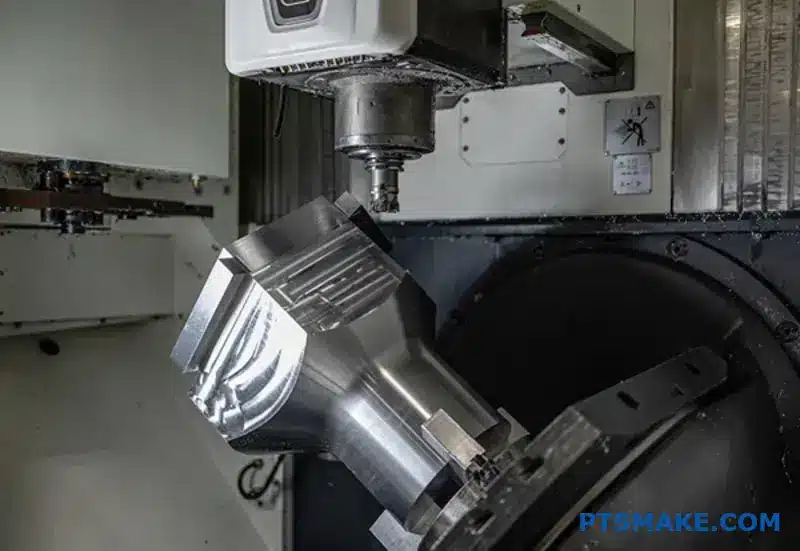
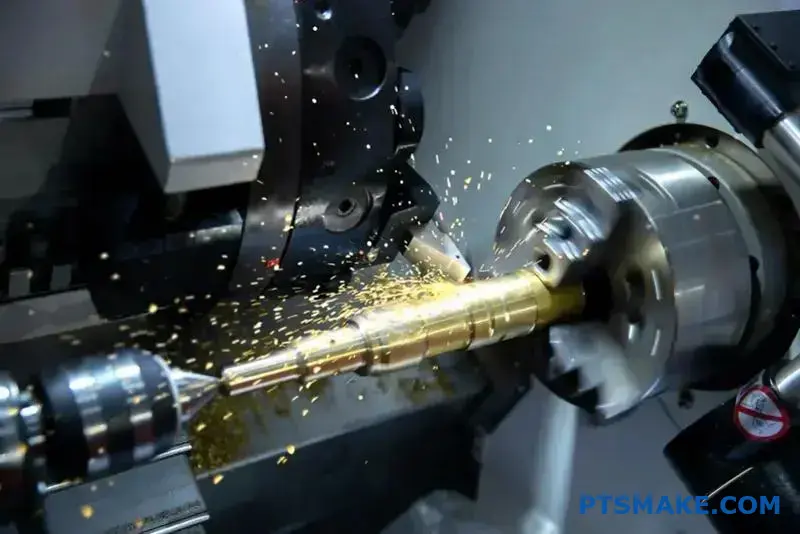
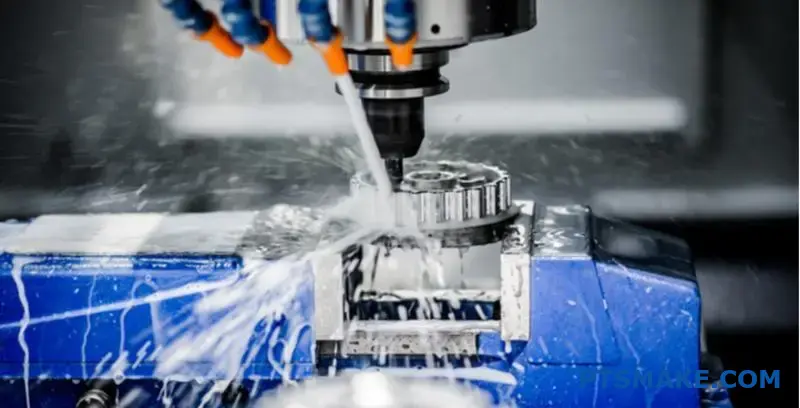
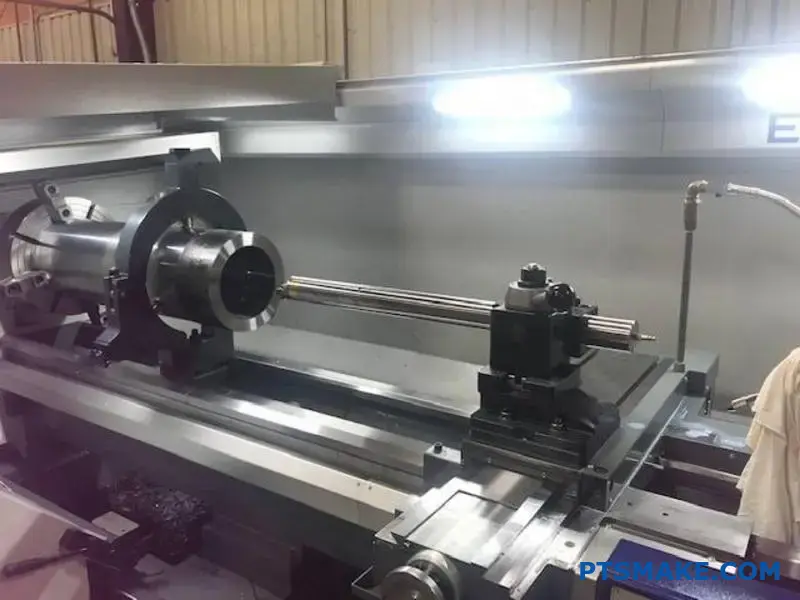
Making a single wrong part choice in nuclear or power energy systems can trigger catastrophic failures, regulatory shutdowns, and millions in losses. Your reputation—and potentially lives—depend on components that perform flawlessly under extreme conditions for decades.
CNC machining serves as the backbone for manufacturing nuclear and power energy components, delivering the precision, material compatibility, and traceability required for critical applications where failure is not an option.
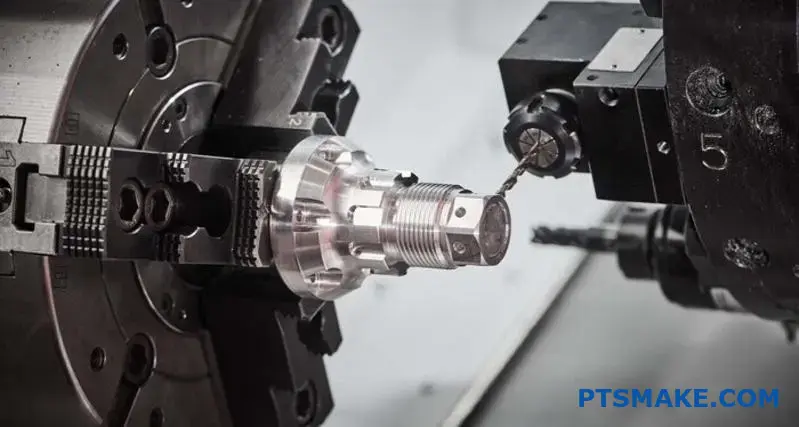
This guide walks you through the essential knowledge for sourcing machined parts that meet the demanding requirements of power generation systems. You’ll discover material selection strategies, tolerance specifications, compliance requirements, and real-world insights that help you make confident decisions when partnering with CNC suppliers for your next critical project.
The Ultimate Challenge: Sourcing Machined Parts for High-Reliability Power Systems
In the power and nuclear energy sectors, reliability is not just a goal. It is an absolute requirement. A single component failure can lead to catastrophic events.
This reality places immense pressure on sourcing. We need high-reliability machined parts that perform flawlessly under extreme conditions.
The High Cost of Failure
The consequences of a single part failing are severe. The risks extend far beyond simple operational disruption.
| Consequence Type | Impact Description |
|---|---|
| Safety Hazard | Risk of accidents and public harm. |
| Financial Loss | Costly downtime and repairs. |
| Reputational Damage | Loss of public and industry trust. |
The Foundational Solution
CNC machining for power energy provides the necessary precision. It is the foundation for manufacturing components that meet these strict safety and performance standards.

Sourcing for the power industry is uniquely demanding. Standard manufacturing practices are often insufficient. We are not just making a part; we are engineering a safety-critical component. This requires a deeper level of control and verification throughout the entire process.
Beyond Standard Machining
For nuclear component manufacturing, every detail matters. This includes material sourcing, handling, and documentation. Full traceability is non-negotiable. We must prove the origin and integrity of every piece of raw material used in production.
This process ensures that materials meet specific performance criteria under harsh conditions. For instance, parts must often resist high pressures, extreme temperatures, and corrosive environments. Failure to account for phenomena like stress corrosion cracking1 can lead to premature failure.
Key Differences in Manufacturing Approach
The table below highlights the critical distinctions between standard and high-reliability production.
| Feature | Standard Machining | High-Reliability Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Material Sourcing | Commercial Grade | Certified & Traceable Lots |
| Tolerances | Standard Industry Specs | Extremely Tight, Verified Tolerances |
| Inspection | Spot Checks | 100% Inspection & NDT |
| Documentation | Basic Work Orders | Comprehensive Certification Packages |
At PTSMAKE, we build our processes around these stringent requirements. We understand that our work directly impacts the safety and reliability of critical power infrastructure.
Sourcing parts for high-reliability power systems presents a unique set of challenges. Failure carries severe consequences, making precision non-negotiable. Advanced CNC machining is the foundational manufacturing process required to meet the extreme safety, reliability, and documentation standards of this demanding industry.
Material Selection Secrets for Extreme Environments: From Reactor Cores to Turbines
Choosing the right material for a nuclear reactor core or power turbine is a critical decision. Performance under extreme conditions is non-negotiable.
The Core Challenge
You face intense radiation, high temperatures, and aggressive corrosion. A material failure in these settings can be catastrophic. The challenge is balancing durability with manufacturability.
Key Material Contenders
We often work with alloys like Inconel, Hastelloy, and Titanium. Each has unique strengths. The final choice always depends on the specific application and its operational demands.
| Environment | Primary Material Family | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| High Radiation | Zirconium, Inconel | Low Neutron Absorption |
| High Temperature | Nickel Superalloys | Creep Resistance |
| High Corrosion | Hastelloy, Titanium | Chemical Inertness |

Making the right choice involves balancing performance, machinability, and cost. It’s never about simply picking the strongest or most resistant alloy. The practicalities of manufacturing are just as important.
Stainless Steel: The Workhorse
For many power generation parts, SS 316 or 316L is a solid starting point. 316L offers better weldability. However, its strength diminishes significantly at the high temperatures where superalloys excel. These are reliable, but have clear limits.
Superalloys: The Elite Performers
This is where you find Inconel and Hastelloy. Machining Inconel for nuclear applications is notoriously difficult. It has a high tendency for work hardening2, which rapidly wears down cutting tools. These are superior corrosion-resistant alloys for power generation, but their cost reflects this elite status.
The Practical Trade-Off
A component made from a high-performance alloy can cost many times more than a stainless steel one. This increase comes from both raw material price and the complex CNC machining required. At PTSMAKE, we help clients analyze if the performance gain justifies the cost increase.
| Material | Temp. Resistance | Corrosion Resistance | Machinability | Relative Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS 316L | Good | Very Good | Good | Base |
| Titanium Gr. 5 | Very Good | Excellent | Fair | 3-5x |
| Inconel 718 | Excellent | Excellent | Poor | 8-12x |
| Hastelloy C-276 | Excellent | Superior | Poor | 10-15x |
Selecting materials for extreme environments is a complex trade-off. While superalloys offer peak performance, their difficult machinability and high cost often make stainless steels or titanium more practical. A careful, application-specific analysis is essential for success.
Beyond the Blueprint: Engineering for Uncompromising Dimensional Accuracy
In the power energy sector, failure is not an option. Parts must perform under extreme stress and temperature. This demands uncompromising dimensional accuracy.
We’re talking about micron-level precision. This is especially true for critical components.
Turbine Blade Tolerances
Turbine blades require complex airfoil geometries. Even a tiny deviation impacts efficiency and safety. Tight tolerance CNC machining is essential here. We machine these parts to ensure perfect balance and airflow.
Valve Body Precision
Valve bodies control the flow of high-pressure fluids. Their sealing surfaces must be flawless. Any imperfection could lead to catastrophic leaks. This is a core focus of nuclear or power energy cnc machining.
A slight difference in tolerance can have a huge impact.
| Feature | Standard Tolerance | Power Energy Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Surfaces | ±0.1 mm | ±0.005 mm |
| Blade Airfoil Profile | ±0.2 mm | ±0.01 mm |
| Positional Features | ±0.05 mm | ±0.01 mm |
Achieving these specs is a daily challenge we meet at PTSMAKE.
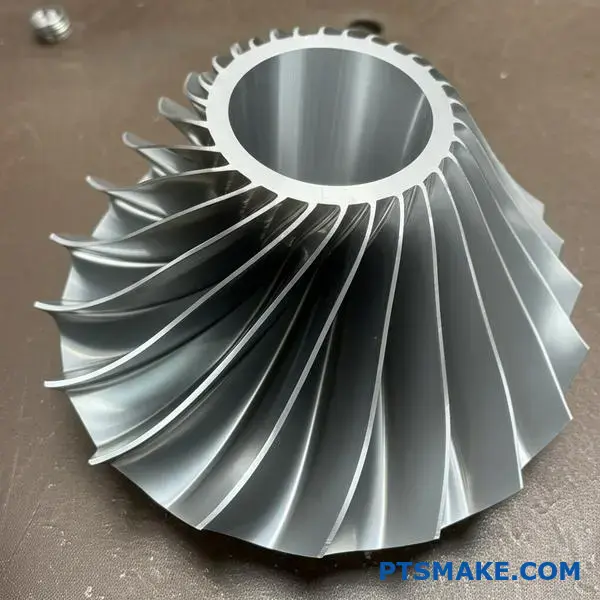

Achieving this level of precision isn’t just about the machine. It involves a holistic approach to manufacturing. The entire process must be controlled.
Advanced CNC Capabilities
We rely on 5-axis CNC machines. They allow us to machine complex shapes in a single setup. This reduces the risk of error from repositioning the workpiece.
In-process probing and laser tool setting are standard procedures. These systems verify tool dimensions and part features during the machining cycle. This ensures dimensional accuracy in energy components from the start.
The Impact of Environmental Factors
The environment of the workshop plays a critical role. Factors like heat and material stress can ruin a perfectly good part. We’ve learned to manage these variables meticulously.
Thermal Expansion
Materials expand with heat. A few degrees change in temperature can push a part out of tolerance. Our machining centers are in climate-controlled environments to maintain isothermal3 conditions, which is crucial for stability.
Stress Relief
Internal stresses in raw materials can cause parts to warp after machining. We use specific heat treatment and cryogenic processes to relieve this stress before the final cuts. This ensures the part remains stable long after it leaves our facility.
| Factor | Control Method | Impact on Precision |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Fluctuation | Climate-Controlled Environment (±1°C) | Prevents material expansion |
| Machine Heat | Cooled Spindles & Coolant Management | Maintains dimensional stability |
| Material Stress | Pre-Machining Heat Treatment | Eliminates post-machining warp |
This careful management is how we deliver reliable precision parts for power plants.
Achieving micron-level precision for power generation parts requires more than just advanced machines. It demands strict control over environmental factors like thermal expansion and a deep understanding of material behavior, ensuring total dimensional accuracy.
Surface Finish Mastery: Why Roughness Impacts Performance and Longevity
In the energy sector, failure is not an option. A component’s surface is its first line of defense. This is especially true for nuclear and power generation parts.
The right finish prevents catastrophic failures. It’s about more than just looks; it’s about operational integrity.
The Dangers of a Rough Surface
Microscopic peaks and valleys on a rough surface act as stress concentrators. These points are where cracks begin under intense pressure and thermal cycling. This is a critical concern for any surface finish for nuclear components.
A lower Ra value means a smoother surface. This drastically reduces weak points.
Friction and Corrosion
In systems like turbines, friction equals inefficiency and heat. A smooth surface reduces parasitic drag. It also limits sites where corrosion can take hold, extending component life.
| Feature | High Ra (Rough) | Low Ra (Smooth) |
|---|---|---|
| Crack Risk | High | Low |
| Friction | High | Low |
| Corrosion | Prone | Resistant |
| Ideal For | General Use | Turbine & Nuclear Parts |

Achieving the specified Ra value for turbine parts or nuclear components often requires more than just standard CNC machining. These post-machining processes are crucial for creating a truly superior and reliable surface. They move the component from "good" to "mission-critical."
Electropolishing for Ultimate Smoothness
Electropolishing is a key process we use at PTSMAKE. It’s an electrochemical process that removes a microscopic layer of material. It targets the "peaks" of a surface, resulting in an exceptionally smooth and clean finish.
This method is ideal for electropolishing machined parts with complex geometries. It enhances corrosion resistance significantly by removing surface impurities and creating a passive layer. This process smooths the surface without inducing mechanical stress.
Specialized Grinding Techniques
For other applications, specialized grinding is necessary. This isn’t your standard workshop grinding. We’re talking about precision-controlled processes. These methods can create a specific surface texture.
This texture can influence lubrication retention or directional strength. The control we have over the material’s surface Anisotropy4 is critical. Our work with clients has shown that the right grinding can improve wear resistance by over 30%.
| Process | Key Benefit | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Electropolishing | Ultimate smoothness, corrosion resistance | Complex shapes, non-stressed finish |
| Specialized Grinding | Controlled texture, wear resistance | Flat surfaces, load-bearing parts |
In high-stakes energy applications, surface finish is a critical safety parameter. Post-machining processes like electropolishing and precision grinding are not optional upgrades; they are essential for preventing cracks, reducing friction, and ensuring long-term reliability for critical components.
The Traceability Imperative: Documenting Every Step for Compliance and Safety
In high-stakes industries, traceability isn’t optional. For nuclear or power energy CNC machining, it’s the bedrock of safety and compliance. It means we can track every component’s journey.
This starts from the raw material’s origin to the final part’s delivery. This chain of documentation is non-negotiable. It ensures every piece meets exacting standards.
Key Traceability Documents
Full documentation provides a clear, auditable trail for every component we manufacture.
| Document Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Certificate of Conformance (C of C) | Confirms parts meet all specifications. |
| Material Certifications | Verifies material composition and origin. |
| Process Sheets | Details every manufacturing step taken. |
| Lot Control Records | Tracks batches for consistency and recall. |
This detailed record-keeping is crucial for traceable CNC machining.

True traceability goes beyond simple paperwork. It is a systematic approach embedded in our manufacturing culture at PTSMAKE. This meticulous process ensures that every part is fully accountable, from raw billet to finished component. For our clients, this means simplified audits and unwavering confidence in the final product.
Meeting Strict Regulatory Standards
In ASME compliant manufacturing, documentation proves adherence to codes. This includes recording heat numbers from the mill, which trace the material back to its specific batch. This level of detail is critical for sectors that demand the highest safety standards.
We document every process parameter. This includes machine settings, operator details, and inspection results. This creates a complete history for each part. Lot control ensures that if an issue ever arises with one component, we can instantly identify and isolate the entire batch. This level of control is essential. It is a core requirement for standards like NQA-15.
The Audit Trail
A strong documentation system makes audits straightforward. Instead of a stressful search for information, everything is organized. The required material certification for nuclear parts is readily available, proving compliance and ensuring safety.
| Traceability Element | Compliance Benefit |
|---|---|
| Heat Numbers | Links part to raw material batch. |
| Process Logs | Verifies correct manufacturing procedures. |
| Inspection Reports | Confirms dimensional and quality checks. |
| Lot Numbering | Enables precise tracking of part groups. |
This systematic approach makes regulatory compliance a routine part of our workflow, not an afterthought.
Traceability is your assurance of quality and safety. It provides a complete, verifiable history for every part. This detailed documentation simplifies audits and ensures strict compliance with standards like ASME and NQA-1, providing absolute peace of mind for critical applications.
Deciphering Key Standards: ASME, ISO, and NQA-1
Navigating standards for critical industries can feel complex. Let’s simplify three key ones to ensure your parts meet strict requirements. This is crucial for nuclear or power energy cnc machining.
ASME Section III: The Nuclear Blueprint
This standard governs nuclear component design, materials, and fabrication. Adhering to it requires deep expertise in ‘ASME Section III machining’.
ISO 19443 & NQA-1: Quality Frameworks
ISO 19443 targets the nuclear supply chain’s quality management. It helps you find an ‘ISO 19443 compliant supplier’. NQA-1 provides a broader ‘NQA-1 quality program’ for nuclear facilities.
| Standard | Primary Focus | Key Implication for Buyers |
|---|---|---|
| ASME Section III | Component Integrity | Ensures parts withstand nuclear service conditions. |
| ISO 19443 | Supply Chain Quality | Vets suppliers for nuclear-specific quality systems. |
| NQA-1 | Overall Quality Program | Confirms a supplier’s comprehensive quality assurance. |

When selecting a partner, understanding the practical impact of these standards is key. They aren’t just badges; they shape the entire manufacturing process from start to finish.
System vs. Component Focus
Think of it this way: ASME Section III is laser-focused on the physical component. It dictates the ‘what’—materials, welding, and inspection criteria for the part itself.
In contrast, ISO 19443 and NQA-1 define the ‘how’. They structure the quality management system. This ensures every step, from quoting to shipping, is controlled and documented. This systemic approach is vital.
What This Means for Your Project
For you, this translates to rigorous documentation. Every material used must be tracked back to its source. This complete material traceability6 is non-negotiable in nuclear applications.
Choosing an ‘ISO 19443 compliant supplier’ means they have proven systems to prevent counterfeit parts. An effective ‘NQA-1 quality program’ ensures that any process deviation is caught, documented, and corrected immediately. This protects your project’s integrity. It is all about risk mitigation.
| Standard Impact | Part Design | Manufacturing Process | Supplier Selection |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASME Section III | Material selection, specific geometries | Certified welding, stringent inspections | Requires specific ‘ASME Section III machining’ capabilities. |
| ISO 19443 | Less direct impact | Focus on process control & anti-counterfeiting | Must be an ‘ISO 19443 compliant supplier’. |
| NQA-1 | Design control processes | Strict procurement and process validation | Demands a robust ‘NQA-1 quality program’ is in place. |
These standards are not interchangeable. ASME Section III governs the part, while ISO 19443 and NQA-1 manage the quality systems. For buyers, this means selecting suppliers who can provide verifiable proof of compliance, ensuring project safety and reliability.
Case Study: Precision Machining for a Next-Generation Reactor Coolant Pump
This project was a true test of our capabilities. We were approached to manufacture a critical component for a next-generation reactor coolant pump.
The part was a complex impeller. It demanded extreme precision in a very tough material. This is a classic challenge in the power energy cnc machining sector.
Success was not optional. The part’s reliability directly impacts the safety and efficiency of the nuclear facility. We delivered on every specification.
Project at a Glance
| Parameter | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Component | Reactor Coolant Pump Impeller |
| Material | Duplex Stainless Steel (UNS S32205) |
| Key Tolerance | ±0.005 mm on blade profiles |
| Surface Finish | Ra 0.2 μm on fluid-contact surfaces |
| Certification | Full Material Traceability & NDT Reports |
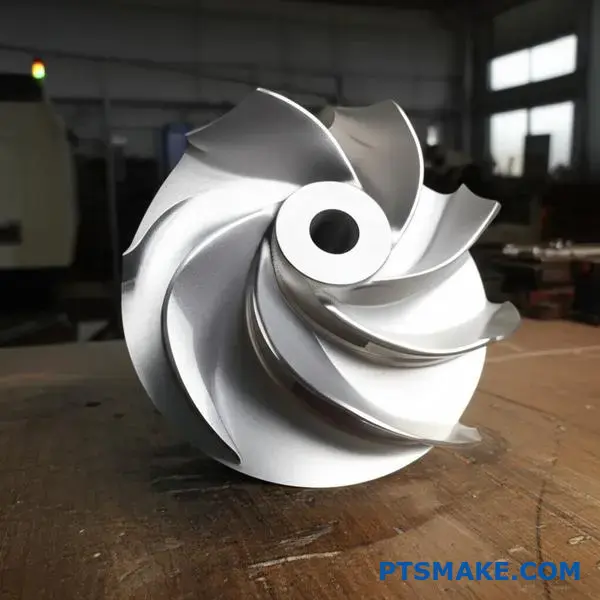

The Machining Challenge in Detail
The client’s requirements pushed the boundaries of standard machining. The component’s role within a nuclear reactor meant there was zero margin for error. This precision machining nuclear application required a flawless result.
The material, Duplex Stainless Steel7, was chosen for its incredible strength and corrosion resistance. However, these same properties make it very difficult to machine. It is tough and tends to work-harden if not handled correctly. We had to develop a specific strategy for these CNC machined reactor components.
Overcoming Technical Hurdles
The primary challenges were the tight geometric tolerances and the surface finish. The impeller’s complex, curved blades required simultaneous 5-axis CNC milling to achieve the specified profiles.
After collaboration with our client, we determined that conventional tooling would wear out too quickly. We invested in specialized ceramic end mills and developed a custom toolpath strategy. This minimized heat and prevented material hardening during the process.
Our quality assurance was rigorous. We used CMM inspection and surface profilometry at multiple stages to validate every dimension and finish.
| Challenge | Our Solution at PTSMAKE | Delivered Value |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Tolerances (±0.005mm) | 5-axis CNC milling, in-process CMM checks | Guaranteed geometric accuracy, optimal pump performance |
| Material Toughness | Specialized ceramic tooling, optimized speeds/feeds | Consistent part quality, reduced tool wear |
| Surface Finish (Ra 0.2 μm) | Multi-stage finishing and polishing process | Minimized fluid friction, enhanced pump efficiency |
| Full Certification | Rigorous documentation and NDT testing | Ensured compliance with nuclear industry standards |
This project highlights how a meticulous machining strategy is crucial for demanding applications. We successfully machined the complex impeller, meeting all extreme tolerances and certification needs, thereby ensuring the reliability and performance required for this critical nuclear component.
The Engineer’s Checklist: 10 Questions to Vet Your Next CNC Partner
Choosing the right CNC partner is critical. This is especially true for the nuclear and power energy sectors. A simple mistake can lead to costly failures.
To help, I’ve created a practical checklist. It simplifies how to choose a CNC machining supplier. Use these questions to get clear, actionable answers. This helps ensure your partner meets your standards for precision and reliability.
| Evaluation Area | Key Focus |
|---|---|
| Technical Skill | Material and complexity experience |
| Quality Systems | Certifications and inspection process |
| Risk Management | Contingency and support plans |

A good checklist goes beyond price. It dives into a supplier’s core capabilities. This is vital when vetting manufacturers for nuclear parts. You need a partner who understands the stakes.
Material & Process Expertise
Ask about their experience with specific alloys. Have they machined Inconel, Hastelloy, or specific grades of stainless steel? Request case studies or part examples. This proves their ability to handle materials common in the power energy field.
Quality and Inspection
What certifications do they hold? Look for ISO 9001 as a baseline. Also, ask about their inspection equipment. Do they have Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs)? What is their calibration schedule? A robust quality system is non-negotiable. At PTSMAKE, our process includes rigorous in-process and final inspections.
Engineering and Contingency
Inquire about their engineering support. Do they offer Design for Manufacturability (DFM)8 analysis? This collaborative process can save time and reduce costs significantly. Finally, ask about their disaster recovery plan. What happens if a key machine goes down? A solid plan shows foresight and protects your supply chain.
| Checklist Item | Question for Supplier |
|---|---|
| Alloy Experience | "Can you provide examples of nuclear or power energy parts you’ve made?" |
| Certifications | "What is the full scope of your ISO 9001 certification?" |
| Engineering Support | "What does your DFM review process involve?" |
| Disaster Recovery | "What is your contingency plan for equipment failure or power loss?" |
This structured approach helps you build a reliable partnership. It moves the conversation from cost to capability, ensuring your project’s success.
This checklist provides a structured framework for vetting suppliers. It helps you assess technical skill, quality systems, and risk management, ensuring you select a capable and reliable partner for critical components.
The Role of 5-Axis Machining in Complex Turbine and Valve Components
In the energy sector, precision isn’t just a goal; it’s a necessity. 5-axis machining is a game-changer for producing complex turbine and valve components. It offers unique advantages that traditional methods can’t match.
The Single Setup Advantage
The biggest benefit is completing intricate parts in a single setup. This minimizes human error from re-fixturing. The result is higher accuracy and consistency, which is critical for components like impellers.
Machining Complex Geometries
5-axis machines can create complex contours and deep cavities with ease. This capability is essential for optimizing fluid dynamics in parts used for power generation. It allows us to produce geometries that were previously impossible.
Setup Comparison: Turbine Blade
| Feature | 3-Axis Machining | 5-Axis Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Setups Required | Multiple (4-6) | Single Setup |
| Positional Accuracy | Lower | Higher |
| Tool Length | Longer (risk of chatter) | Shorter, more rigid |
| Cycle Time | Longer | Significantly Shorter |
This approach is central to effective 5-axis machining for turbine parts.

Let’s dive deeper into the specific applications. For parts with complex internal channels, like manifold blocks, 5-axis machining is indispensable. We can create integrated features that reduce part count, weight, and potential failure points.
Machining Deep Pockets and Cavities
A key advantage is the ability to machine deep cavities. The tilting spindle or table allows the use of shorter, more rigid cutting tools. This reduces tool deflection and vibration. It leads to better surface finishes and tighter tolerances, especially crucial in valve body 5-axis machining. At PTSMAKE, we’ve found this technique enhances part integrity for nuclear or power energy cnc machining.
Creating Integrated Features
Consider a complex manifold block. Traditionally, it would be assembled from several machined pieces. This introduces potential leak paths at every joint. With 5-axis technology, we can machine the entire block from a single piece of material. This creates a stronger, more reliable component. The machine kinematics9 allow for precise tool paths around complex features.
Component Integrity: Manifold Block
| Approach | Traditional Assembly | 5-Axis Integrated Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Part Count | High | Single Piece |
| Potential Leak Paths | Multiple | None |
| Structural Integrity | Lower | Higher |
| Assembly Time | Required | Eliminated |
This method is fundamental for complex geometry CNC energy applications, where reliability is paramount.
In summary, 5-axis machining provides superior accuracy for energy components by enabling single-setup production. It excels at creating complex contours, deep cavities, and integrated features in parts like impellers and manifolds, enhancing both performance and reliability.
Unlock Next-Level Nuclear & Power Energy Machining with PTSMAKE
Ready to solve your toughest reliability and compliance challenges for nuclear or power energy CNC machining? Partner with PTSMAKE for precision, traceability, and seamless certification. Request a quote now and experience the highest standards in safety, quality, and trust—your components deserve nothing less!
Discover how environmental factors combined with tensile stress can cause unexpected material failures. ↩
Learn how this material property affects tool life and machining strategies for high-temperature alloys. ↩
Learn how temperature stability is foundational for achieving ultra-precision tolerances. ↩
Explore the technical details of how surface directionality impacts component performance and material integrity. ↩
Learn more about this crucial quality standard for nuclear facility applications. ↩
Learn how full traceability prevents material failures and ensures the integrity of your critical components. ↩
Learn about the unique microstructure and properties of this high-performance alloy. ↩
Learn how DFM analysis optimizes your design for production efficiency and reduces costs. ↩
Learn how a machine’s axes move in concert to create complex shapes. ↩







