinc plating advantages shine with complex parts. This method is for large, delicate, or intricate geometries that would be damaged in a barrel.
Each part is individually wired. This ensures a consistent, high-quality finish with no contact marks. The process is governed by principles like ファラデーの電気分解の法則9, ensuring precise coating thickness. It’s perfect for visible automotive components or high-spec electronic chassis.
At PTSMAKE, here’s how we typically guide the decision:
| 部品特性 | 推奨方法 | 理由 |
|---|---|---|
| 小型でシンプル、耐久性がある | バレルめっき | Highest cost-efficiency |
| Large or complex shape | ラックめっき | Prevents damage, ensures coverage |
| Delicate, easily tangled | ラックめっき | Individual handling protects parts |
| High cosmetic requirement | ラックめっき | Superior, uniform finish |
Barrel plating is the cost-effective choice for high-volume, durable small parts. Rack plating delivers superior finishes for larger or delicate components at a higher cost. Your part’s specific requirements—not price alone—should guide your zinc plating decision.
The Role Of Base Material Choice In Zinc Plating Adhesion
The base material is the foundation of your plated part. Its properties directly influence how well the zinc coating will stick. Not all metals are created equal for zinc plating.
Understanding material compatibility with zinc coatings is key. Some metals bond easily with zinc. Others require special, multi-step preparations to achieve a durable finish.
The choice impacts everything. It affects the process, cost, and the final part’s performance.
| ベースメタル | General Plating Difficulty |
|---|---|
| スチール | 低い |
| 真鍮 | ミディアム |
| アルミニウム | 高い |
| ステンレス鋼 | 高い |
Selecting the best base metals for zinc plating from the start can save significant time and resources.

The success of zinc plating varies greatly across different metals. Each substrate presents unique surface chemistry and metallurgical properties. These factors demand distinct pre-treatment strategies to ensure strong adhesion. Without the correct preparation, the plating will fail.
Steel: The Ideal Candidate
Carbon steel is the most common and straightforward material for zinc plating. Its surface is receptive, making adhesion strong with standard cleaning and activation. However, plating on alloy steel can be trickier. Alloying elements like chromium or manganese can alter surface properties, sometimes requiring adjusted pre-treatment.
Aluminum: The Oxide Challenge
Aluminum naturally forms a tough, thin oxide layer. This layer prevents direct zinc adhesion. To plate aluminum, we must first apply a zincate conversion coating. This process removes the oxide and deposits a thin zinc film, which acts as a base for the final electroplated layer.
Brass and Copper Alloys: The Diffusion Risk
Brass is relatively easy to plate. The challenge is zinc diffusion. Over time, zinc from the brass can migrate into the plating layer. This can cause cosmetic issues or reduce corrosion resistance. A barrier layer of copper or nickel is often applied first to prevent this.
Stainless Steel: The Passive Problem
Stainless steel is difficult to plate due to its パッシベーション層10 of chromium oxide. This layer makes the steel corrosion-resistant but also non-receptive to plating. We must activate the surface, often using a specialized acid pickle or a Woods nickel strike, to enable proper adhesion.
| 素材 | プライマリー・チャレンジ | Typical Pre-Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| スチール | Minimal; rust/scale | Alkaline cleaning, acid pickle |
| アルミニウム | 酸化物層 | Zincate immersion |
| 真鍮 | Zinc Diffusion | Copper or Nickel strike |
| ステンレス鋼 | Passive Surface | Woods nickel strike |
Your choice of base material is not just a design decision. It’s a critical process variable. Steel offers a direct path to quality zinc plating, while aluminum, brass, and stainless steel require specialized knowledge and intermediate steps to achieve reliable adhesion and performance.
Avoiding Color Variation In Cosmetic Zinc-Plated Parts
Achieving a uniform finish on cosmetic zinc-plated parts is a common challenge. Inconsistencies often stem from the plating process itself.
Effective supplier control is the first step. Without it, you’ll see constant variation.
Part Orientation Matters
How a part is held during plating drastically affects the outcome. Different orientations lead to different thicknesses and colors. This is crucial for appearance control zinc plating.
| ファクター | 仕上がりへの影響 |
|---|---|
| Supplier Process | 高い |
| パート・オリエンテーション | 高い |
| Bath Chemistry | ミディアム |
This requires strict cosmetic part QC from start to finish.

Controlling finish variation requires a deep understanding of the zinc plating process. Minor drifts in bath chemistry, temperature, or electrical current can cause visible shifts in color and brightness.
Mastering Supplier Controls
You need a supplier who documents every step. This includes pre-treatment, plating parameters, and post-treatment chromate processes. We work with partners who provide full transparency. This helps us achieve a uniform finish on zinc surfaces.
The orientation of parts on the plating rack is also critical. Areas closer to the anode receive more current, resulting in a thicker, sometimes brighter deposit. This uneven 電流密度分布11 is a primary cause of inconsistency. We often design custom racking to minimize this effect.
Cosmetic Part QC Standards
Establishing clear visual standards is non-negotiable. We use approved boundary samples to define acceptable color ranges.
| 制御方法 | ベネフィット |
|---|---|
| プロセス・ドキュメンテーション | Repeatability & Traceability |
| カスタムラック | Uniform Plating Thickness |
| Boundary Samples | Clear Acceptance Criteria |
| Regular Audits | Proactive Problem Solving |
These controls are essential for any project where appearance is key.
Controlling finish inconsistencies in zinc plating relies on strict supplier process management and strategic part orientation. Establishing clear cosmetic quality control standards with visual samples is essential for achieving the desired uniform appearance and avoiding costly rework.
Zinc Plating For Assemblies: How To Manage Fit, Threads, And Fasteners
When dealing with zinc plating for assemblies, precision is key. The added layer, though thin, can disrupt perfect fits. This is especially true for threaded components.
Understanding Plating Thickness
The thickness of zinc plating directly impacts dimensional tolerances. A few microns can make a big difference in tight-fitting parts. Effective dimensional management for assemblies is crucial.
Here’s a quick look at common thicknesses:
| クラス | 厚さ(マイクロメートル) | 申し込み |
|---|---|---|
| Fe/Zn 5 | 5 µm | Mild, indoor |
| Fe/Zn 12 | 12 µm | Moderate, outdoor |
| Fe/Zn 25 | 25 µm | Severe, industrial |
Managing these changes ensures a successful final assembly.

The Ripple Effect of Plating
The real challenge isn’t a single part. It’s how multiple plated parts interact. This cumulative effect is known as トレランス・スタックアップ12. Each plated component adds to the total dimensional variance.
This can lead to interference fits where a clearance fit was intended. For projects at PTSMAKE, we always account for this during the design phase.
Surface Interactions and Galling
Zinc is a relatively soft metal. After plating, the surface properties change. This can sometimes lead to galling, especially with certain fastener materials. The zinc layer can shear and seize the threads during tightening.
成功のために zinc plating fasteners, consider post-plating lubricants. Here are some assembly after coating tips we’ve found useful:
| Tip | 説明 | ベネフィット |
|---|---|---|
| マスキング | Protect critical threads from plating. | Guarantees original fit. |
| Undersizing | Machine threads slightly undersize. | Accommodates plating thickness. |
| 潤滑 | Apply wax or anti-seize compound. | Prevents galling during assembly. |
These strategies are core to our dimensional management assemblies. They ensure parts go together smoothly after coating.
Zinc plating adds material, which can cause thread binding and tolerance issues. Proactive dimensional management, like adjusting pre-plating dimensions and using post-plating lubricants, is essential for smooth assembly and preventing surface problems like galling.
When To Choose Black Zinc Over Clear Or Yellow Zinc Coating
Choosing the right zinc coating is crucial. It impacts performance, cost, and appearance. It’s more than just picking a color. Each finish offers distinct advantages for specific applications.
This decision directly affects your part’s lifespan. Let’s compare black, clear, and yellow zinc plating.
Key Factors at a Glance
Consider these primary differences.
| 特徴 | Black Zinc | Yellow Zinc | Clear Zinc |
|---|---|---|---|
| 外観 | Sleek, matte/glossy | Iridescent, yellowish | ブライト、メタリック |
| 腐食 | Moderate to good | 素晴らしい | ベーシック |
| コスト | より高い | 中程度 | 最低 |
Understanding these basics helps narrow down your options quickly. This is a common discussion I have with clients.

When selecting a zinc plating finish, we must look beyond the surface. The chromate conversion coating applied after plating defines these properties. The choice between them involves a trade-off.
Detailed Comparison: Performance vs. Aesthetics
Black zinc finish benefits are often aesthetic. It provides a non-reflective, uniform black finish. This is ideal for automotive interiors or electronics. It also offers good corrosion resistance.
Yellow vs Black Chromate
Yellow chromate provides superior corrosion protection. This is due to its thicker hexavalent chromium film. However, black chromate, often trivalent, is a close second. It also meets many RoHS compliance standards. Many of our clients in the automotive sector prefer yellow for under-hood components.
Clear Zinc Coating Comparison
Clear zinc offers the least corrosion resistance. It’s mainly for a clean, metallic look with basic protection. It’s suitable for parts used in dry, indoor environments. The 不動態化13 layer is very thin compared to yellow or black.
UV Resistance and Application
In our tests, black zinc has shown better UV resistance than dyed clear or yellow coatings. This prevents color fading in sun-exposed parts. Yellow is the workhorse for industrial fasteners. Clear is common for consumer goods where aesthetics are key.
| 属性 | Black Zinc | Yellow Zinc | Clear Zinc |
|---|---|---|---|
| 紫外線安定性 | グッド | フェア | Poor (can discolor) |
| 一般的な使用 | 自動車、エレクトロニクス | Industrial, Outdoor | Indoor, Decorative |
| ROHS | Often Trivalent (Yes) | Hexavalent (No) | Trivalent (Yes) |
Choosing the right zinc plating depends on your priorities. Black zinc is excellent for aesthetics and moderate protection. Yellow zinc is the top choice for harsh environments. Clear zinc is a cost-effective option for basic needs where a metallic look is desired.
How 3D Part Geometry Impacts Zinc Plating Coverage
The 3D geometry of a part is not just about function; it directly controls the success of your zinc plating. Uniform coating is often assumed, but complex shapes present real challenges.
Areas like deep recesses, sharp internal corners, and overhangs naturally resist even zinc deposition. This can lead to thin spots, compromising corrosion resistance. Understanding the geometry effect on coating is crucial before production.
一般的な幾何学上の課題
| 特徴 | 亜鉛めっきへの影響 |
|---|---|
| 深い穴 | Poor throwing power inside |
| シャープなコーナー | Excessive buildup on edges |
| Large Flat Areas | Potential for uneven finish |
| Recessed Zones | Insufficient coating thickness |

Let’s explore why these features cause problems. Zinc plating relies on an electrical current to deposit zinc onto the part’s surface. This current follows the path of least resistance.
High-current-density areas, like external corners and edges, attract more zinc ions, leading to a thicker coating. Conversely, low-current-density areas, such as the inside of holes or deep grooves, receive far fewer ions.
This creates zinc plating low-deposit areas. In extreme cases, the interior of a complex part acts like a ファラデーケージ効果14, effectively shielding the internal surfaces from the electrical field and preventing any meaningful deposition. At PTSMAKE, we guide our clients on design modifications to avoid this.
Complex Shape Plating Tips
To achieve a uniform finish, we often recommend slight design changes. These adjustments can make a huge difference in manufacturing efficiency and final part quality.
| Design Modification | Plating Benefit |
|---|---|
| Add generous radii to corners | Promotes even current flow |
| Use through-holes instead of blind holes | Allows solution to flow freely |
| Minimize deep recesses | Reduces low-deposit areas |
| Add auxiliary anodes for complex parts | Helps direct current to recessed zones |
Understanding how geometry affects coating is the first step. By designing for plating, you can prevent uneven coverage, avoid costly rework, and ensure your parts meet corrosion resistance specifications from the start.
Hidden Pitfalls In Outsourced Zinc Plating For International Supply Chains
Sourcing zinc plating overseas seems cost-effective. But the initial quote rarely tells the whole story. Unexpected logistical hurdles can quickly erode those savings.
Your project timeline is at risk. Delays are common.
The True Cost of Distance
When planning an international supply plating strategy, you must account for shipping, customs, and communication. These factors often add weeks to lead times.
Navigating Global Shipping
Logistics are not just about transport. They involve coordination across time zones. A simple documentation error can cause significant setbacks.
| ステージ | Expected Time | Potential Actual Time |
|---|---|---|
| 製造 | 10日 | 12 days |
| Ocean Freight | 25 days | 35+ days |
| Customs | 2日 | 7+ days |
Thinking about zinc plating sourcing overseas requires a realistic view of the total timeline.

When dealing with global coating vendor issues, communication is your biggest challenge and greatest tool. A delayed response due to time differences can halt production or shipping for an entire day. This problem compounds quickly.
Communication Breakdowns and Their Impact
Misunderstandings about zinc plating specifications are common. Language barriers can turn a simple technical query into a major quality issue. These aren’t just inconveniences; they directly affect your bottom line.
The Customs Maze
Customs clearance is a major bottleneck. Incorrect paperwork is a frequent culprit. Your parts can be held for weeks, awaiting correct documentation. This unpredictably extends your lead times.
Calculating the true Landed Cost15 is critical. It includes the price of the part plus all logistics, customs, and insurance fees. Many companies underestimate this figure significantly.
A solid international supply plating strategy must include buffers for these events.
| Hidden Cost Factor | Potential Impact on Total Cost |
|---|---|
| Port Demurrage Fees | +5-10% |
| Air Freight (to expedite) | +20-40% |
| Rework due to Miscommunication | +15-25% |
| Customs Broker Fees | +2-5% |
At PTSMAKE, we help clients build supply chains that anticipate these issues, ensuring smoother delivery.
Logistics, customs, and communication gaps are significant risks in overseas zinc plating. These hidden variables can inflate costs and delay projects, turning apparent savings into substantial losses if not managed with an expert strategy.
Take Your Zinc Plating Projects Further With PTSMAKE Precision
Supercharge your CNC machined or injection molded parts with reliable zinc plating! Send your RFQ to PTSMAKE and get expert advice, fast turnaround, and world-class quality—trusted by leading businesses globally. Request your custom zinc plating quote today and experience manufacturing without compromise!
Discover the electrochemical science behind how this coating protects the base metal from corrosion. ↩
Explore the science of how a sacrificial anode provides electrochemical corrosion protection for the base metal. ↩
Understand how this specific type of material failure occurs and its impact on threaded connections. ↩
Learn how metal ions form a solid, protective coating on a part’s surface through this controlled process. ↩
Understand this electrical principle to improve your part designs for better plating outcomes. ↩
Learn how this chemical process creates a non-reactive surface layer, greatly enhancing a part’s corrosion resistance. ↩
Learn how zinc sacrificially protects steel from corrosion, even when the coating is scratched. ↩
Understand how this electrochemical process works to protect the steel base metal. ↩
Understand the scientific principle controlling coating thickness and efficiency in zinc plating processes. ↩
Learn about the invisible protective film that makes some metals resistant to both corrosion and plating. ↩
Understand how this electrical principle directly impacts the uniformity and quality of your zinc-plated finish. ↩
Learn how to calculate and control the cumulative effect of tolerances in your designs. ↩
Learn how this chemical process enhances corrosion resistance on zinc plated parts. ↩
Discover how this electrical shielding phenomenon can impact your part’s final coating quality and performance. ↩
Understand how to calculate the total expense of your zinc-plated parts beyond the vendor’s price. ↩